- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Sorafenib tosylate Raf inhibitor
Cat.No.S1040
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 637.03
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.99%
99.99
Products Often Used Together with Sorafenib tosylate
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-435 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| UACC257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| MCF7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=2.5 μM | 22560627 | ||
| EKVX | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=2.5 μM | 22560627 | ||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=2.5 μM | 22560627 | ||
| SNB19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=3.2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| OVCAR3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=3.2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| CAKI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=3.2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=3.2 μM | 22560627 | ||
| TK10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | GI50=5 μM | 22560627 | ||
| endothelial precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of endothelial cord area formation in endothelial precursor cells by CD31 cord area detection based phenotypic drug discovery based assay, IC50 = 0.00421 μM. | 22409666 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of GST-tagged recombinant human VEGFR2 expressed in Sf9 cells by radiometric assay, IC50 = 0.0125 μM. | 24368209 | |||
| endothelial precursor cells/ADSC cells | Toxicity assay | Toxicity in endothelial precursor cells co-cultured with stromal precursor ADSC cells by total nuclei count detection based phenotypic drug discovery based assay, EC50 = 5.46 μM. | 22409666 | |||
| endothelial precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of cell migration in endothelial precursor cells by Oris cell migration kit based phenotypic drug discovery based assay, IC50 = 16.7 μM. | 22409666 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 127 mg/mL
(199.36 mM)
Water : 0.01 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 637.03 | Formula | C21H16ClF3N4O3.C7H8O3S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 475207-59-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | BAY 43-9006 tosylate,NSC-724772 tosylate | Smiles | CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O.CNC(=O)C1=NC=CC(=C1)OC2=CC=C(C=C2)NC(=O)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)Cl)C(F)(F)F | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Raf-1
(Cell-free assay) 6 nM
VEGFR2/Flk1
(Cell-free assay) 15 nM
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 22 nM
B-Raf (V599E)
(Cell-free assay) 38 nM
PDGFRβ
(Cell-free assay) 57 nM
mPDGFRβ
(Cell-free assay) 57 nM
FLT3
(Cell-free assay) 58 nM
c-Kit
(Cell-free assay) 68 nM
VEGFR2
(Cell-free assay) 90 nM
FGFR1
(Cell-free assay) 580 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Sorafenib tosylate inhibits both wild-type and V599E mutant B-Raf activity with IC50 of 22 nM and 38 nM, respectively. This compound also potently inhibits mVEGFR2 (Flk-1), mVEGFR3, mPDGFRβ, Flt3, and c-Kit with IC50 of 15 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 58 nM, and 68 nM, respectively. It weakly inhibits FGFR-1 with IC50 of 580 nM. This chemical is not active against ERK-1, MEK-1, EGFR, HER-2, IGFR-1, c-Met, PKB, PKA, cdk1/cyclinB, PKCα, PKCγ, and pim-1. It markedly inhibits VEGFR2 phosphorylation in NIH 3T3 cells with IC50 of 30 nM, and Flt-3 phosphorylation in HEK-293 cells with IC50 of 20 nM. It potently blocks MEK 1/2 and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation in most cell lines but not in A549 or H460 cells, while having no effect on inhibition of the PKB pathway. It inhibits the proliferation of HAoSMC and MDA-MB-231 cells with IC50 of 0.28 μM and 2.6 μM, respectively. In addition to inhibition of the RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, it significantly inhibits the phosphorylation of eIF4E and down-regulates Mcl-1 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a MEK/ERK-independent manner. It inhibits the proliferation of PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 cells with IC50 of 6.3 μM and 4.5 μM, respectively, and leads to the significant induction of apoptosis. |
| Kinase Assay |
Biochemical assays
|
|
Recombinant baculoviruses expressing Raf-1 (residues 305–648) and B-Raf (residues 409–765) are purified as fusion proteins. Full-length human MEK-1 is generated by PCR and purified as a fusion protein from Escherichia coli lysates. Sorafenib tosylate is added to a mixture of Raf-1 (80 ng), or B-Raf (80 ng) with MEK-1 (1 μg) in assay buffer [20 mM Tris (pH 8.2), 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, and 0.15% β-mercaptoethanol] at a final concentration of 1% DMSO. The Raf kinase assay (final volume of 50 μL) is initiated by adding 25 μL of 10 μM γ[33P]ATP (400 Ci/mol) and incubated at 32 °C for 25 minutes. Phosphorylated MEK-1 is harvested by filtration onto a phosphocellulose mat, and 1% phosphoric acid is used to wash away unbound radioactivity. After drying by microwave heating, a β-plate counter is used to quantify filter-bound radioactivity. Human VEGFR2 (KDR) kinase domain is expressed and purified from Sf9 lysates. Time-resolved fluorescence energy transfer assays for VEGFR2 are performed in 96-well opaque plates in the time-resolved fluorescence energy transfer format. Final reaction conditions are as follows: 1 to 10 μM ATP, 25 nM poly GT-biotin, 2 nM Europium-labeled phospho (p)-Tyr antibody (PY20), 10 nM APC, 1 to 7 nM cytoplasmic kinase domain in final concentrations of 1% DMSO, 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.015% Brij-35, 0.1 mg/mL BSA, and 0.1% β-mercaptoethanol. Reaction volumes are 100 μL and are initiated by addition of enzyme. Plates are read at both 615 and 665 nM on a Perkin-Elmer VictorV Multilabel counter at ~1.5 to 2.0 hours after reaction initiation. Signal is calculated as a ratio: (665 nm/615 nM) × 10,000 for each well. For IC50 generation, this compound is added before the enzyme initiation. A 50-fold stock plate is made with this chemical serially diluted 1:3 in a 50% DMSO/50% distilled water solution. Final concentrations of this compound range from 10 μM to 4.56 nM in 1% DMSO.
|
|
| In vivo |
Oral administration of Sorafenib tosylate (~60 mg/kg) demonstrates broad spectrum, dose-dependent anti-tumor activity against a variety of human tumor xenograft models including MDA-MB-231, Colo-205, HT-29, DLD-1, NCI-H460, and A549, with no evidence of toxicity. In association with the anti-tumor efficacy, this compound treatment potently inhibits MEK 1/2 phosphorylation and pERK 1/2 levels in HT-29 and MDA-MB-231 xenografts but not in Colo-205 xenografts, and significantly suppresses tumor microvessel area (MVA) and microvessel density (MVD) in MDA MB-231, HT-29 and Colo-205 tumor xenografts. This compound treatment produces dose-dependent growth inhibition of PLC/PRF/5 tumor xenografts in SCID mice with TGIs of 49% and 78% at 10 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg, respectively, consistent with the inhibition of ERK and eIF4E phosphorylation, reduction of the microvessel area, and induction of tumor cell apoptosis. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | LC3-I / LC-3II / ATG5 p-STAT3 / STAT3/ Mcl-1 β-catenin / Survivin / Mcl-1 / PTMA pERK / ERK p-PKM2(Y105) / PMK2 / Caspase-9 RET(pY1016) / VEGFR2(pY1214) / MEK1(pT292) / ERK(pY204) Cyclin D1 |
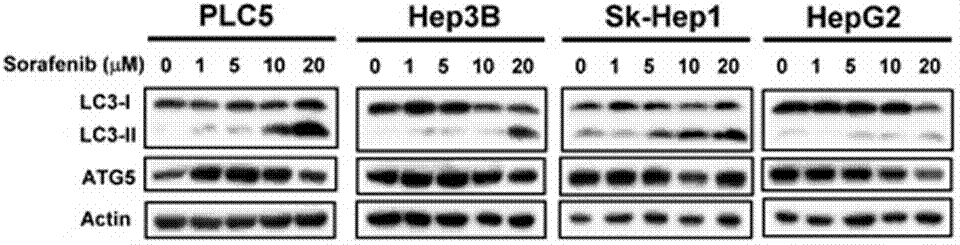
|
23392173 |
| Immunofluorescence | p65 cytochrome c |
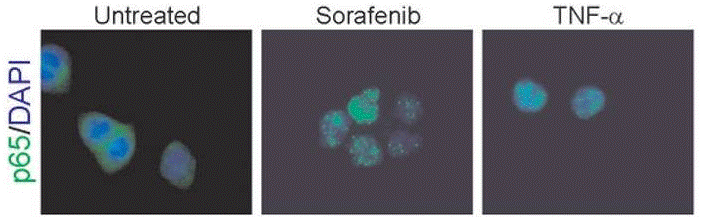
|
22286758 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
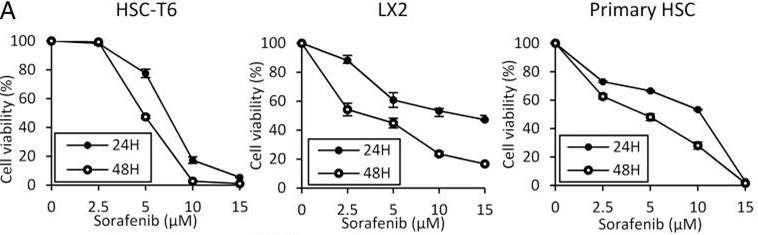
|
26039995 |
| ELISA | TGF-beta / CD206 Caspase-9 / Caspase-3 |
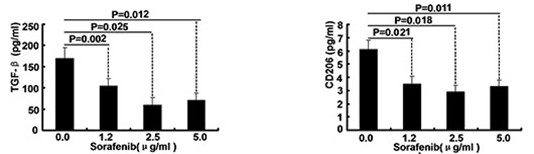
|
26158762 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05068752 | Recruiting | Pancreas Cancer |
HonorHealth Research Institute|Bayer|Genentech Inc. |
October 28 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04763408 | Active not recruiting | Carcinoma Hepatocellular |
Eisai Inc. |
April 9 2021 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































