- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
TW-37 Bcl-2 inhibitor
Cat.No.S1121
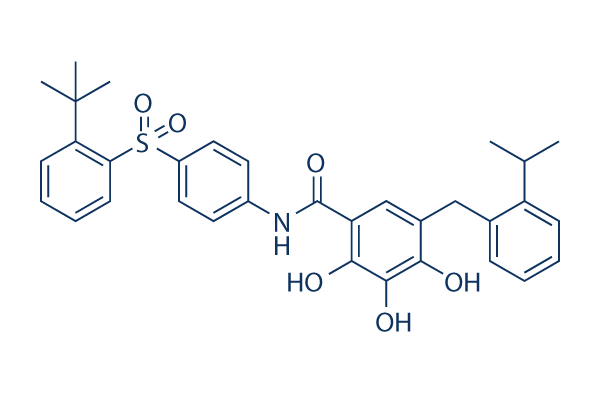
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 573.7
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.78%
99.78
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human JAR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human JAR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.6 nM | ||||
| human Ca9-22 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Ca9-22 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=3.82 nM | ||||
| human CHL-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CHL-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.9 nM | ||||
| human A549 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A549 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=14.09 nM | ||||
| human RKO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RKO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.17 nM | ||||
| human GCIY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GCIY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.83 nM | ||||
| human BHT-101 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHT-101 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.83 nM | ||||
| human Hs-578-T cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Hs-578-T cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.59 nM | ||||
| human SK-UT-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-UT-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=28.68 nM | ||||
| human NB7 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.28 nM | ||||
| human YKG-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human YKG-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.76 nM | ||||
| human HuH-7 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HuH-7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.82 nM | ||||
| human SAS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SAS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=33.18 nM | ||||
| human UACC-62 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human UACC-62 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.35 nM | ||||
| human AGS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AGS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.53 nM | ||||
| human SK-MEL-30 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-30 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.97 nM | ||||
| human A427 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A427 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.69 nM | ||||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=52.13 nM | ||||
| human HCT-116 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCT-116 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=52.66 nM | ||||
| human A673 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A673 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=53.85 nM | ||||
| human SF126 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SF126 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=57.07 nM | ||||
| human SW872 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW872 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=58.9 nM | ||||
| human NCI-H1581 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1581 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=67.64 nM | ||||
| human SK-MEL-5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=69.25 nM | ||||
| human CP50-MEL-B cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CP50-MEL-B cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=69.59 nM | ||||
| human YH-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human YH-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=70.59 nM | ||||
| human LXF-289 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LXF-289 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=72.85 nM | ||||
| human MC-IXC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MC-IXC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=75.33 nM | ||||
| human NB14 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB14 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=76.45 nM | ||||
| human HEC-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HEC-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=81.37 nM | ||||
| human U-87-MG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U-87-MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=82.24 nM | ||||
| human HOS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HOS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=84.71 nM | ||||
| human HUTU-80 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HUTU-80 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=87.01 nM | ||||
| human A375 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A375 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=88.83 nM | ||||
| human A204 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A204 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=97.84 nM | ||||
| human GB-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GB-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=98.69 nM | ||||
| human MDA-MB-231 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.10807 μM | ||||
| human SW982 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW982 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.1107 μM | ||||
| human SW756 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW756 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.11236 μM | ||||
| human MG-63 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MG-63 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.11248 μM | ||||
| human Daoy cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Daoy cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.14073 μM | ||||
| human MDA-MB-453 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MDA-MB-453 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.15188 μM | ||||
| human HT-144 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HT-144 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.15201 μM | ||||
| human LoVo cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LoVo cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.16093 μM | ||||
| human NY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.17762 μM | ||||
| human SW1783 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1783 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.21301 μM | ||||
| human A2780 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A2780 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.21846 μM | ||||
| human MDA-MB-361 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MDA-MB-361 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.2264 μM | ||||
| human RPMI-2650 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RPMI-2650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.23831 μM | ||||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 115 mg/mL
(200.45 mM)
Ethanol : 4 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 573.7 | Formula | C33H35NO6S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 877877-35-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)C1=CC=CC=C1CC2=CC(=C(C(=C2O)O)O)C(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4C(C)(C)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Mcl-1
(Cell-free assay) 0.26 μM(Ki)
Bcl-2
(Cell-free assay) 0.29 μM(Ki)
Bcl-xL
(Cell-free assay) 1.11 μM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
TW-37 targets the BH3-binding groove in Bcl-2 where proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins bind, and shows higher affinity and selectivity for Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 over Bcl-xL with Ki values of 0.29 μM, 0.26 μM and 1.11 μM, respectively. In vitro, this compound shows significant anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect in a de novo chemo-resistant WSU-DLCL2 lymphoma cell line and primary cells obtained from a lymphoma patient without effects on normal peripheral blood lymphocytes. It exhibits the inhibitory effect on both cell growth and cell death in endothelial cell with IC50 of approximately 1.8 μM without effect on the fibroblasts exposed to the same concentration range as the endothelial cells. In addition, this chemical also shows the anti-proliferation effects in MCF-7, LNCaP, and SLK tumor cell lines with the same or lower concentration range than those required to inhibit endothelial cell growth. |
| Kinase Assay |
Fluorescence polarization-based binding assay for recombinant Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1 protein
|
|
For this assay, the 21-residue BH3 peptide QEDIIRNIARHLAQVGDSMDR derived from Bid labeled with the FAM-Bid and recombinant proteins derived from human Bcl-2,Bcl-X L,and Mcl-1 are employed. It is determined that FAM-Bid has a Ki of 11 nM to Bcl-2 protein,25 nM to Bcl-XL protein,and 5.7 nM to Mcl-1 protein. The competitive binding assay for Bcl-XL is same as that for Bcl-2 with the following exceptions: 30 nM Bcl-XL protein and 2.5 nM FAM-Bid peptide in the following assay buffer [50 mM Tris-Bis (pH 7.4) and 0.01% bovine gamma-globulin].
|
|
| In vivo |
TW-37 shows a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of 40 mg/kg for three i.v. injections in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice when given alone, and enhances tumor inhibitory effect of the CHOP regimen. This compound, administrated by i.v. produces the antiangiogenic effect by decreasing the density of functional human microvessels in the severe combined immunodeficient mouse model of human angiogenesis. The combination of this chemical and MEK inhibitors synergistically block melanoma cell growth in mice by a significant reduction in tumor volume and tumor mass. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































