research use only
Triflusal COX inhibitor
Cat.No.S3200
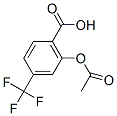
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 248.16
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 50 mg/mL
(201.48 mM)
Ethanol : 50 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 248.16 | Formula | C10H7F3O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 322-79-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | UR1501 | Smiles | CC(=O)OC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C(F)(F)F)C(=O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
COX-1
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
The main Triflusal metabolite, HTB, preserves 6-keto-PGF1α synthesis in porcine aortic endothelial cells (PAEC) cells without a significant decline for up to 24 h even at the higher concentration. This compound at 10 mM, 100 mM and 1 M decreases LDH efflux in rat brain slices after anoxia/reoxygenation by 24%, 35% and 49% respectively. It also reduces inducible NO synthase activity by 18%, 21% and 30%.
|
| In vivo |
Triflusal (10 mg/kg i.v.) reduces platelet deposition on subendothelium-induced primary thrombus by about 68% in rabbits. This compound reduces platelet deposition on a fresh thrombus formed over tunica media by about 48% in rabbits. It (40 mg/kg p.o.) reduces platelet deposition on a primary thrombus triggered by subendothelium and tunica media by 53% in rabbits. This chemical significantly reduces Cox-2 mRNA levels and protein levels without influence Cox-1 mRNA levels on the vascular wall in rabbits. It (600 mg/day for 5 days) results in an increase in NO production by neutrophils and an increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) protein expression in neutrophils in healthy volunteers. This compound (300 mg, twice-daily orally) shows a more important increase in total walking distance and in pain-free walking distance over the basal values than those treated with placebo, together with an improvement of the symptomatology correlated with claudication in patients with chronic peripheral arteriopathy. It shows an increase in the peak-flow recorded through strain-gauge plethysmography in patients with chronic peripheral arteriopathy. This chemical (30 mg/kg) strongly decreases iNOS immunolabeling at both survival times analyzed, attenuating iNOS immunoreactivity in astroglial cells and infiltrated neutrophils in rats. It decreases neuronal and microglial COX-2 expression at 10 and 24 hours after lesion and microglial and astroglial expression of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha at 24 hours after lesion in rats.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































