research use only
Cinnamaldehyde TRP Channel agonist
Cat.No.S3763
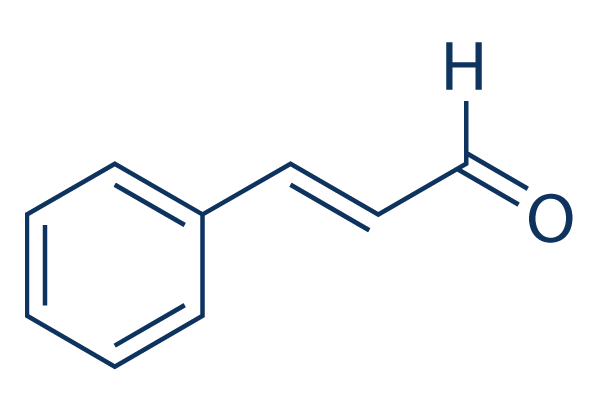
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 132.16
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Sodium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor ATPase GluR |
|---|---|
| Other TRP Channel Inhibitors | 2-APB (2-Aminoethyl Diphenylborinate) SKF96365 AMG-517 GSK2193874 GSK1016790A Capsazepine HC-030031 EIPA (L593754) HC-067047 SB705498 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 132.16 | Formula | C9H8O |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | 2 years -20°C liquid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 14371-10-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
TRPA1
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Cinnamaldehyde (40 μM) could enhance the expression of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and suppress the expression of perilipin and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as well as reduce adipocyte genes expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (CEBP-α) in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. It also increases expression of PPARδ and PPARγ as well as its targeted genes such as aP2 and CD36 in 3T3-L1 differentiated adipocytes. This compound treatment increases GLUT4 expression via activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and triggering its downstream effector myocyte enhancer factors 2 (MEF2) in C2C12 cells. Its treatment regulates oxidative metabolism through increasing expressions of 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), NAD+-dependent deacetylases sirtuin 1, PGC-1α and cytochrome C as well as improving PPARα and PPARβ/δ expression, which contributes to mitochondrial biogenesis. However, it is demonstrated to inhibit mitochondrial metabolism by reducing basal and chemically-induced peak myotube oxidative metabolism in C2C12 cells. This chemical exerts cytotoxic effects on human leukemia K562 cells by inducing apoptosis and synergizing the cytotoxicity of CIK cells against K562 cells.
|
| In vivo |
Cinnamaldehyde exhibits glucolipid lowering effects in diabetic animals by increasing glucose uptake and improving insulin sensitivity in adipose and skeletal muscle tissues, improving glycogen synthesis in liver, restoring pancreatic islets dysfunction, slowing gastric emptying rates, and improving diabetic renal and brain disorders. This compound exerts these effects through its action on multiple signaling pathways, including PPARs, AMPK, PI3K/IRS-1, RBP4-GLUT4, and ERK/JNK/p38MAPK, TRPA1-ghrelin and Nrf2 pathways. In addition, this compound seems to regulate the activities of PTP1B and α-amylase. Oral administration of this chemical ranging from 20mg/kg to 40 mg/kg per day for a duration lasting from 21 to 60 days results in a significant improvement in the levels of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) as well as insulin sensitivity in STZ-induced diabetic rats. It is not stable in the body, with the possibility of metabolizing into cinnamic acid and transforming into cinnamyl alcohol. Excessive doses of this compound may generate the toxic response. In human, 3% of this substance may cause skin irritation. It is demonstrated to decrease serum IL-1β and inhibit inflammatory gene expression (COX-2, MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-6) in WAT of HFD insulted male Swiss albino mice and C57BLKS db/db mice, while increased expression of Cpt1a protects against pro-inflammatory adipokines release and promotes fatty acid oxidation, which contributes to an improvement in insulin resistance.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05654298 | Completed | Migraine |
Universitaire Ziekenhuizen KU Leuven |
March 15 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04183283 | Completed | Healthy |
Eli Lilly and Company |
December 12 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04415892 | Unknown status | Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy |
Universitaire Ziekenhuizen KU Leuven |
October 1 2019 | Not Applicable |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































