research use only
Cl-amidine PAD inhibitor
Cat.No.S8141
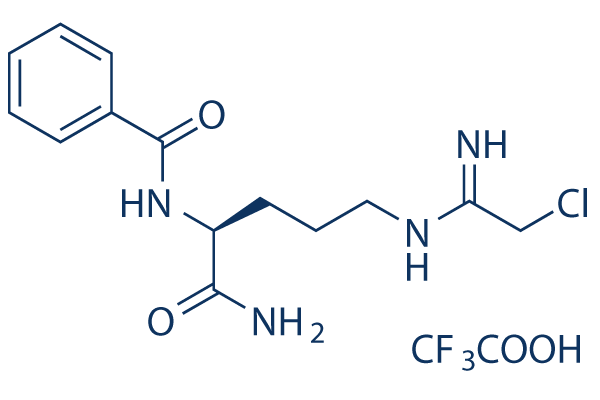
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 424.8
Quality Control
| Related Targets | PD-1/PD-L1 CXCR STING AhR CD markers Interleukins Anti-infection Antioxidant COX Histamine Receptor |
|---|---|
| Other Immunology & Inflammation related Inhibitors | Bestatin (Ubenimex) Bindarit (AF 2838) Tranilast Tempol Sinomenine GI254023X (GI4023) ATP Geniposidic acid CORM-3 Acacetin |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 400 uM | 96 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as decrease in cell number at 400 uM after 96 hrs by trypan blue assay | 23420624 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 200 to 400 uM | 96 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as decrease in cell viability at 200 to 400 uM after 96 hrs by trypan blue assay | 23420624 | |
| HL60 | Function assay | 5 to 10 uM | 15 mins | Inhibition of PAD4 in human HL60 cells assessed as reduction in A23187-induced citrullinated H4 level at 5 to 10 uM preincubated for 15 mins followed by A23187 addition measured after 15 mins by Western blot analysis | 30344909 | |
| HEK293T | Function assay | 10 nM to 100 uM | Inhibition of human recombinant PAD3 expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as conversion of BAEE to sodium benzoyl-L-citrulline at 10 nM to 100 uM by colorimetric analysis | ChEMBL | ||
| HEK293T | Function assay | 100 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of thapsigargin-induced cell death in human HEK293T cells overexpressing human recombinant PAD3 assessed as increase in cell survival at 100 uM treated 15 mins prior to thapsigargin addition measured after 24 hrs drug treatment by methylene blu | ChEMBL | |
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 84 mg/mL
(197.74 mM)
Ethanol : 84 mg/mL Water : 35 mg/mL (Ultrasonic and heating.) |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 424.8 | Formula | C14H19ClN4O2.C2HF3O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1043444-18-3 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(CCl)N)C(=O)N.C(=O)(C(F)(F)F)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PAD1
(Cell-free assay) 0.8 μM
PAD4
(Cell-free assay) 5.9 μM
PAD3
(Cell-free assay) 6.2 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
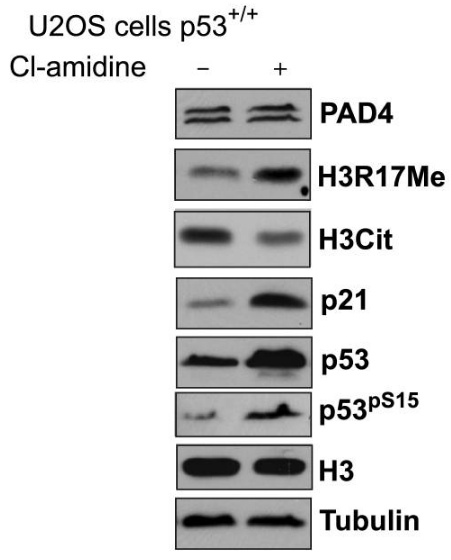
Cl-amidine antagonizes the PAD4-mediated enhancement of the the p300GBD-GRIP1 interaction in a dose-dependent manner. The inhibitory effect of this compound is not a nonspecific one but is targeted at the active PAD4 enzyme. This compound increases p53 expression in CD45 positive immune cells. It triggers the differentiation and apoptosis of multiple cancer cell lines that are p53+/+ and p53−/− (e.g., HL60, HT29, TK6, and U2-OS cells). This chemical induces the expression of p53 and several downstream target genes including the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p21, GADD45, and the proapoptotic protein PUMA in U2-OS osteosarcoma cells.
|
| In vivo |
Cl-amidine treatment inhibits NZM(New Zealand mixed 2328) NET(neutrophil extracellular trap) formation in vivo and significantly alters circulating autoantibody profiles and complement levels while reducing glomerular IgG deposition. Further, this compound increases the differentiation capacity of bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells, improves endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation, and markedly delays time to arterial thrombosis induced by photochemical injury. It delays thrombosis development in NZM mice. This chemical inhibits PADs in mice without significant toxicity and improves disease phenotypes in animal models of inflammatory arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. And it is shown to reduce disease severity in mouse models of ulcerative colitis and RA.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | PAD4 / H3R17Me / H3Cit / p21 / p53 / p-p53 iNOS MMP-2 / MMP-9 p-Elk-1 / Elk-1 |
|
18505818 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































