- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Veliparib (ABT-888)
PARP inhibitor
research use only
Veliparib (ABT-888, NSC 737664) is a potent inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 with Ki of 5.2 nM and 2.9 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. It is inactive to SIRT2. Veliparib increases autophagy and apoptosis. Phase 3.
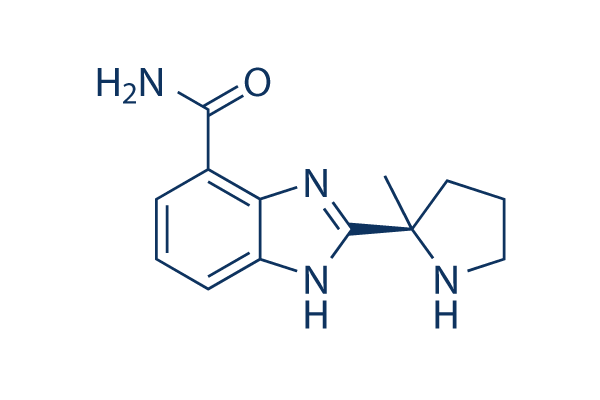
Veliparib (ABT-888) Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 244.29
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.94%
99.94
Veliparib (ABT-888) Related Products
| Related Targets | PARP1 PARP2 PARP3 Tankyrase-1 Tankyrase-2 PARP14 PARP7 TNKS1 TNKS2 | Click to Expand |
|---|---|---|
| Related Products | XAV-939 PJ34 HCl AG-14361 Iniparib (BSI-201) A-966492 G007-LK UPF 1069 AZD2461 Pamiparib ME0328 3-Aminobenzamide NMS-P118 Stenoparib (E7449) NVP-TNKS656 WIKI4 Benzamide BGP-15 2HCl NU1025 BYK204165 Fluzoparib (SHR-3162) Picolinamide | Click to Expand |
| Related Compound Libraries | FDA-approved Drug Library Natural Product Library Apoptosis Compound Library DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library Cell Cycle compound library | Click to Expand |
Signaling Pathway
Cell Culture and Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4-Fuk | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.5691 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.9207 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.2538 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.4818 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.2771 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.7031 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0998 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGROV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.3304 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-54 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.966 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.7018 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.567 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.7345 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8499 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6001 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.5868 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-280 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3889 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3642 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.3599 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7457 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.4241 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4901 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.4798 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3814 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.3748 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.0235 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB771 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8373 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4663 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.434 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.8862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KASUMI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.89266 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.43603 μM | SANGER | |||
| C41 | Kinase Assay | 30 min | Inhibition of PARP1 with EC50 of 0.002 μM | 19888760 | ||
| Jurkat | Kinase Assay | 96 h | DMSO | Inhibition of PARP1 assessed as reduction of cell viability with EC50 of 3 μM | 23850199 | |
| Capan1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Antiproliferative activity against BRCA2 gene mutated human Capan1 cells with IC50 of 39.7 μM | 24398383 | |
| ML-1 | Apoptotic Assay | 2.5 μM | 24 h | DMSO | Synergistically enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in ML-1 cells | 24895135 |
| HCT-116 | Kinase Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | PARP activity decreases | 23054213 | |
| UM-SCC1 | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| FaDu | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Reduces the cell viability | 21912620 | |
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| LoVo | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of PARP in human LoVo cells assessed as inhibition of poly(ADP)-ribose polymerization for 30 mins by fluorescence assay, EC50 = 0.00594 μM. | 26652717 | ||
| VC8 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | Cytotoxicity against Chinese hamster VC8 cells harboring BRCA2 deficient after 3 days by CCK8 assay, CC50 = 2.344 μM. | 29335205 | ||
| LoVo | Cytotoxicity assay | 0.4 uM | 5 days | Potentiation of -induced cytotoxicity in human LoVo cells assessed as GI50 at 0.4 uM after 5 days by Celltiter-Glo assay, GI50 = 6.203 μM. | 26652717 | |
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.8517 μM | SANGER | |||
| BALL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.9532 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.8414 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.3063 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.952 μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9566 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.7246 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1693 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2898 μM | SANGER | |||
| HLE | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.054 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2029 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.4238 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.8969 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC11TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.6863 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.746 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-NB-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.1363 μM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.9091 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7455 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5649 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-150 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.9986 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5119 μM | SANGER | |||
| H9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.2833 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-668 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.6294 μM | SANGER | |||
| GP5d | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.053 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.6717 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.5325 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.2042 μM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.9589 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5565 μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9053 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5389 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.166 μM | SANGER | |||
| HEC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9196 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.485 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.4752 μM | SANGER | |||
| DT40 | Cytotoxic Assay | 72 h | DMSO | Cytotoxicity against chicken BRCA2-deficient DT40 cells | 24922587 | |
| PC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | Induces a significant inhibition in colony formation | 21571912 | ||
| C41 | Function assay | Inhibition of PARP1 in human C41 cells, EC50 = 0.002 μM. | 19143569 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.0798 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.12841 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.45409 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.75173 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-680 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21406 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.79704 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.81924 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mo-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.6389 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.7585 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.3791 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H510A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.9034 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.7856 μM | SANGER | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Mechanism of Action
| Description | Veliparib (ABT-888, NSC 737664) is a potent inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 with Ki of 5.2 nM and 2.9 nM in cell-free assays, respectively. It is inactive to SIRT2. Veliparib increases autophagy and apoptosis. Phase 3. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Increases the efficacy of common cancer therapies such as radiation and alkylating agents. | ||||
| Targets |
|
In vitro |
||||
| In vitro | ABT-888 is inactive to SIRT2 (>5 μM). [1] ABT-888 inhibits the PARP activity with EC50 of 2 nM in C41 cells. [2] ABT-888 could decrease the PAR levels in both irradiated and nonirradiated H460 cells. ABT-888 also reduces clonogenic survival and inhibits DNA repair by PARP-1 inhibition in H460 cells. ABT-888 increases apoptosis and autophagy in H460 cells when combination with radiation. [3] ABT-888 also inhibits PARP activity in H1299, DU145 and 22RV1 cells and the inhibition is independent of p53 function. ABT-888 (10 μM) suppresses the surviving fraction (SF) by 43% in the clonogenic H1299 cells. ABT-888 shows effective radiosensitivity in oxic H1299 cells. Furthermore, ABT-888 could attenuate the SF of hypoxic-irradiated cells including H1299, DU145 and 22RV1. [4] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | In vitro PARP assays | |||
| PARP assays are conducted in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 1 mM DTT, 1.5 μM [3H]NAD+ (1.6 μCi/mmol), 200 nM biotinylated histone H1, 200 nM slDNA, and 1 nM PARP-1 or 4 nM PARP-2 enzyme. Reactions are terminated with 1.5 mM benzamide, transferred to streptavidin Flash plates, and counted using a TopCount microplate scintillation counter. | ||||
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | p-STAT3 / STAT3 / p-AKT(S473) / p-AKT(T308) / p-ERK / p-p38 |
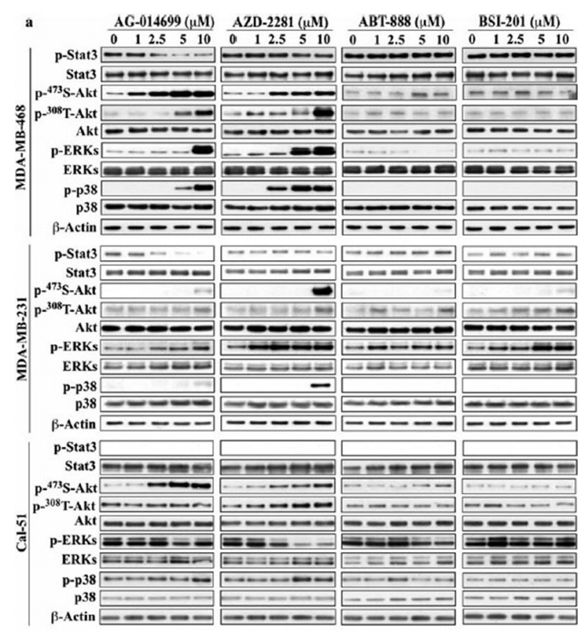
|
22678161 | |
| Immunofluorescence | HuR BRCA1 |
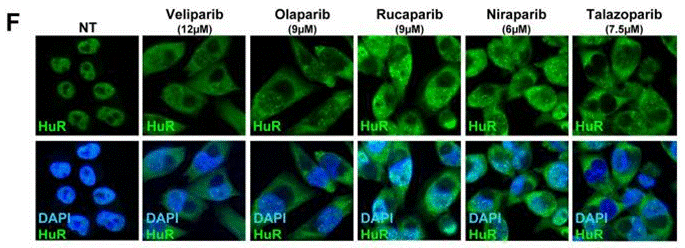
|
28687616 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability (TNBC cell lines) Cell viability (melanoma cells) |
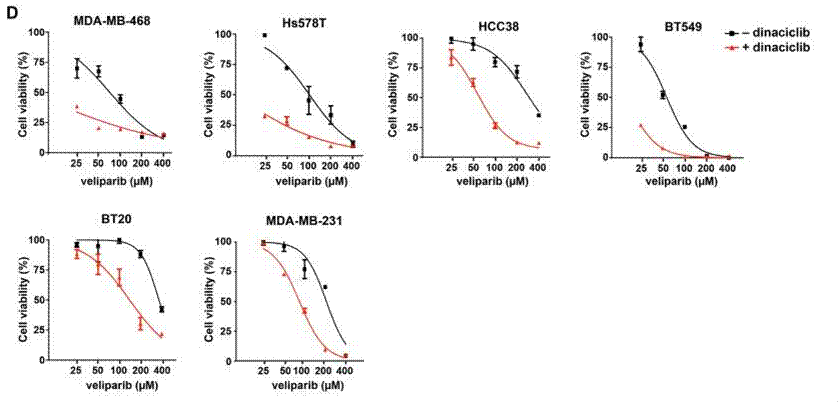
|
27880910 | |
In Vivo |
||
| In vivo | The oral bioavailability of ABT-888 is 56%-92% in mice, Sprague-Dawley rats, beagle dogs, and cynomolgus monkeys after oral administration. [1] ABT-888 (25 mg/kg i.p.) could improve tumor growth delay in a NCI-H460 xenograft model with well tolerated. Combination with radiation, ABT-888 decreases the tumor vessel formation. [3] ABT-888 reduces intratumor PAR levels by more than 95% at a dose of 3 and 12.5 mg/kg in A375 and Colo829 xenograft models and the suppression could be maintained over time. [4] |
|
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | NCI-H460, H460, B16F10 and 9L xenografts in C57BL/6 mice |
| Dosages | ~25 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Orally administered | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03044795 | Withdrawn | Cancer |
University Medical Center Groningen|AbbVie|Dutch Cancer Society |
November 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02723864 | Completed | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
August 9 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02483104 | Completed | Ovarian Cancer |
AbbVie |
July 2015 | Phase 1 |
References |
|
Chemical Information
| Molecular Weight | 244.29 | Formula | C13H16N4O |
| CAS No. | 912444-00-9 | SDF | Download Veliparib (ABT-888) SDF |
| Synonyms | NSC 737664 | ||
| Smiles | CC1(CCCN1)C2=NC3=C(C=CC=C3N2)C(=O)N | ||
Storage and Stability
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 49 mg/mL ( (200.58 mM) Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
|||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field