PDGFR inhibitors, a class of targeted therapeutic agents designed to modulate the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) pathway, have emerged as a pivotal focus in cancer research and precision medicine. The PDGFR family, consisting of PDGFRα and PDGFRβ, plays a crucial role in regulating fundamental cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, and angiogenesis. Dysregulation of PDGFR signaling, often driven by receptor overexpression, mutation, or abnormal ligand activation, is closely associated with the initiation and progression of various malignancies, making PDGFR an attractive therapeutic target. Over the past few decades, extensive scientific efforts have been devoted to understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying PDGFR-mediated oncogenesis, developing novel PDGFR inhibitors, and optimizing their clinical application.
PDGFR Inhibitors
Other Protein Tyrosine Kinase Related Inhibitors
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Information | Product Use Citations | Product Validations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
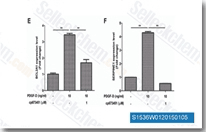
| S1536 | CP-673451 | CP-673451 is a selective inhibitor of PDGFRα/β with IC50 of 10 nM/1 nM in cell-free assays, exhibits >450-fold selectivity over other angiogenic receptors, has antiangiogenic and antitumor activity. |
|
|
| S8553 | Avapritinib (BLU-285) | Avapritinib (BLU-285) is a small molecule kinase inhibitor that potently inhibits PDGFRα D842V mutant activity in vitro (IC50 = 0.5 nM) and PDGFRα D842V autophosphorylation in the cellular setting (IC50 = 30 nM). It is also a potent inhibitor of the analogous Kit (c-Kit) mutation, D816V in Kit (c-Kit) Exon 17 (IC50 = 0.5 nM). |
|
|
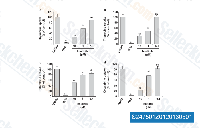
| S2475 | Imatinib (STI571) | Imatinib is a multi-target inhibitor of tyrosine kinase with inhibition for v-Abl, c-Kit and PDGFR, IC50 values are 0.6 μM, 0.1 μM and 0.1 μM in cell-free or cell-based assays, respectively. Imatinib (STI571) induces autophagy. |
|
|
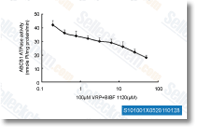
| S1010 | BIBF 1120 (Nintedanib) | Nintedanib is a potent triple angiokinase inhibitor for VEGFR1/2/3, FGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β with IC50 of 34 nM/13 nM/13 nM, 69 nM/37 nM/108 nM and 59 nM/65 nM in cell-free assays. Phase 3. |
|
|
| S8401 | Erdafitinib (JNJ-42756493) | Erdafitinib is a potent and selective orally bioavailable, pan fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. This compound also binds to RET (c-RET), CSF-1R, PDGFR-α/PDGFR-β, FLT4, Kit (c-Kit) and VEGFR-2 and induces cellular apoptosis. |
|
|
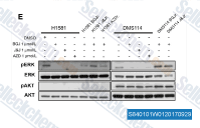
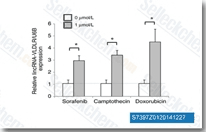
| S7397 | Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor of Raf-1 and B-Raf with IC50 of 6 nM and 22 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. Sorafenib inhibits VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 and c-KIT with IC50 of 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM and 68 nM, respectively. Sorafenib induces autophagy and apoptosis and activates ferroptosis with anti-tumor activity. |
|
|
| S8161 | ON123300 | ON123300 is a potent and multi-targeted kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 3.9 nM, 5 nM, 26 nM, 26 nM, 9.2 nM and 11nM for CDK4, Ark5/NUAK1, PDGFRβ, FGFR1, RET (c-RET), and Fyn, respectively. |
|
|
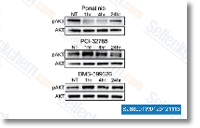
| S1490 | Ponatinib (AP24534) | Ponatinib is a novel, potent multi-target inhibitor of Abl, PDGFRα, VEGFR2, FGFR1 and Src with IC50 of 0.37 nM, 1.1 nM, 1.5 nM, 2.2 nM and 5.4 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. Ponatinib (AP24534) inhibits autophagy. |
|
|
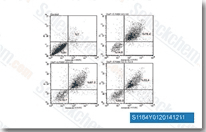
| S1164 | E7080 (Lenvatinib) | Lenvatinib is a multi-target inhibitor, mostly for VEGFR2(KDR)/VEGFR3(Flt-4) with IC50 of 4 nM/5.2 nM, less potent against VEGFR1/Flt-1, ~10-fold more selective for VEGFR2/3 against FGFR1, PDGFRα/β in cell-free assays. Lenvatinib (E7080) also inhibits FGFR1-4, PDGFR, Kit (c-Kit), RET (c-RET), and shows potent antitumor activities. Phase 3. |
|
|
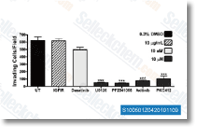
| S1005 | Axitinib (AG-013736) | Axitinib is a multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRβ and c-Kit with IC50 of 0.1 nM, 0.2 nM, 0.1-0.3 nM, 1.6 nM and 1.7 nM in Porcine aorta endothelial cells, respectively. |
|
|
Signaling Pathway Map
PDGFR Receptor Biology and Signaling Pathways
The PDGFR family belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) superfamily, characterized by an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a single transmembrane domain, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. The two main isoforms, PDGFRα and PDGFRβ, are encoded by different genes and exhibit distinct expression patterns and ligand specificities. PDGFRα binds to PDGF-A, PDGF-B, and PDGF-C, while PDGFRβ primarily interacts with PDGF-B and PDGF-D. Ligand binding induces receptor dimerization (homo- or heterodimerization between PDGFRα and PDGFRβ), which activates the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, leading to autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues.
PDGFR Signaling Cascade in Normal and Pathological Conditions
The phosphorylated tyrosine residues of PDGFR serve as docking sites for various downstream signaling molecules, initiating multiple intracellular pathways that regulate cellular functions. Key signaling pathways activated by PDGFR include the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway, which promotes cell proliferation and survival; the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, which regulates cell metabolism and anti-apoptotic processes; and the JAK/STAT pathway, which mediates gene transcription involved in cell growth and differentiation. In normal physiological conditions, PDGFR signaling is tightly regulated, ensuring proper tissue development, wound healing, and angiogenesis. However, in pathological states such as cancer, dysregulated PDGFR signaling disrupts this balance, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation, enhanced cell migration and invasion, and increased angiogenesis, all of which contribute to tumor growth and metastasis.
Structural Differences Between PDGFRα and PDGFRβ
Although PDGFRα and PDGFRβ share high homology in their tyrosine kinase domains (approximately 85% amino acid sequence identity), they exhibit significant differences in their extracellular ligand-binding domains and tissue expression profiles. PDGFRα is highly expressed in embryonic tissues, and in adult tissues, it is found in fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, and certain types of stem cells. PDGFRβ, on the other hand, is predominantly expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells, pericytes, and macrophages. These structural and expression differences contribute to the distinct roles of PDGFRα and PDGFRβ in normal physiology and disease. For example, PDGFRα mutations are frequently associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), while PDGFRβ overexpression is often observed in gliomas and hematological malignancies.
PDGFR Mutation and Its Role in Cancer Oncogenesis
Mutations in the PDGFR gene are a major driver of dysregulated PDGFR signaling in cancer. These mutations can occur in the extracellular ligand-binding domain, the transmembrane domain, or the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, leading to constitutive activation of the receptor independent of ligand binding. The identification and characterization of PDGFR mutations have provided critical insights into the molecular mechanisms of cancer development and have guided the development of targeted PDGFR inhibitors.
Common PDGFR Mutations in Human Cancers
One of the most well-characterized PDGFR mutations is the c-KIT/PDGFRα mutation in GISTs. Approximately 5-10% of GISTs harbor PDGFRα mutations, with the most common being the D842V mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain. This mutation renders PDGFRα constitutively active, promoting tumor cell proliferation and survival. Other common PDGFR mutations include the V561D mutation in the extracellular domain of PDGFRα, which enhances ligand binding affinity, and the R841W mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of PDGFRβ, which is associated with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). In addition, PDGFR gene amplifications and translocations have also been reported in various cancers, such as lung cancer, breast cancer, and glioblastoma, leading to receptor overexpression and hyperactivation.
Mechanisms of Mutation-Driven PDGFR Activation in Cancer
PDGFR mutations drive oncogenesis primarily by inducing constitutive receptor activation. For example, mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain, such as D842V in PDGFRα, disrupt the autoinhibitory conformation of the receptor, allowing the kinase domain to remain active even in the absence of ligand. This leads to continuous autophosphorylation of the receptor and sustained activation of downstream signaling pathways. Mutations in the extracellular domain, on the other hand, may enhance ligand binding or promote receptor dimerization, leading to increased receptor activation. In addition, PDGFR mutations can also confer resistance to certain PDGFR inhibitors, highlighting the need for personalized therapeutic strategies based on the specific mutation profile of the tumor.
Development and Evaluation of PDGFR Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
Based on the critical role of PDGFR signaling in cancer, numerous PDGFR inhibitors have been developed and evaluated in preclinical and clinical studies. These inhibitors can be classified into two main categories: multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that inhibit PDGFR along with other RTKs, and selective PDGFR inhibitors that specifically target PDGFRα or PDGFRβ. The development of PDGFR inhibitors has been guided by a deep understanding of PDGFR structure, signaling pathways, and mutation profiles, with the goal of improving efficacy and reducing off-target effects.
Preclinical Evaluation of PDGFR Inhibitors
Preclinical studies play a crucial role in the development of PDGFR inhibitors, providing insights into their mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety. In vitro studies using cancer cell lines harboring PDGFR mutations or overexpression have been used to evaluate the inhibitory activity of PDGFR inhibitors on cell proliferation, migration, and survival. In vivo studies using xenograft mouse models or genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) of cancer have been used to assess the antitumor efficacy of PDGFR inhibitors in vivo, as well as their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. For example, preclinical studies have shown that imatinib, a multi-targeted TKI that inhibits PDGFRα, PDGFRβ, and c-KIT, effectively inhibits the growth of GIST cells harboring PDGFRα mutations. Similarly, sunitinib, another multi-targeted TKI, has been shown to inhibit PDGFR signaling and suppress tumor angiogenesis in various preclinical cancer models.
Clinical Trials of PDGFR Inhibitors in Cancer Patients
Numerous clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of PDGFR inhibitors in cancer patients. Imatinib was the first PDGFR inhibitor approved for the treatment of GISTs, and it has significantly improved the prognosis of patients with GISTs harboring c-KIT or PDGFRα mutations. However, some patients develop resistance to imatinib over time, often due to secondary mutations in PDGFRα or c-KIT. This has led to the development of second-generation PDGFR inhibitors, such as regorafenib and ripretinib, which have shown efficacy in imatinib-resistant GISTs. In addition, PDGFR inhibitors have also been evaluated in other cancers, such as lung cancer, breast cancer, glioblastoma, and hematological malignancies. For example, clinical trials have shown that sunitinib is effective in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma, in part by inhibiting PDGFR-mediated angiogenesis. However, the efficacy of PDGFR inhibitors varies depending on the type of cancer and the specific PDGFR mutation profile of the tumor, emphasizing the importance of biomarker-driven patient selection.
Challenges and Future Directions in PDGFR Inhibitor Research
Despite the significant progress in PDGFR inhibitor research, several challenges remain. One of the main challenges is the development of drug resistance, which limits the long-term efficacy of PDGFR inhibitors. Secondary mutations in PDGFR, activation of alternative signaling pathways, and tumor microenvironment changes are among the main mechanisms of resistance. Another challenge is the off-target effects of multi-targeted PDGFR inhibitors, which can lead to adverse events such as hypertension, fatigue, and gastrointestinal toxicity. Future research directions include the development of more selective PDGFR inhibitors that target specific PDGFR isoforms or mutations, the identification of novel biomarkers for predicting response to PDGFR inhibitors, and the combination of PDGFR inhibitors with other therapeutic agents (such as immunotherapies) to overcome resistance and improve efficacy. In addition, further studies are needed to understand the role of PDGFR signaling in the tumor microenvironment and its interaction with immune cells, which may provide new opportunities for the development of combination therapies.
In conclusion, PDGFR inhibitors have become an important class of targeted therapeutic agents in cancer treatment, with significant progress made in understanding their mechanism of action, developing novel inhibitors, and optimizing their clinical application. The identification of PDGFR mutations and the characterization of PDGFR signaling pathways have provided critical insights into the molecular basis of cancer, guiding the development of personalized therapeutic strategies. Despite the challenges, ongoing research in PDGFR inhibitors holds great promise for improving the prognosis of cancer patients with dysregulated PDGFR signaling.





































