research use only
2-Methylenebutyrolactone Drug Metabolite chemical
Cat.No.S5148
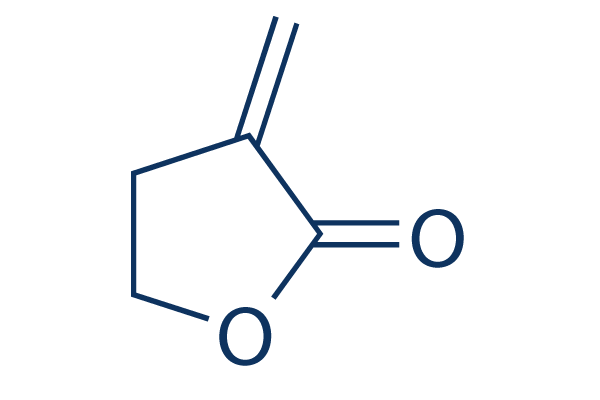
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 98.10
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Other Drug Metabolite Inhibitors | Vinburnine Hydroxyhexamide Isonicotinic acid Monobutyl phthalate Endoxifen 3-Methoxytyramine hydrochloride |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 98.10 | Formula | C5H6O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | 2 years -20°C liquid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 547-65-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
After exposure of Jurkat T cells to 2-Methylenebutyrolactone (Tulipalin A , TUPA) for 72 h, a dose dependent toxicity is detected. Concentrations higher than 20 μM lead to a significant reduction of viable cells. Compared to vehicle-treated control cells, concentrations of 47.6 and 26.8 μM decrease the cell viability significantly by 50% (IC50) and 10% (IC10), respectively. In contrast, THP-1 cells are less sensitive toward TUPA. Concentrations >41 μM lead to a significant reduction of viable cells. IC10 is calculated with 50 μM, whereas a concentration of 83 μM is necessary to decrease the cell viability to 50% (IC50). In Jurkat T cells, four proteins responsible for the de novo purine synthesis, namely phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine synthase (PFAS), GMP synthase (GMPS), and ribosephosphate pyrophosphokinases 1 and 2 (PRPS1/2) are increased through TUPA treatment. Glutamine is also increased after TUPA treatment. In addition to the proteins belonging to the purine synthesis pathway, the abundances of proteins for DNA synthesis and repair (XRCC5, XRCC6, MCM3, MCM6, MCM7, TRA1) are also increased/induced during the treatment. While in THP-1 cells, no indication for higher purine synthesis induced by TUPA in subtoxic concentrations is discovered. TUPA induces the expression of proteins in Jurkat T cells responsible for cell stress, drug response, and protein folding: HYOU1, PDIA3, and DNAJB11. Additionally, the treatment with TUPA leads to the induction of three heat shock proteins (HSP90AA1, HSP90AB1, and HSP90B1) and three proteins belonging to the TRiC complex (CCT3,6,8) that are also responsible for proper protein folding. Treatment with TUPA leads to the induction of ROS that have adverse effects on Jurkat T cells and evokes slight cell stress responses in THP-1 cells. TUPA has influence on proteins in Jurkat T cells that contribute to different immune-specific, especially immunostimulating, reactions as allergic contact dermatitis. In THP-1 cells, no proteins regarding immune-specific reactions are up- or downregulated due to TUPA treatment.
|
References |
|---|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05850871 | Recruiting | Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infection |
Qianfoshan Hospital |
January 6 2023 | Not Applicable |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































