research use only
Valdecoxib COX inhibitor
Cat.No.S4049
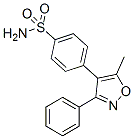
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 314.36
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 63 mg/mL
(200.4 mM)
Ethanol : 18 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 314.36 | Formula | C16H14N2O3S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 181695-72-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1=C(C(=NO1)C2=CC=CC=C2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)S(=O)(=O)N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Valdecoxib is more potent in inhibiting COX-2 than COX-1.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
COX-2
5 nM
|
| In vitro |
Valdecoxib inhibits LPS-induced PGE2 production in plasma with IC50 of 0.89 μM for assessment of the extent of COX-2 inhibition. This compound inhibits TxB2 production in plasma with IC50 of 25.4 μM for assessment of the extent of COX-1 inhibition. It binds to COX-2 with Ka of 1.1×105 M/s. The overall saturation binding affinity for COX-2 of this chemical is 2.6 nM. It shows similar activity in the human whole-blood COX assay (COX-2 IC50 = 0.24 μM; COX-1 IC50 = 21.9 μM). The affinity of [3H]Valdecoxib for COX-2 with KD of 3.2 nM. The binding of this compound to COX-2 seems to be both rapid and slowly reversible with association rates of 4.5 × 106/M/min and dissociation rates of 7.0 × 10-3/min (t1/2 of 98 min). The percent of dissolved this chemical at 15 min (DP15) is 10.5% for Valdecoxib and 50%, 91% and 93% for its hydrophilic derivatives (VALD-βCd, VALD-HPβCd and VALD-SBE7βCd complexes), respectively.
|
| In vivo |
Valdecoxib administrated orally inhibits rat carrageenan foot pad edema with ED50 of 10.2 mg/kg. This compound administrated orally shows chronic antiinflammatory activity with ED50 of 0.032 mg/kg/day in rat adjuvant arthritis model. It shows blockade of prostaglandin production at the inflammatory site with ED50 of 0.02 mg/kg in the rat carrageenan air pouch model. This chemical demonstrates marked potency in acute and chronic models of inflammation (air pouch ED50 = 0.06 mg/kg; paw edema ED50 = 5.9 mg/kg; adjuvant arthritis ED50 = 0.03 mg/kg) in rats. It alone shows slow in vivo absorption giving maximum % inhibition of edema (16%) after a period of 3 hour. In contrast, VALD-βCd and VALD-SBE7βCd complexes shows high absorption rate in vivo achieving more than 50% inhibition of edema in the 1 hour and maximum percentage of inhibition of edema (66%) after a period of 3 hours. This compound (5 mg/kg, po) results in AUC in plasma of 3.58 μg*h/mL and 2.08 μg*h/mL in males and female mice, respectively. It (5 mg/kg, po) results in AUC red blood cells of 12.1 μg*h/mL and 6.42 μg*h/mL in males and female mice, respectively.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00122096 | Completed | Neurosurgery|Pain |
University of Washington|Pfizer |
November 2002 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































