research use only
SU 5402 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
Cat.No.S7667
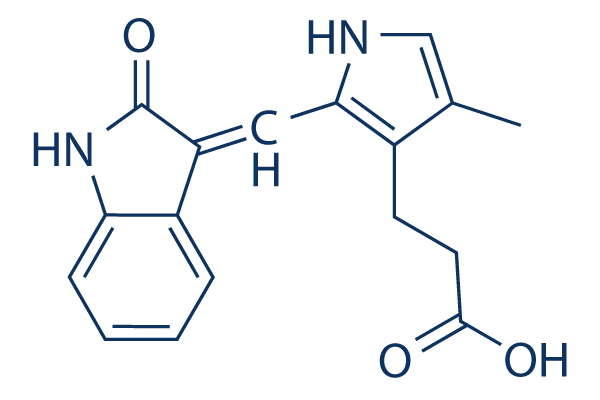
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 296.32
Quality Control
| Related Targets | EGFR PDGFR FGFR c-Met Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 c-Kit |
|---|---|
| Other VEGFR Inhibitors | SAR131675 Cediranib (AZD2171) Vatalanib (PTK787) 2HCl Linifanib (ABT-869) Anlotinib (AL3818) Dihydrochloride Apatinib (YN968D1) Apatinib (YN968D1) mesylate Ki8751 ZM 323881 HCl Semaxanib (SU5416) |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HUVEC or NIH3T3 | Function assay | Evaluated for the inhibition of cell proliferation induced by VEGF in HUVEC or NIH3T3 cells, IC50=0.05μM | 10893303 | |||
| HUVEC or NIH3T3 | Function assay | Evaluated for the inhibition of cell proliferation induced by FGF in HUVEC or NIH3T3 cells, IC50=2.8μM | 10893303 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of acidic FGF-stimulated FGFR1 tyrosine autophosphorylation in mouse NIH/3T3 cells by immunoblotting, IC50=10μM | 9139660 | |||
| NIH 3T3 | Function assay | 5 mins | Inhibition of FGF induced FGFR1 autophosphorylation in mouse NIH 3T3 cells preincubated for 5 mins followed by FGF-stimulation for 5 mins in presence of [gamma-32P]ATP by SDS-PAGE based autoradiography, IC50=10μM | 27914362 | ||
| HUVEC or NIH3T3 | Function assay | Evaluated for the inhibition of cell proliferation induced by PDGF in HUVEC or NIH3T3 cells, IC50=28.4μM | 10893303 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of acidic FGF-stimulated [3H]thymidine incorporation | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of FGFR1 in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of aFGF-stimulated pp90 phosphoprotein phosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of FGFR1 in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of acidic FGF-stimulated ERK1 phosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of FGFR1 in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of acidic FGF-stimulated ERK2 phosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIHIR | Function assay | Inhibition of insulin-stimulated insulin receptor beta subunit autophosphorylation in mouse NIHIR cells | 9139660 | |||
| HER14 | Function assay | Inhibition of EGF-stimulated EGFR phosphorylation in mouse HER14 cells by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| HER14 | Function assay | Inhibition of EGFR in mouse HER14 cells assessed as inhibition of EGF-stimulated Shc phosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| HER14 | Function assay | Inhibition of EGFR in mouse HER14 cells assessed as inhibition of EGF-stimulated ERK2 activation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIHIR | Function assay | Inhibition of insulin receptor in mouse NIHIR cells assessed as inhibition of insulin-stimulated IRS1 phosphorylation | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of PDGFR in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of PDGF-stimulated tyrosine autophosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of PDGFR in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as inhibition of PDGF-stimulated phospholipase C gamma phosphorylation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Inhibition of PDGFR in mouse NIH/3T3 cells assessed as PDGF-stimulated Erk2 activation by immunoblotting | 9139660 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 59 mg/mL
(199.1 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 296.32 | Formula | C17H16N2O3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 215543-92-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1=CNC(=C1CCC(=O)O)C=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
VEGFR2
(Cell-free assay) 20 nM
FGFR1
(Cell-free assay) 30 nM
PDGFRβ
(Cell-free assay) 510 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
SU5402 inhibits VEGF-, FGF-, PDGF- dependent cell proliferation with IC50 of 0.05 μM, 2.80μM, 28.4 μM, respectively. In HUVECs, this compound selectively inhibits VEGF-driven mitogenesis in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 of 0.04 μM. In nasopharyngeal epithelial cells, it attenuates LMP1-mediated aerobic glycolysis, cellular transformation, cell migration, and invasion. In mouse C3H10T1/2 cells, this chemical diminishes the effect of FGF23 on cell differentiation.
|
| Kinase Assay |
FGF-R1 and Flk-1/KDR kinase assays.
|
|
The catalytic portion of FGF-R1 and Flk-1/KDR are expressed as GST fusion proteins following infection of Spodoptera frugiperda (sf9) cells with engineered baculoviruses. GST-FGFR1 and GST-Flk1 are purified to homogeneity from infected sf9 cell lysates by glutathione sepharose chromatography. The assays are performed in 96-well microtiter plates that had been coated overnight with 2.0 μg of a polyGlu-Tyr peptide (4:1) in 0.1 mL of PBS per well. The purified kinases are diluted in kinase assay buffer (100 mM Hepes pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, and 0.1 mM sodium orthovanadate) and added to all test wells at 5 ng of GST fusion protein per 0.05 mL volume buffer. Test compounds are diluted in 4% DMSO and added to test wells (0.025 mL/well). The kinase reaction is initiated by the addition of 0.025 mL of 40 μM ATP/40 mM MnCl2, and plates are shaken for 10 min before stopping the reactions with the addition of 0.025 mL of 0.5 M EDTA. The final ATP concentration was 10 μM, which is twice the experimentally determined Km value for ATP. Negative control wells receive MnCl2 alone without ATP. The plates are washed three times with 10 mM Tris pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, and 0.05% Tween-20 (TBST). Rabbit polyclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antiserum is added to the wells at a 1:10000 dilution in TBST for 1 h. The plates are then washed three times with TBST. Goat anti-rabbit antiserum conjugated with horseradish peroxidase was then added to all wells for 1 h. The plates are washed three times with TBST, and the peroxidase reaction is detected with the addition of 2,2‘-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS). The color readout of the assay is allowed to develop for 20−30 min and read on a Dynatech MR5000 ELISA plate reader using a 410 nM test filter.
|
|
| In vivo |
In mice, SU5416 (25 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits subcutaneous growth of a panel of tumor cell lines by inhibiting the angiogenic process associated with tumor growth.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































