research use only
BGP-15 2HCl PARP inhibitor
Cat.No.S8370
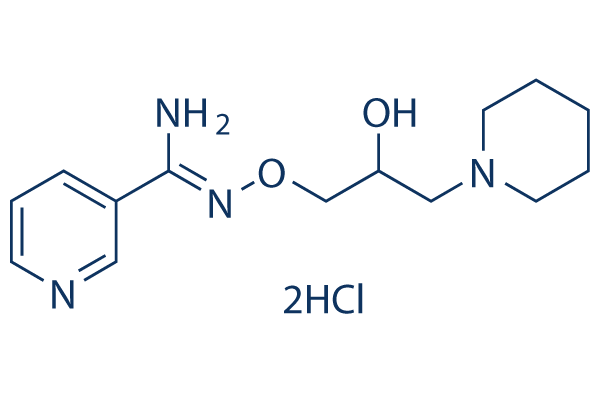
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 351.27
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Other PARP Inhibitors | XAV-939 AZD5305 (Saruparib) Veliparib (ABT-888) PJ34 HCl AG-14361 Iniparib (BSI-201) G007-LK Pamiparib UPF 1069 A-966492 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 70 mg/mL
(199.27 mM)
Water : 70 mg/mL Ethanol : 70 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 351.27 | Formula | C14H22N4O2.2HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 66611-37-8 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1CCN(CC1)CC(CON=C(C2=CN=CC=C2)N)O.Cl.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PARP
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
The hydroxylamine derivative BGP-15 is a coinducer of HSP72 in vitro, but only in the presence of cotreatment with heat and had no effect on HSP90 levels. BGP-15 (200 μM) prevented the imatinib mesylate-induced oxidative damages, attenuated the depletion of high-energy phosphates, altered the signaling effect of imatinib mesylate by preventing p38 MAP kinase and JNK activation, and induced the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK-3beta. The suppressive effect of BGP-15 on p38 and JNK activation could be significant because these kinases contribute to the cell death and inflammation in the isolated perfused heart.
|
| In vivo |
BGP-15 improves cardiac function and reduces arrhythmic episodes in two independent mouse models, which progressively develop HF and AF. BGP-15 administered in 100-200 mg/kg oral doses shortly before cisplatin treatment either prevented or significantly inhibited the development of cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. BGP-15 had a significant effect on the antioxidant status of kidney during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. It elevated the decreased glutathione and catalase levels, but did not affect SOD activity. BGP-15 treatment decreased the cisplatin-caused ROS production and restored the level of high energy phosphate intermediates. While BGP-15 protected against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity, it did not reduce the antitumor efficacy of this cytostatic agent. BGP-15 increased the survival of cisplatin-treated P-388 leukemia bearing mice. BGP-15 inhibits the cisplatin-induced poly-ADP-ribosylation in the kidney. At the same time, BGP-15 restored the cisplatin-induced disturbance in energy metabolism and preserved the ATP level in the protected tissue.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































