- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
SRT1720 HCl Sirtuin activator
SRT1720 HCl is a selective SIRT1 activator with EC50 of 0.16 μM in a cell-free assay, but is >230-fold less potent for SIRT2 and SIRT3. SRT1720 induces autophagy.
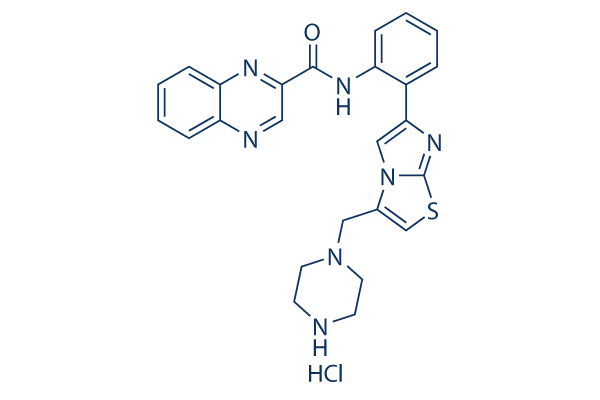
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 506.02
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.61%
99.61
Products Often Used Together with SRT1720 HCl
It increases endometriotic lesions in Pgrcre/+Rosa26mTmG/+ mice, while Selisistat significantly reduces the number of endometriotic lesions.
Quercetin is more efficacious than this compound in combatting the cytotoxic effects of D-GalN/LPS in Male Wistar rats.
It and Astragaloside exhibit similar effects in calpain-1 knockout on Vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED).
In combination with MDL-28170, this compound restores the increased level of mitoROS and the reduced membrane potential in human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs), including As-IV.
Related Products
| Related Targets | SIRT1 SIRT2 SIRT3 SIRT6 SIRT5 | Click to Expand |
|---|---|---|
| Related Products | Selisistat (EX 527) Sirtinol Fisetin 3-TYP AGK2 OSS_128167 SRT2104 (GSK2245840) SirReal2 Thiomyristoyl Salvianolic acid B SRT2183 UBCS039 Salermide SRT3025 HCl AK 7 NRD167 Inauhzin CAY10602 | Click to Expand |
| Related Compound Libraries | Kinase Inhibitor Library FDA-approved Drug Library Natural Product Library Bioactive Compound Library-I Highly Selective Inhibitor Library | Click to Expand |
Signaling Pathway
Cell Culture and Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CACs | Function Assay | 4 μM | 30 min | DMSO | induces acute SIRT1 activation | 26254104 |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 µM | 1 h | reduces the TGF-β-stimulated VEGF release in dose- and time-dependent manner | 26136978 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 µM | 12 h | reduces the VEGF mRNA expression levels stimulated by TGF-β | 26136978 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 1 h | suppresses the TGF-β-induced phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAP kinase or SAPK/JNK | 26136978 | |
| WE-68 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-24 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| SK-ES-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| SK-N-MC | Apoptosis Assay | 0-2.5 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| WE-68 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| SK-ES-1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| SK-N-MC | Function Assay | 3 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | increases expression of α-SMA and fibronectin dose dependently | 26022003 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | enhances phosphorylation of EGFR and PDGFRβ | 26022003 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | enhances STAT3 phosphorylation | 26022003 | |
| RAW264.7 | Function Assay | 1 μM | 6 h | upregulates the reduced SIRT1 protein or mRNA levels by high glucose | 25793995 | |
| MCF10A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| SKBR3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| SUM149 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| HS578T | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| BT20 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| A459 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| HCT116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| Neu | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 8 h | increases the number of acidic vesicular organelles | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 16 h | induces lysosomal membrane permeabilization | 25411356 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the FGF-2-stimulated osteoprotegerin release | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the FGF-2-induced osteoprotegerin mRNA expression | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the FGF-2-induced osteoprotegerin mRNA expression | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the BMP-4-stimulated VEGF release | 24435444 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the PGF2α-stimulated OPG release | 24333336 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | reduces the PGF2α-stimulated phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAP kinase | 24333336 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the PGF2α-induced phosphorylation of both MEK1/2 and Raf-1 | 24333336 | |
| RPE | Cell Viability Assay | 5 µM | 1 h | attenuates OAβ-induced decrease of cell viability | 24036938 | |
| 9607 | Cell Viability Assay | 1 μM | 36 h | increases the cell viability compared with melatonin alone | 23726949 | |
| 9607 | Function Assay | 1 μM | 36 h | increases SIRT1 and decreased acetylated-p53 expression | 23726949 | |
| RPMI.8226 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| U266 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| MM.1S | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| KMS12 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| LR5 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| MM.1R | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| Ina6 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| RPMI-8226 | Apoptosis Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | induces a significant increase in the Annexin V+/PI− apoptosis | 21950728 | |
| MM.1R | Apoptosis Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | induces a significant increase in the Annexin V+/PI− apoptosis | 21950728 | |
| H411EC3 | Function Assay | 50/100 nM | 6 h | increases SIRT1 activity in the presence of TSA, PEPCK activity, mRNA levels of Pck1 and Pgc1α, and elevating glucose production | 21212096 | |
| hepatocytes | Function Assay | 10 nM | 6 h | increases SIRT1 activity in the presence of TSA, PEPCK activity, mRNA levels of Pck1 and Pgc1α, and elevating glucose production | 21212096 | |
| hepatocytes | Function Assay | 10 nM | 6 h | increases Hmgcr and Acc gene expression | 21212096 | |
| U2OS | Function assay | 0.10 uM | Activation of SIRT1 in human U2OS cells assessed as decrease in p53 deacetylation level at 0.10 uM | 18046409 | ||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets |
|
|---|
In vitro |
||||
| In vitro | The maximum activation ratio of SRT1720 versus the closest sirtuin homologues, SIRT2 (EC1.5 = 37 μM) and SIRT3 (EC1.5 > 300 μM) is up to 781%. SRT1720 binds to the SIRT1 enzyme-peptide substrate complex at an allosteric site amino-terminal to the catalytic domain and lower the Michaelis constant for acetylated substrates. SRT1720 could reduce fed glucose levels. SRT1720 does not have an effect on fasting glucose in chow-fed mice, revealing that pharmacological SIRT1 activation is unlikely to induce hypoglycaemia. SRT1720 significantly reduces the hyperinsulinaemia after 4 weeks, partially normalizing increased insulin levels. SRT1720 treatment increases mitochondrial capacity by 15% in gastrocnemius muscle as measured by citrate synthase activity. [1] Higher concentrations of SRT1720 (15 μM) induces a modest (10-20%) decrease in normal cell viability. SRT1720 also significantly inhibits VEGF-dependent MM cell migration. [2] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | SIRT1 fluorescence polarization assay | |||
| In the SIRT1 FP assay, SIRT1 activity is monitored using a 20 amino acid peptide (Ac-Glu-Glu-Lys(biotin)-Gly-Gln-Ser-Thr-Ser-Ser-His-Ser-Lys(Ac)-Nle-Ser-Thr-Glu-Gly–Lys(MR121 or Tamra)-Glu-Glu-NH2) derived from the sequence of p53. The peptide is N-terminally linked to biotin and C-terminally modified with a fluorescent tag. The reaction for monitoring enzyme activity is a coupled enzyme assay where the first reaction is the deacetylation reaction catalyzed by SIRT1 and the second reaction is cleavage by trypsin at the newly exposed lysine residue. The reaction is stopped and streptavidin is added in order to accentuate the mass differences between substrate and product. The sensitivity of the FP assay allows identification of SRT1720. The fluorescence polarization reaction conditions are as follows: 0.5 μM peptide substrate, 150 μM βNAD+, 0-10 nM SIRT1, 25 mM Tris-acetate pH 8, 137 mM Na-Ac, 2.7 mM K-Ac, 1 mM Mg-Ac, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.1% Pluronic F127, 10 mM CaCl 2, 5 mM DTT, 0.025% BSA, and 0.15 mM nicotinamide. The reaction is incubated at 37 °C and stopped by addition of nicotinamide, and trypsin is added to cleave the deacetylated substrate. This reaction is incubated at 37 °C in the presence of 1 μM streptavidin. Fluorescent polarization is determined at excitation (650 nm) and emission (680 nm) wavelengths. | ||||
| Cell Research | Cell lines | Human vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) | ||
| Concentrations | 5 μM | |||
| Incubation Time | 2 hours | |||
| Method | Transwell Insert Assays are utilized to measure migration. In vitro angiogenesis is assessed by Matrigel capillary-like tube structure formation assay. For endothelial tube formation assay, human vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) are obtained from Clonetics and maintained in endothelial cell growth medium-2 containing 5% FBS. After three passages, HUVEC cell viability is measured with the trypan blue exclusion assay, and <5% of cell death is observed with SRT1720 treatment. |
|||
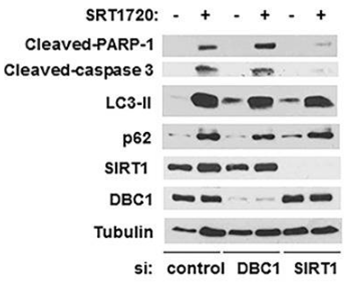
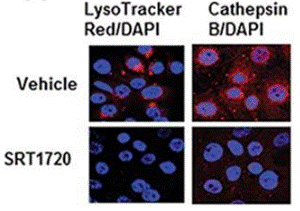
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | Cleaved-PARP-1 / Cleaved-caspase-3 / LC3-II / p62 / SIRT1 |
|
26655844 | |
| Immunofluorescence | Cathepsin B |
|
26655844 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
25411356 | |
In Vivo |
||
| In vivo | In DIO mice SRT1720 mimics several of the effects observed after calorie restriction including improved insulin sensitivity, normalized glucose and insulin levels, and increased mitochondrial capacity. In addition, in diet-induced obese and genetically obese mice, SRT1720 improves insulin sensitivity, lower plasma glucose, and increase mitochondrial capacity. Thus, SRT1720 is a promising new therapeutic agent for treating diseases of ageing such as type 2 diabetes. Consistent with improved glucose tolerance, the glucose infusion rate required to maintain euglycaemia is approximately 35% higher in SRT1720-treated fa/fa rats, and the total glucose disposal rate is increased by approximately 20%. [1] SRT1720 also prevents multiple myeloma tumor growth. |
|
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | Chase-SCID mice with MM.1S cells |
| Dosages | 200 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Orally | |
References |
|
Chemical Information
| Molecular Weight | 506.02 | Formula | C25H23N7OS.HCl |
| CAS No. | 1001645-58-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| Synonyms | N/A | ||
| Smiles | C1CN(CCN1)CC2=CSC3=NC(=CN23)C4=CC=CC=C4NC(=O)C5=NC6=CC=CC=C6N=C5.Cl | ||
Storage and Stability
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 100 mg/mL ( (197.62 mM) Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
|||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
How can we prepare it for in vivo mouse studies?
Answer:
It can be dissolved in 30% PEG 400+0.5% Tween 80+5% Propylene glycol at 30mg/ml as a suspension, which is fine for oral gavage. We’ve also found that it can be dissolved in 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+1% Tween 80+ddH2O at 3mg/ml clearly, making it suitable for injection. When preparing the solution, please dissolve the compound in DMSO clearly first, then add PEG and Tween. After they are mixed well, dilute with water.