research use only
SB216763 GSK-3 inhibitor
Cat.No.S1075
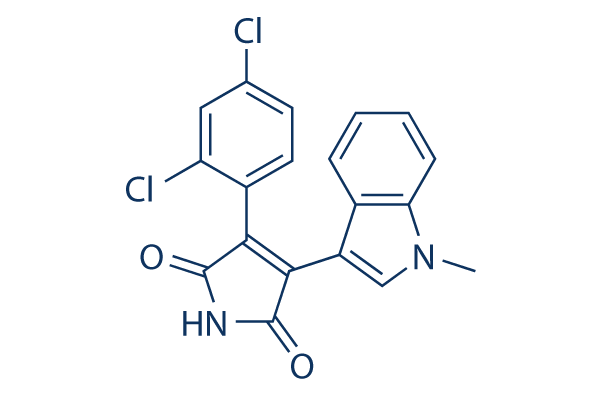
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 371.22
Quality Control
| Related Targets | PI3K Akt mTOR ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Other GSK-3 Inhibitors | CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) Hydrochloride TWS119 CHIR-98014 BIO LY2090314 Tideglusib SB415286 AR-A014418 1-Azakenpaullone |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | Function assay | Glycogen synthase activity of HEK293 cells, inhibition of GSK3-beta, EC50=0.2μM | 12941331 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Effective concentration of compound against glycogen synthase kinase-3 in HEK293 cells, EC50=0.2μM | 15149684 | |||
| MIAPaCa2 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MIAPaCa2 cells after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=25μM | 19338355 | ||
| ST14A | Function assay | 6 hrs | Inhibition of GSK-3-beta-mediated Wnt signaling in human ST14A cells assessed as increase in accumulation of beta-casein around nucleus after 6 hrs by microscopic analysis | 20708937 | ||
| neural precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of neurosphere proliferation of mouse neural precursor cells by MTT assay | 17417631 | |||
| ReNcell VM | Antiproliferative assay | 3 uM | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human ReNcell VM cells assessed as reduction of cell proliferation at 3 uM after 72 hrs | 20708937 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Increase in glucose incorporation in human HepG2 cells at 34 uM after 12 hrs by glucose assay | 25467150 | |
| 3T3L1 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Increase in glucose incorporation in mouse 3T3L1 cells at 34 uM after 12 hrs by glucose assay | 25467150 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | 34 uM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of GSK3beta in human HepG2 cells assessed as decrease in ratio of phosphorylated GS/GS at 34 uM after 12 hrs by Western blot analysis | 25467150 | |
| Sf9 | Function assay | 30 min | Inhibition of GSK3beta (unknown origin) expressed in Sf9 cells using GS1 as substrate and [gamma32]ATP after 30 min by scinitllation counting, IC50=0.03388μM | SANGER | ||
| human HDLM-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HDLM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.20984 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1770 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1770 cell growth in a cell viability assay. IC50=0.29392 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HOP-62 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HOP-62 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.85256 μM | SANGER | |||
| human JAR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human JAR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.21044 μM | SANGER | |||
| human K5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human K5 cell growth in a cell viability, IC50=1.53698 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MV-4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MV-4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.69685 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BT-549 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BT-549 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=5.29376 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LB2241-RCC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LB2241-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.42874 μM | SANGER | |||
| human GAMG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GAMG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.65409 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HMV-II cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HMV-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=7.67607 μM | SANGER | |||
| human RS4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RS4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.24141 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1993 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1993 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.36534 μM | SANGER | |||
| human IST-SL1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IST-SL1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.0204 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-OV-3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-OV-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.1002 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ESS-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ESS-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.59872 μM | SANGER | |||
| human G-361 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human G-361 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=10.1798 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ALL-PO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ALL-PO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=10.3477 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NB5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.2157 μM | SANGER | |||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.6535 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NMC-G1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NMC-G1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.7264 μM | SANGER | |||
| human RPMI-7951 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RPMI-7951 cell growth in a cell viability assay. IC50=11.7864 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H2009 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2009 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.2427 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LoVo cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LoVo cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.3771 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A2058 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A2058 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.469 μM | SANGER | |||
| human D-566MG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human D-566MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.9481 μM | SANGER | |||
| human QIMR-WIL cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human QIMR-WIL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.6394 μM | SANGER | |||
| human S-117 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human S-117 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.4022 μM | SANGER | |||
| human YH-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human YH-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.6865 μM | SANGER | |||
| human IGROV-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IGROV-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.2001 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BHT-101 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHT-101 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.6099 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MKN45 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MKN45 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=18.4128 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A498 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A498 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.4549 μM | SANGER | |||
| human U-266 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U-266 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.8797 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BFTC-905 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BFTC-905 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.1879 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BxPC-3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BxPC-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.3554 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-SNU-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-SNU-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.5558 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SF539 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SF539 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.0198 μM | SANGER | |||
| human VA-ES-BJ cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human VA-ES-BJ cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.5763 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HuO-3N1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HuO-3N1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.6151 μM | SANGER | |||
| human EM-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.6689 μM | SANGER | |||
| human T98G cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human T98G cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.3009 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1783 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1783 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.5243 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NKM-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NKM-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.8512 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KOSC-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KOSC-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.1292 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW48 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW48 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.6067 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H28 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H28 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=25.2104 μM | SANGER | |||
| human 5637 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 5637 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=25.8111 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NB69 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB69 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=26.1764 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HT-29 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HT-29 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.1752 μM | SANGER | |||
| human PFSK-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PFSK-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.593 μM | SANGER | |||
| human UACC-257 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human UACC-257 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.743 μM | SANGER | |||
| human D-423MG cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human D-423MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9106 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NH-12 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NH-12 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=28.4059 μM | SANGER | |||
| human DEL cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DEL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.0474 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LS-513 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LS-513 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.1334 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NBsusSR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NBsusSR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.5678 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BV-173 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BV-173 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.7649 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A101D cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A101D cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.9784 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LU-134-A cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LU-134-A cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=31.0238 μM | SANGER | |||
| human ES3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ES3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=31.3376 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.2965 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H1975 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1975 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.3582 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A704 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A704 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2059 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-MEL-24 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-24 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2523 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1088 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1088 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.3452 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SK-MEL-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-1 cell growth in a cell viability, IC50=34.714 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MOLT-4 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MOLT-4 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.1467 μM | SANGER | |||
| human T47D cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human T47D cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.1647 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW1710 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1710 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.3608 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MKN7 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MKN7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.0909 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-72 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-72 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.1178 μM | SANGER | |||
| human AGS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AGS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.2039 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BE-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BE-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.7783 μM | SANGER | |||
| human Calu-6 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Calu-6 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=39.6964 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-27 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-27 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.0054 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BB49-HNC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BB49-HNC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.0278 μM | SANGER | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 23 mg/mL
(61.95 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 371.22 | Formula | C19H12N2O2Cl2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 280744-09-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)C3=C(C(=O)NC3=O)C4=C(C=C(C=C4)Cl)Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GSK-3α
(Cell-free assay) 34.3 nM
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) ~34.3 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
SB 216763 displays similar potency for GSK-3β with 96% inhibition at 10 μM while exhibiting minimal activity against 24 other protein kinases including PKBα and PDK1 with IC50 of >10 μM. This compound stimulates glycogen synthesis in human liver cells with EC50 of 3.6 μM, and induces dose-dependent transcription of a β-catenin-LEF/TCF regulated reporter gene in HEK293 cells with a maximum 2.5-fold induction at 5 μM. It protects the cerebellar granule neurones from apoptotic cell death induced by LY-294002 or potassium-deprivation in a concentration-dependent manner, with a maximal neuroprotection at 3 μM in contrast with the effect of lithium chloride at which 10 mM is required. This chemical at 3 μM also completely prevents death of chicken dorsal root ganglion sensory neurones induced by LY-294002 regardless of NGF. It treatment at 5 μM markedly inhibits the GSK-3-dependent phosphorylation of neuronal-specific microtubule-associated protein tau in cerebellar granule neurones or recombinant tau in HEK293 cells, and induces increased levels of cytoplasmic β-catenin in both cells mimicking the effect of Wnt-mediated inhibition of GSK-3. In pancreatic cancer cell lines including BXPC-3, MIA-PaCa2, PANC1, ASPC1, and CFPAC, this compound treatment at 25-50 μM reduces cell viability in a dose-dependent manner, and leads to significant increase in apoptosis by 50% at 72 hours due to the specific down regulation of GSK-3β, while has no effect in HMEC or WI38 cell lines.
|
| Kinase Assay |
GSK-3 activity assay
|
|
GSK-3 kinase activity is measured, in the presence of various concentrations of SB 216763, in a reaction mixture containing final concentrations of 1 nM human GSK-3α, 50 mM MOPS pH 7.0, 0.2 mM EDTA, 10 mM Mg-acetate, 7.5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 5% (w/v) glycerol, 0.01% (w/v) Tween-20, 10% (v/v) DMSO, and 28 μM GS-2 peptide substrate. The GS-2 peptide sequence corresponds to a region of glycogen synthase that is phosphorylated by GSK-3. The assay is initiated by the addition of 0.34 μCi [33P]γ-ATP. The total ATP concentration is 10 μM. Following 30 minutes incubation at room temperature the assay is stopped by the addition of one third assay volume of 2.5% (v/v) H3PO4 containing 21 mM ATP. Samples are spotted onto P30 phosphocellulose mats and washed six times in 0.5% (v/v) H3PO4. The filter mats are sealed into sample bags containing Wallac betaplate scintillation fluid. 33P incorporation into the substrate peptide is determined by counting the mats in a Wallac microbeta scintillation counter.
|
|
| In vivo |
Administration of SB 216763 at 20 mg/kg significantly prevents lung inflammation and the subsequent fibrosis in bleomycin (BLM)-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis model in mice by significantly blocking the production of inflammatory cytokines MCP-1 and TNF-α by macrophages, and significantly improves the survival of BLM-treated mice. This compound treatment causes a significant reduction in BLM-induced alveolitis by inhibiting alveolar epithelial cell damage.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | pGSK-3β / GSK-3β / E2F1 / β-catenin c-Myb |
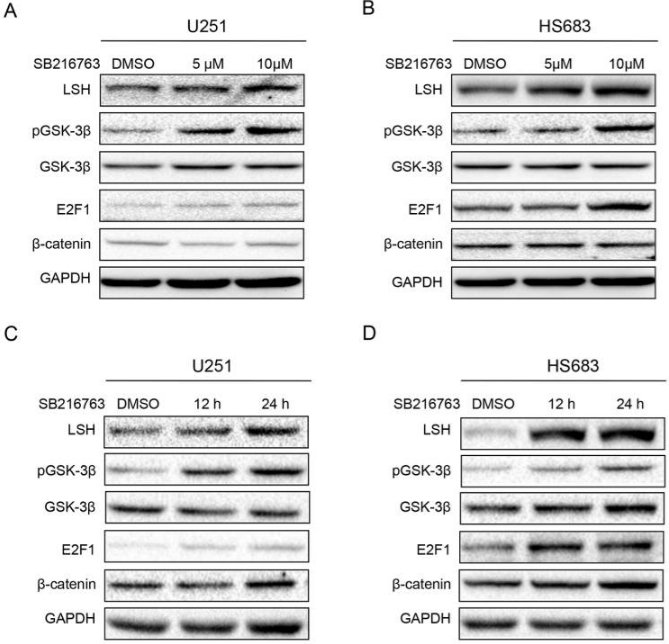
|
28042322 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
24779365 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































