research use only
Acesulfame Potassium
Cat.No.S2884
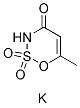
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 202.25
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(197.77 mM)
Water : 40 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 202.25 | Formula | C4H5NO4S.K |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 55589-62-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1=CC(=O)[N-]S(=O)(=O)O1.[K+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Acesulfame potassium activates two members of the human TAS2R family (hTAS2R43 and hTAS2R44) to stimulate bitter taste. Acesulfame potassium elicited robust elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ in hTAS2R44-expressing cells, with a threshold value of activation of 0.25 mM and an EC50 value of 2.5 mM. Acesulfame potassium elicited response of hTAS2R43-expressing cells with a threshold value of 3.1 mM and an estimated EC50 value ﹥10 mM
Acesulfame potassium acts directly on the pancreatic islets and potentiates glucose-induced insulin release. Acesulfame potassium (1.0-15.0 mM) augmented insulin release from islets incubated in the presence of 7.0 mM d-glucose.
Acesulfame Potassium enhanced glucose absorption via activating sweet taste receptors in the enterocyte to translocate GLUT2 to the apical membrane through the PLC βII. In Caco-2 and RIE-1 cells, Acesulfame potassium (10 mM) increased glucose uptake by 20-30 % when incubated for 10 min with glucose >25 mM.
Acesulfame potassium increased the contractile response of isolated rat detrusor muscle strips via increased extracellular Ca2+ influx. Acesulfame potassium (10-7 M to 10-2 M) enhanced the contractile response to 10 Hz EFS compared to control. The atropine-resistant response to EFS is marginally increased by Acesulfame potassium (10-6 M). Acesulfame potassium (10-6 M) increased the maximum contractile response to α, β methylene ATP by 35% and to KCl by 12%. Acesulfame potassium (10-6 M) increased the log EC50 from -2.7 to -3.03.
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Acesulfame potassium acts on two members of the TAS1R family of G-protein-coupled receptors (TAS1R2 and TAS1R3) to stimulate sweet taste. Selective elimination of T1R-subunits differentially abolishes de tection and perception of these two taste modalities.
Acesulfame potassium can also induce insulin secretion in rats. Injection of Acesulfame potassium (150 mg/kg body weight) increased the plasma insulin concentration at 5 min from 27.3 mU/mL to 58.6 mU/mL. Infusion of Acesulfame potassium (20 mg/kg body weight/min) for one hour maintained the insulin concentration at a high level (about 85-100 mU/mL). When using different amounts of Acesulfame potassium, the insulin secretion is stimulated in a dose-dependent fashion.
Oral administration of Acesulfame potassium (60, 450, 1500 and 2250 mg/kg body weight) induced a significant increase in the frequency of cellular damage and chromosome aberrations in the Bone marrow cells isolated from mice femora. Oral administration of Acesulfame potassium at the concentration of 150, 300, and 600 mg/kg body weight is found to induce DNA damage in bone marrow cells of mice with a minimum effective concentration (MEC) value of 150 mg/kg in the comet assay.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05379270 | Active not recruiting | Breastfeeding |
George Washington University |
February 28 2022 | Not Applicable |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































