research use only
Sirtinol Sirtuin inhibitor
Cat.No.S2804
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 394.47
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC JAK BET Histone Methyltransferase PKC PARP HIF PRMT EZH2 AMPK |
|---|---|
| Other Sirtuin Inhibitors | SRT 1720 Hydrochloride Selisistat (EX-527) Fisetin 3-TYP AGK2 SRT2104 (GSK2245840) OSS_128167 SirReal2 Thiomyristoyl NRD167 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human MCF7 cells | Proliferation assay | 30 μM | 24-72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells at 30 uM after 24 to 72 hrs | 24340169 | |
| human MCF7 cells | Function assay | 50 μM | 24 h | Inhibition of SIRT1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase in acetylation of p53 at lys 382 at 50 uM after 24 hrs by Western blot analysis | 24340169 | |
| human U937 cells | Apoptosis assay | 50 μM | 45 h | Induction of apoptosis in human U937 cells at 50 uM after 45 hrs by flow cytometry | 23189967 | |
| Hs683 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human Hs683 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=33.9μM | 28475330 | ||
| U373 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human U373 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=39.3μM | 28475330 | ||
| Hs683 | Cell cycle assay | 24 to 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human Hs683 cells assessed as accumulation at G1 phase at IC50 after 24 to 48 hrs by propidium iodide staining-based flow cytometry | 28475330 | ||
| Hs683 | Cell cycle assay | 24 to 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human Hs683 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase at IC50 after 24 to 48 hrs by propidium iodide staining-based flow cytometry | 28475330 | ||
| U373 | Cell cycle assay | 24 to 48 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human U373 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase at IC50 after 24 to 48 hrs by propidium iodide staining-based flow cytometry | 28475330 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 23 mg/mL
(58.3 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 394.47 | Formula | C26H22N2O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 410536-97-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC(C1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2N=CC3=C(C=CC4=CC=CC=C43)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Sirtinol does not inhibit class I and class II HDACs.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
SIRT2
(Cell-free assay) 38 μM
SIRT1
(Cell-free assay) 131 μM
|
| In vitro |
Sirtinol potently inhibits recombinant yeast Sir2p activity in vitro with IC50 of 68 μM. Unlike TSA, this compound has shown no effect on human HDAC1, indicating that it is a selective sirtuin inhibitor. Unlike TSA, treatment of human primary fibroblasts with this chemical does not cause global changes in acetylation of histones and tubulin, nor does it induce a morphological change in the HeLa tumor cell line. Treatment with this inhibitor at 100 μM for 24 hours causes a sustained growth arrest in MCF-7 and H1299 cells for up to 9 days after its withdrawal. This treatment induces increased SA-β-gal activity and expression of PAI-1 in both MCF-7 and H1299 cells, more potently than Splitomicin. It inhibits colony formation at concentrations of 33 μM and higher in MCF-7 and H1299 cells, more effectively compared with Splitomicin. This compound (100 μM) significantly attenuates both basal and EGF- or IGF-I-stimulated phosphorylation of ERK, JNK/SAPK and p38 MAPK in MCF-7 and H1299 cells. It blocks the basal and EGF-stimulated activation of Ras. Consistent, basal and EGF- or IGF-I-stimulated phosphorylation of Raf-1, MEK, SEK1/MKK4 and MKK7 is attenuated in cells treated with this inhibitor. Inhibition of Sirt1 by this chemical enhances UV- and H2O2-induced p53 acetylation to enhance cell death in cultured skin keratinocytes. Blocking of Sirt1 by this treatment results in a significant inhibition in the growth and viability of human PCa cells while having no effect on normal prostate epithelial cells.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Inhibition in vitro of human Sirt2 activity
|
|
1.5 μg of recombinant human GST-Sirt2 (amino acids 18-340) are incubated at 30°C for 2 hours in 50 μL of assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, 4 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dithiothreitol with different concentrations of Sirtinol, 50 μM NAD, and tritiated acetylated HeLa histones (1000 cpm), purified by acid extraction. HDAC activity is determined by scintillation counting of the ethyl acetate-soluble [3H]acetic acid.
|
|
| In vivo |
Administration of Sirtinol at 1 mg/kg attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine production and protects against hepatic injury following trauma-hemorrhage in male Sprague-Dawley rats.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
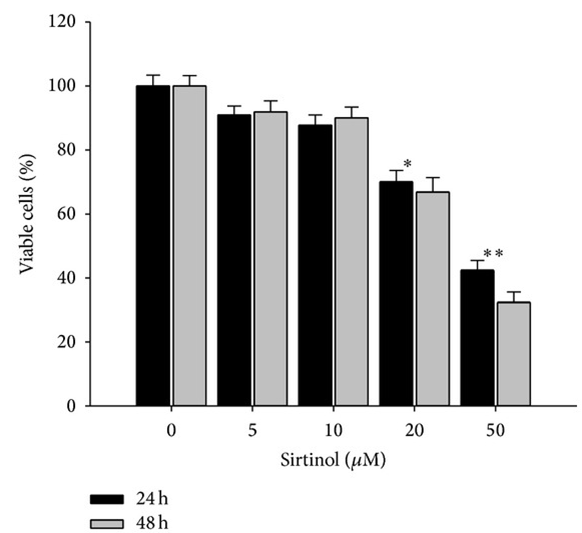
|
25184156 |
| Western blot | SIRT1 / p-AKT / Foxo3a / β-catenin Foxp3 / RORγt Ac-H3K9 / Fibrobectin / Collagen 1 / α-SMA |

|
25184156 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































