research use only
Gambogic Acid Bcl-2 inhibitor
Cat.No.S2448
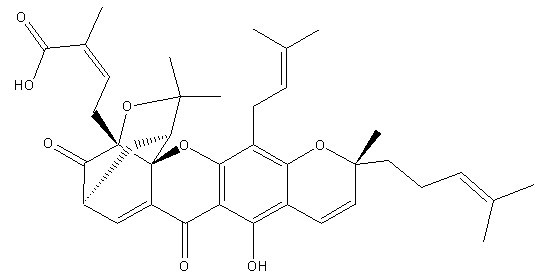
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 628.75
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Caspase PD-1/PD-L1 Ferroptosis p53 Apoptosis related Synthetic Lethality STAT TNF-alpha Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Other Bcl-2 Inhibitors | Navitoclax (ABT-263) S63845 ABT-737 Obatoclax Mesylate (GX15-070) A-1331852 A-1210477 TW-37 A-1155463 Dihydrochloride AZD5991 UMI-77 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(159.04 mM)
Ethanol : 100 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 628.75 | Formula | C38H44O8 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 2752-65-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Guttatic Acid, Guttic Acid, Beta-Guttiferrin | Smiles | CC(=CCCC1(C=CC2=C(C3=C(C(=C2O1)CC=C(C)C)OC45C6CC(C=C4C3=O)C(=O)C5(OC6(C)C)CC=C(C)C(=O)O)O)C)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Bcl-w
0.02 μM
Bcl-B
0.66 μM
Mcl-1
0.79 μM
Bfl-1
1.06 μM
Bcl-2
1.21 μM
Bcl-xL
1.47 μM
Caspase
<1.64 μM(EC50)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Gambogic Acid is a caged xanthone that is derived from Garcinia hanburyi and functions as a strong apoptotic inducer in many types of cancer cells by inhibiting human Bcl-2 family proteins and activating caspases. This compound also blocks Kir2.1 channels with EC50 of ≤ 100 nM. It significantly inhibits human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation, migration, invasion, tube formation, and micro-vessel growth at nM concentration.
|
| In vivo |
Gambogic Acid effectively inhibits tumor angiogenesis and suppressed tumor growth with low side effects using metronomic chemotherapy with this compound. It has multiple functional effects including the induction of apoptosis, the inhibition of proliferation and the prevention of cancer metastasis and tumor angiogenesis. In both animal tumor models and clinical trials, this agent efficiently inhibits tumor growth with minimal side effects, with little toxicity on immune and hemopoietic systems. This chemical can produce tissue-specific proteasome inhibition and tumor-specific toxicity. LD50: Mice 45mg/kg (i.p.).
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































