- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
3BDO mTOR activator
Cat.No.S8317
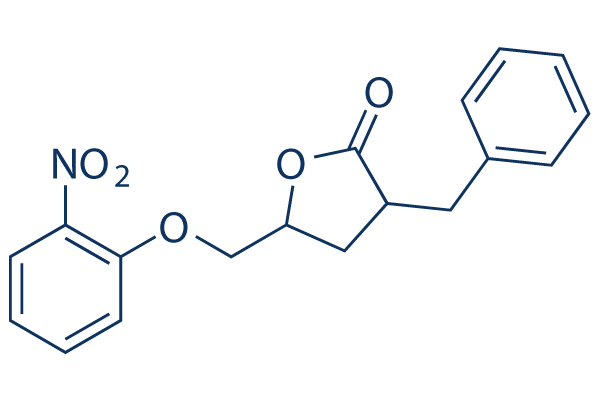
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 327.33
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.95%
99.95
| Related Targets | PI3K Akt GSK-3 ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Other mTOR Inhibitors | Torin 1 Torin 2 AZD8055 Ridaforolimus (Deforolimus, MK-8669) Sapanisertib (INK-128) Torkinib (PP242) Vistusertib (AZD2014) MHY1485 KU-0063794 OSI-027 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 65 mg/mL
(198.57 mM)
Ethanol : 19.7 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 327.33 | Formula | C18H17NO5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 890405-51-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | 3-benzyl-5-((2-nitrophenoxy) methyl)-dihydrofuran-2(3H)-one | Smiles | C1C(C(=O)OC1COC2=CC=CC=C2[N+](=O)[O-])CC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
FKBP1A
(Cell-free assay) |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
3BDO inhibits autophagy in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and neuronal cells. It suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced HUVEC autophagic injury by downregulating the protein levels of NUPR1 (nuclear protein, transcriptional regulator) and TP53 (tumor protein p53), TP53 nuclear translocation and reactive oxygen species overproduction. This compound activates MTOR by targeting FKBP1A (FK506-binding protein 1A, 12 kDa). It greatly decreases the level of a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) derived from the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of TGFB2, known as FLJ11812, but does not affect TGFB2 expression. ATG13 protein level is decreased along with this compound-decreased FLJ11812 level. It inhibits excessive Aβ (25 to 35) peptide-induced autophagy in PC12 neuronal cells and increased the phosphorylation of RPS6KB1. This chemical could inhibit human umbilical vein EC (HUVEC) apoptosis and senescence induced by deprivation of serum and basic fibroblast growth factor 2. iT selectively protecteS vascular ECs (VECs) and inhibitS vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation and migration. It (20-60 μg/ml) could inhibit VEC apoptosis and suppress integrin β4 expression, but it could not depress the ROS level induced by deprivation of serum and FGF-2.
|
| In vivo |
In vivo experiments showed that 3BDO had a good safety profile. This compound treatment could significantly reduce the number of autophagosomes and improve neuronal function in App and Psen1 transgenic mice. It activated mTOR in vivo and decreased the protein level of ATG13 in the plaque endothelium of apoE-/- mice. It does not affect the activity of mTOR and autophagy in macrophage cell line RAW246.7 and vascular smooth muscle cells of apoE-/- mice, but suppressed plaque endothelial cell death and restricted atherosclerosis development in the mice. This chemical protecteS VECs by activating mTOR and thus stabilized atherosclerotic lesions in apoE-/- mice.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































