research use only
Fenofibric acid PPAR inhibitor
Cat.No.S4527
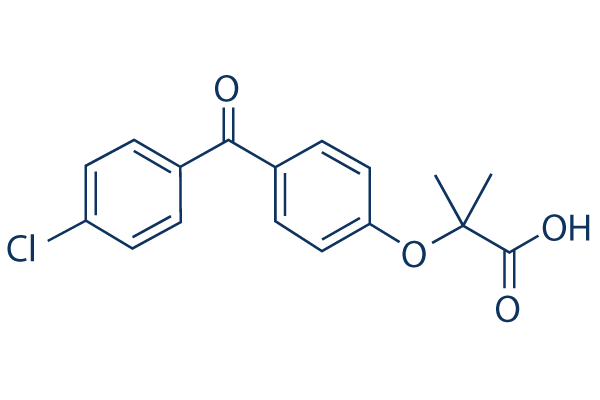
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 318.75
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism Drug Metabolite |
|---|---|
| Other PPAR Inhibitors | T0070907 GW9662 GW6471 WY-14643 (Pirinixic Acid) GSK3787 GW0742 AZ6102 Astaxanthin Eupatilin GSK0660 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 64 mg/mL
(200.78 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 318.75 | Formula | C17H15ClO4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 42017-89-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC 281318, Trilipix, FNF acid | Smiles | CC(C)(C(=O)O)OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PPARα
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Fibric acids, active forms of fibrate drugs and activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARα), are also known for an HDL-raising effect. Fibric acids enhance fatty acid catabolism and accordingly reduce plasma lipid level, predominantly triglyceride (TG). Fenofibric acid increases the expression of ABCA1 and apoA-I–mediated HDL production. The effect on ABCA1 expression was through the enhancement of the transcription of the ABCA1 gene being dependent on LXR.
|
| In vivo |
Fenofibric acid attenuates aberrant increases of circulating EPC(Endothelial Progenitor Cells) in OIR mice. Inhibitory effect of this compound on EPC mobilization in the OIR model is PPARα-dependent. It inhibits hypoxia-induced retinal EPC increase in a PPARα-dependent manner. This chemical decreases CXCR4-positive EPC in the circulation, downregulates the serum SDF-1 level and suppresses HIF-1a and SDF-1 overexpression in the retina.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03382756 | Completed | Dyslipidemias |
Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical |
October 12 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03515213 | Completed | Huntington Disease |
University of California Irvine |
April 27 2017 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02891408 | Completed | Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) |
Gilead Sciences |
September 23 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02651753 | Completed | Dyslipidemia |
Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical |
January 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02422030 | Completed | Healthy |
Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical |
March 17 2015 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































