research use only
Quercitrin Immunology & Inflammation related chemical
Cat.No.S3824
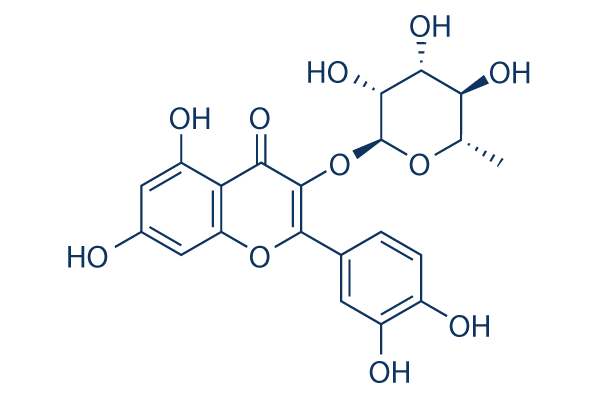
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 448.38
Quality Control
| Related Targets | PD-1/PD-L1 CXCR STING AhR CD markers Interleukins Anti-infection Antioxidant COX Histamine Receptor |
|---|---|
| Other Immunology & Inflammation related Inhibitors | Cl-amidine Bestatin (Ubenimex) Bindarit (AF 2838) Tranilast Tempol Sinomenine GI254023X (GI4023) ATP Geniposidic acid CORM-3 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 89 mg/mL
(198.49 mM)
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 448.38 | Formula | C21H20O11 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 522-12-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | 3-rhamnosyl quercetin, Sophoretin, Meletin, Xanthaurine | Smiles | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(OC3=CC(=CC(=C3C2=O)O)O)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)O)O)O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Quercitrin ameliorates cytokine-impaired viability of RINm5F cells and improves Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in cytokine-treated RINm5F cells. It also reduces production of cellular ROS from cytokines and restrains the enhancement of NO production caused by cytokines in RINm5F cells via inhibition of iNOS expression. |
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Quercitrin significantly suppresses the elevation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, reduces tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) activity, enhances the antioxidant enzyme activities and abrogates cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) induction in mouse brains. This compound also prevents CCl4 induced cerebral function disorders associated with its ability to inhibit the activities of monoamine oxidase (MAO), acetylcholine esterase (AChE) and the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 2B subunit (NR2B). It is known to have biological effects such as anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptosis effects and it might be a more potent antioxidant and a neuroprotective agent than quercetin due to its high bioavailability in the digestive track. This chemical significantly reduces acute systemic inflammation in LPS-induced models as well as attenuates inflammation in the livers of mice. It could also reduce inflammation and apoptosis in cytokine-induced models. In streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic models, quercitrin displays organ protective properties in the pancreas, liver and kidney by improving the antioxidant status. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































