research use only
KRN 633 VEGFR inhibitor
Cat.No.S1557
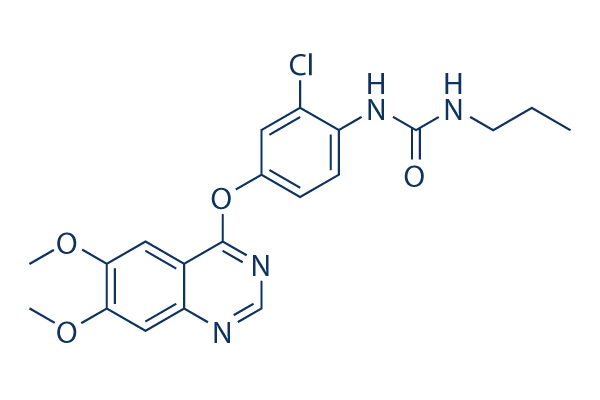
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 416.86
Quality Control
| Related Targets | EGFR PDGFR FGFR c-Met Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 c-Kit |
|---|---|
| Other VEGFR Inhibitors | SAR131675 SU 5402 Cediranib (AZD2171) Vatalanib (PTK787) 2HCl Anlotinib (AL3818) Dihydrochloride Linifanib (ABT-869) Apatinib (YN968D1) Apatinib (YN968D1) mesylate Semaxanib (SU5416) Ki8751 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 9 mg/mL
(21.58 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 416.86 | Formula | C20H21ClN4O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 286370-15-8 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CCCNC(=O)NC1=C(C=C(C=C1)OC2=NC=NC3=CC(=C(C=C32)OC)OC)Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
VEGFR3
125 nM
VEGFR2
160 nM
VEGFR1
170 nM
PDGFRα
965 nM
c-Kit
4330 nM
BTK
9200 nM
PDGFRβ
9850 nM
Tie-2
9900 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
KRN 633, a novel quinazoline urea derivative, strongly inhibits VEGFR1, VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 receptors with IC50 values of 170 nM, 160 nM and 125 nM respectively. It shows lower inhibitory activity towards non-RTKs, such as PDGF receptor (PDGFRα and β, c-Kit, breast tumor kinase, and tunica interna endothelial cell kinase tyrosine kinases (IC50 = 965, 9850, 4330, 9200, and 9900 nM, respectively). This compound potently inhibits ligand VEGF induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 in HUVECs with an IC50 of 1.16 nM. It also inhibits VEGF-dependent, but not bFGF-dependent, phosphorylation of the MAP kinases in endothelial cells, with IC50 values of 3.51 nM and 6.08 nM for ERK1 and ERK2, respectively. This chemical has also been shown to inhibit the VEGF-driven proliferation of HUVECs with an IC50 of 14.9 nM, but it only suppresses FGF-driven proliferation at 3 μM weakly. It inhibits hypoxia-induced transcriptional activation of HIF-1α in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 3.79 μM, through the inhibition of both Akt and ERK phosphorylation signaling pathways.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Cell-Free Kinase Assays
|
|
Cell-free kinase assays are done to obtain IC50 values against a variety of recombinant VEGF receptors. KRN633 is tested at concentrations varying from 0.3 nM to 10 μM. All assays are done in quadruplicate with 1 μM ATP.
|
|
| In vivo |
Although not cytotoxic to various cancer cells in vitro, KRN633 exhibits excellent antitumor activity in vivo due to its inhibitory effect on tumor vessel formation and vascular permeability. Once-daily administration of this compound at 100 mg/kg/d produces significant tumor growth inhibition in A549, LC-6-LCK, HT29, Ls174T, LNCap and Du145 cells while twice-daily administration of this compound at 100 mg/kg induces ~90% growth inhibition of HT29 tumors. Treatment of mid-pregnancy mice with this chemical (300 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces the blood supply to fetal tissues due to diminished vascularization in both placenta and fetal organs and consequently increases the risk of induction of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































