research use only
Sodium butyrate HDAC inhibitor
Cat.No.S1999
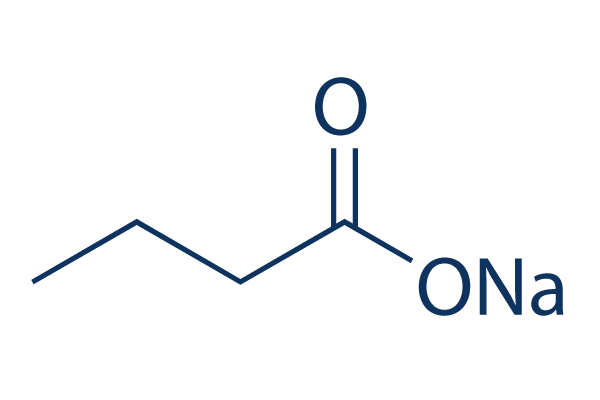
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 110.09
Quality Control
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human K562 cells | Proliferation assay | 1 mM | Antiproliferative activity against human K562 cells at 1 mM in presence of guanosine | |||
| human H1299 cells | Function assay | 7 days | Inhibition of human USP1/UAF1 in human H1299 cells assessed as reduction in colony formation after 7 days, EC50=3 μM | |||
| human JEG3 cells | Function assay | Inhibition of aromatase in human JEG3 cells by scintillation spectrometry, IC50=0.0015 μM | ||||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 22 mg/mL Ethanol : 8 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 110.09 | Formula | C4H7NaO2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 156-54-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NaB, Butanoic acid sodium salt | Smiles | CCCC(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Histone deacetylase
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Butyrate mediates growth inhibition of colonic cancer cells and thereby to elucidate the molecular link between a high-fiber diet and the arrest of colon carcinogenesis. This compound induces p21 mRNA expression in an immediate-early fashion, through transactivation of a promoter cis-element(s) located within 1.4 kb of the transcriptional start site, independent of p53 binding. Sodium butyrate, at physiological concentrations, induces apoptosis in 2 adenoma cell lines, RG/C2 and AA/Cl, and in the carcinoma cell line PC/JW/FI. It exerts potent effects on a variety of colonic mucosal functions such as inhibition of inflammation and carcinogenesis, reinforcing various components of the colonic defence barrier and decreasing oxidative stress. This chemical inhibits most HDAC except class III HDAC and class II HDAC6 and -10. It also is the most effective fatty acid in stimulating or repressing the expression of specific genes.
|
| In vivo |
Sodium butyrate significantly extends survival in a dose-dependent manner, improves body weight and motor performance, and delays the neuropathological sequelae in the R6/2 transgenic mouse model of Huntington's disease (HD). This compound also increases histone and specificity protein-1 acetylation and protects against 3-nitropropionic acid neurotoxicity.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | Cyclin D3 / CDK4 / CDK6 / CDK2 p15INK4b / p21Cip1 Phospho-H3 Ser10 / Acetyl-H3Lys9 / Acetyl-H3Lys14 / Dimethyl-H3 |
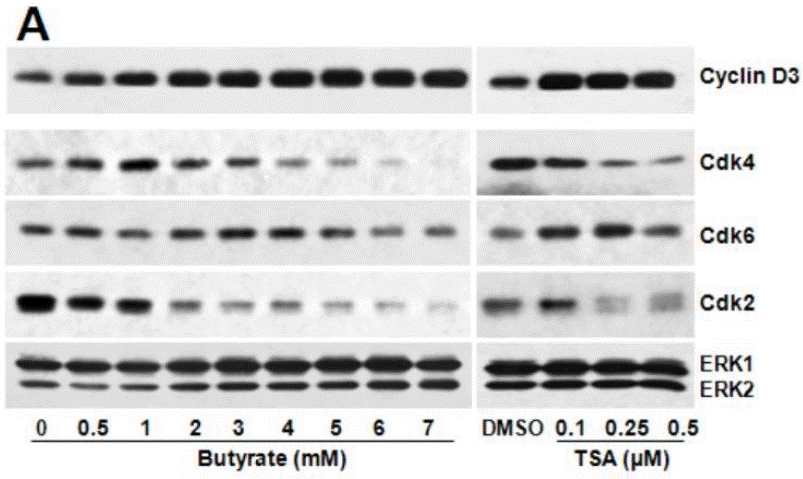
|
24280698 |
| Immunofluorescence | Acetyl-H3Lys9 |
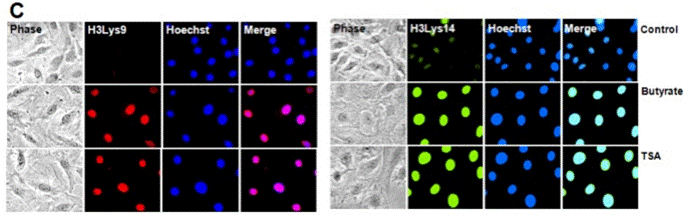
|
24280698 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00800930 | Completed | Shigellosis |
International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research Bangladesh|Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (SIDA)|Karolinska Institutet |
January 2005 | Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































