research use only
m6A (N6-methyladenosine) DNA/RNA Synthesis chemical
Cat.No.S3190
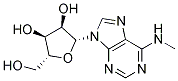
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 281.27
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC PARP ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Other DNA/RNA Synthesis Inhibitors | B02 CX-5461 (Pidnarulex) SCR7 EED226 Favipiravir (T-705) RK-33 Carmofur Triapine (3-AP) BMH-21 YK-4-279 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| adipocytes, heart and brain cells | Function assay | Affinity constant for inhibition of A1 receptor control of adenylate cyclase in adipocytes, heart and brain cells, Affinity constant=0.1μM | 6279840 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 56 mg/mL
(199.09 mM)
Water : 14 mg/mL Ethanol : 9 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 281.27 | Formula | C11H15N5O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1867-73-8 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) is an abundant modification in mRNA and is found within some viruses, and most eukaryotes including mammals, insects, plants and yeast. It is also found in tRNA, rRNA, and small nuclear RNA(snRNA) as well as several long non-coding RNA, such as Xist. This compound is an endogenous urinary nucleoside product of the degradation of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA). It is a widespread RNA modification in many tissues with high levels in the brain. It is enriched near stop codons and within 3’UTRs in both mouse and human mRNAs. The recent discovery that FTO, an obesity risk gene, encodes an m6A demethylase implicates it as an important regulator of physiological processes.
|
|---|---|
| In vivo |
LD50: Mice >1g/kg (i.g.). This compound is also known as N6-methyladenosine.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05682001 | Recruiting | Cataract|Pathogenesis |
Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University|National Natural Science Foundation of China |
January 1 2022 | -- |
| NCT04696094 | Unknown status | Moyamoya Disease |
Beijing Tiantan Hospital |
January 1 2021 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































