research use only
CHIR-98014 GSK-3 inhibitor
Cat.No.S2745
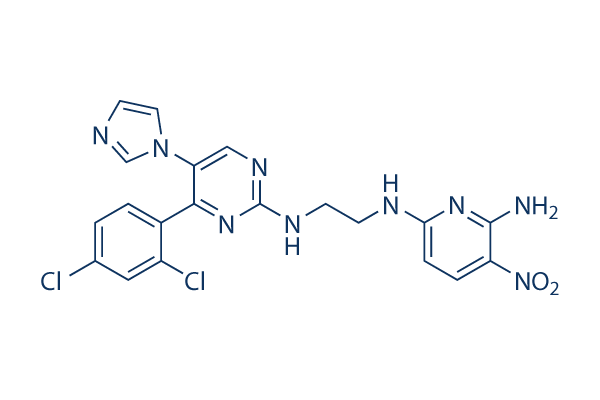
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 486.31
Quality Control
| Related Targets | PI3K Akt mTOR ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Other GSK-3 Inhibitors | CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) Hydrochloride SB216763 TWS119 GSK-3 Inhibitor IX (BIO) LY2090314 Tideglusib SB415286 AR-A014418 IM-12 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGC-823 | Proliferation assay | 50 nM | 48 h | abrogated rLMO3 protein-induced proliferation | 29436606 | |
| HGC-27 | Proliferation assay | 50 nM | 48 h | abrogated rLMO3 protein-induced proliferation | 29436606 | |
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 10 mg/mL
(20.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 486.31 | Formula | C20H17Cl2N9O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 252935-94-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | CT98014 | Smiles | C1=CC(=C(C=C1Cl)Cl)C2=NC(=NC=C2N3C=CN=C3)NCCNC4=NC(=C(C=C4)[N+](=O)[O-])N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) 0.58 nM
GSK-3α
(Cell-free assay) 0.65 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
CHIR-98014 inhibits human GSK-3β with Ki of 0.87 nM. This compound is very effective in preventing murine and rat GSK-3. Although it acts as a simple competitive inhibitor of ATP binding, it displays from 500-fold to >1000-fold selectivity for GSK-3 versus 20 other protein kinases including Cdc2, ERK2, Tie-2 and KDR. This inhibitor prevents Cdc2 with IC50 of 3.7 μM. However, it reveals similar potency against the highly homologous ɑ and β isoforms of GSK-3, it is noteworthy that it strongly discriminated between GSK-3 and its closest homologs CDC2 and ERK2. Exposure of insulin receptor-expressing CHO-IR cells or primary rat hepatocytes to increasing concentrations of this chemical results in a two- to three-fold stimulation of the GS activity ratio above basal. The concentrations giving rise to half-maximal GS stimulation (EC50) is 106 nM and 107 nM for CHO-IR and rat hepatocytes, respectively.
|
| Kinase Assay |
Kinase assays
|
|
Polypropylene 96-well plates are filled with 300 μL/well buffer (50 mM tris HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 25 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM NaF, 0.01% BSA, pH 7.5) containing kinase, peptide substrate, and any activators. CHIR-98014 or controls are added in 3.5 μL of DMSO, followed by 50 μL of ATP stock to yield a final concentration of 1 μM ATP in all cell-free assays. After incubation, triplicate 100-μL aliquots are transferred to Combiplate eight plates containing 100 μL/well 50 μM ATP and 20 mM EDTA. After 1 hour, the wells are rinsed five times with PBS, filled with 200 μL of scintillation fluid, sealed, left 30 min, and counted in a scintillation counter. All steps are performed at room temperature.
|
|
| In vivo |
GSK-3 inhibitor CHIR-98014 activates the GS activity ratio in isolated type I skeletal muscle from insulin-sensitive lean Zucker and from insulin-ressitant ZDF rats. Soleus muscle isolated from ZDF rats shows significant resistance to insulin for activation of GS but responded to 500 nM of this compound to the same extent (40% increase) as muscle from lean Zucker rats. Notably, GS activation by insulin plus this chemical is additive in muscle from lean Zucker rats and greater than additive in muscle from the ZDF rats. Total GS activity is not altered by either this inhibitor or insulin in these cells and muscles. Meanwhile, this compound does not influence the insulin dose-response in muscle from lean animals. The reduction in hyperglycemia and improved glucose disposal are not limited to db/db mice and ZDF rats, as similar results are observed with ob/ob mice, diet-induced diabetic C57BL/6 mice, and glucose-intolerant SHHF rats treated with this chemical. Additionally, this compound decreases the phosphorylation (Ser396) of tau protein in the cortex and hippocampus of postnatal rats.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
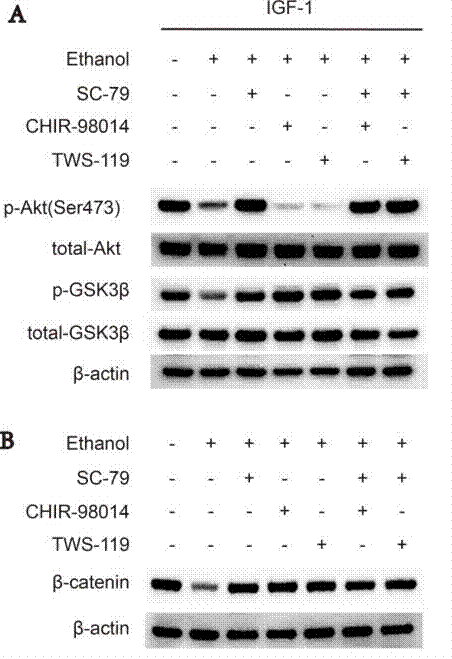
| Western blot | p-AKT / AKT / p-GSK3β / GSK3β / β-catenin |
|
28415692 |
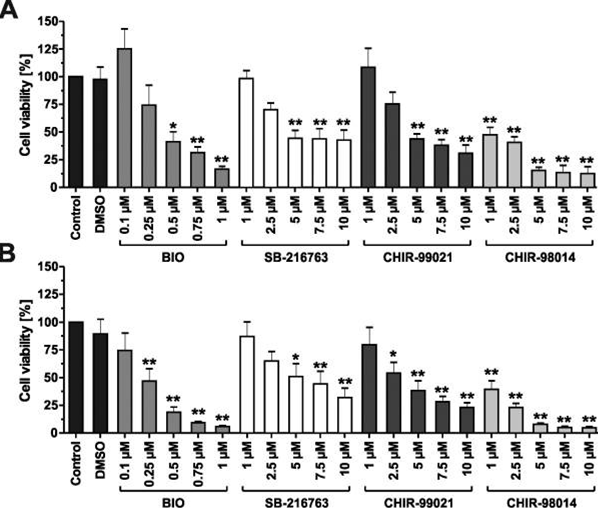
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
24779365 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































