- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
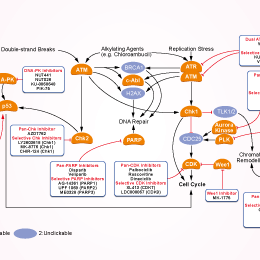
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Gemcitabine Hydrochloride DNA/RNA Synthesis inhibitor
Gemcitabine is a pyrimidine nucleoside analog antitumor drug that can inhibit DNA synthesis and repair, leading to cell autophagy and apoptosis. It is mainly used to treat various solid tumors such as pancreatic cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, and is often combined with chemotherapy to enhance efficacy.
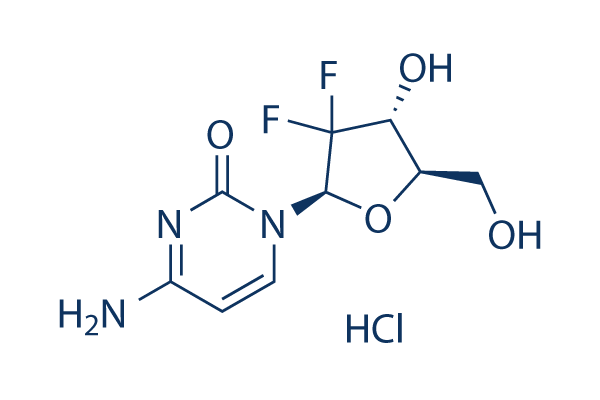
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 299.66
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.96%
99.96
Related Products
| Related Targets | tRNA synthetase RdRp DNA synthesis helicase ribonucleotide reductase | Click to Expand |
|---|---|---|
| Related Products | CX-5461 (Pidnarulex) SCR7 Favipiravir (T-705) RK-33 Carmofur Triapine (3-AP) B02 BMH-21 YK-4-279 Bergapten Tegafur (FT-207) Azaguanine-8 Halofuginone Adenine HCl Mizoribine Cyclocytidine HCl Thymidine APX-3330 Nedaplatin 6-Thio-dG | Click to Expand |
| Related Compound Libraries | FDA-approved Drug Library Natural Product Library Apoptosis Compound Library DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library Cell Cycle compound library | Click to Expand |
Signaling Pathway
Cell Culture and Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCRF-CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.9 ± 1.8 nM | 22425885 | |||
| CCRF-CEM/dCK−/− | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=240.4 ± 29.0 μM | 22425885 | |||
| L1210 wt | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.3 ± 0.3 nM | 22425885 | |||
| L1210 10K | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.2 ± 3.7 μM | 22425885 | |||
| TC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.7 ± 2.8 nM | 22425885 | |||
| TC-1-GR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.7 ± 5.1 μM | 22425885 | |||
| MIA PaCa-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.7 ± 17.7 nM | 22425885 | |||
| PANC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=> 400 μM | 22425885 | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.9 ± 1.8 nM | 22425885 | |||
| CCRF-CEM-AraC-8C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=998.8 ± 9.4 nM | 22425885 | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=2.0 ± 0.6 nM | 21851843 | ||
| MV-4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0005 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0007 nM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0009 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-510 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.001 nM | SANGER | |||
| EW-7 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0026 nM | SANGER | |||
| BFTC-905 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0051 nM | SANGER | |||
| KE-37 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0056 nM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0057 nM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0071 nM | SANGER | |||
| RH-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0072 nM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0083 nM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0089 nM | SANGER | |||
| A375 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0099 nM | SANGER | |||
| SIG-M5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0104 nM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0108 nM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0112 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.016 nM | SANGER | |||
| PSN1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0165 nM | SANGER | |||
| HUTU-80 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0166 nM | SANGER | |||
| 786-0 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.023 nM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.023 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0268 nM | SANGER | |||
| RKO | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0278 nM | SANGER | |||
| ESS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0286 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-UT-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0297 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0318 nM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0324 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW1783 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0336 nM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-JUSO | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0391 nM | SANGER | |||
| HT-29 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0413 nM | SANGER | |||
| SNG-M | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0425 nM | SANGER | |||
| TE-15 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0464 nM | SANGER | |||
| HOS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.048 nM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0512 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCE-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0528 nM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-ES-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0531 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-7951 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0541 nM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0584 nM | SANGER | |||
| CMK | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0586 nM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0595 nM | SANGER | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0622 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-6666 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0652 nM | SANGER | |||
| LC-2-ad | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0653 nM | SANGER | |||
| ARH-77 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0711 nM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0726 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW1710 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0751 nM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0887 nM | SANGER | |||
| AGS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0902 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2122 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0945 nM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1022 nM | SANGER | |||
| AM-38 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1215 nM | SANGER | |||
| 769-P | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1231 nM | SANGER | |||
| RT-112 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1273 nM | SANGER | |||
| MCF7 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1359 nM | SANGER | |||
| IGROV-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.145 nM | SANGER | |||
| OCI-AML2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1466 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1299 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1566 nM | SANGER | |||
| A431 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.1831 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2133 nM | SANGER | |||
| BB30-HNC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2312 nM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2436 nM | SANGER | |||
| 647-V | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2481 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-PN-DW | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2656 nM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2673 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2688 nM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2702 nM | SANGER | |||
| C-33-A | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.2733 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.314 nM | SANGER | |||
| TE-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.3157 nM | SANGER | |||
| HC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.3273 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MES-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.3279 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.3806 nM | SANGER | |||
| YKG-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.4194 nM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.4326 nM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.4565 nM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.5512 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.5545 nM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.5647 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LMS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.5776 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.5856 nM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6162 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2009 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6187 nM | SANGER | |||
| A4-Fuk | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6263 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-270 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6341 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6552 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW872 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.7647 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES8 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.7802 nM | SANGER | |||
| G-402 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.7844 nM | SANGER | |||
| ATN-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.8069 nM | SANGER | |||
| DoTc2-4510 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.9012 nM | SANGER | |||
| MES-SA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.9049 nM | SANGER | |||
| SF268 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.9274 nM | SANGER | |||
| SF539 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.023 nM | SANGER | |||
| NB69 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.046 nM | SANGER | |||
| 8505C | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.063 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.084 nM | SANGER | |||
| BHY | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.141 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB647-SCLC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.18 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-62 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.215 nM | SANGER | |||
| MEG-01 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.266 nM | SANGER | |||
| MG-63 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.335 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW620 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.346 nM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.365 nM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.452 nM | SANGER | |||
| P30-OHK | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.459 nM | SANGER | |||
| Ca9-22 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.538 nM | SANGER | |||
| VMRC-RCZ | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.542 nM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.596 nM | SANGER | |||
| L-540 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.602 nM | SANGER | |||
| NTERA-S-cl-D1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.641 nM | SANGER | |||
| MFH-ino | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.656 nM | SANGER | |||
| Calu-6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.735 nM | SANGER | |||
| HEL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.791 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.893 nM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.905 nM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.913 nM | SANGER | |||
| EB2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.012 nM | SANGER | |||
| SR | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.121 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2087 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.143 nM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.175 nM | SANGER | |||
| EW-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.223 nM | SANGER | |||
| MC-IXC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.264 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H727 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.506 nM | SANGER | |||
| MRK-nu-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.567 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-668 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.66 nM | SANGER | |||
| CGTH-W-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.723 nM | SANGER | |||
| CHP-212 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.752 nM | SANGER | |||
| GI-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.764 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.908 nM | SANGER | |||
| HLE | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.004 nM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.03 nM | SANGER | |||
| DMS-273 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.07 nM | SANGER | |||
| DU-4475 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.143 nM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.314 nM | SANGER | |||
| PANC-03-27 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.513 nM | SANGER | |||
| GAMG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.739 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H522 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.337 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW626 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.464 nM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.92 nM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-HO | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.162 nM | SANGER | |||
| BE-13 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.21 nM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.256 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H441 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.597 nM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.611 nM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.714 nM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1080 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.834 nM | SANGER | |||
| GB-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.845 nM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.906 nM | SANGER | |||
| 8-MG-BA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.93 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-HEP-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.136 nM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.247 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-450 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.315 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2998 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.339 nM | SANGER | |||
| HD-MY-Z | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.679 nM | SANGER | |||
| OS-RC-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.681 nM | SANGER | |||
| SF126 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.054 nM | SANGER | |||
| Ca-Ski | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.093 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| J82 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.41 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2342 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.634 nM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-8 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.904 nM | SANGER | |||
| TE-8 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.001 nM | SANGER | |||
| ETK-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.076 nM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.195 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-150 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.469 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H810 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.558 nM | SANGER | |||
| ONS-76 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.677 nM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.762 nM | SANGER | |||
| C3A | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.839 nM | SANGER | |||
| PA-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.993 nM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.022 nM | SANGER | |||
| EFO-27 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.046 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAPAN-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.227 nM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.29 nM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.373 nM | SANGER | |||
| ST486 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.406 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1437 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.418 nM | SANGER | |||
| HGC-27 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.601 nM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.64 nM | SANGER | |||
| OCUB-M | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 10.03 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-679 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 10.07 nM | SANGER | |||
| Detroit562 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 10.42 nM | SANGER | |||
| A204 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1734 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.29 nM | SANGER | |||
| MC-CAR | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.58 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2170 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.97 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 12.13 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCE-T | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 12.42 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-180 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 12.81 nM | SANGER | |||
| C8166 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.08 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.54 nM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.77 nM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-468 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.12 nM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.13 nM | SANGER | |||
| CTV-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| BL-41 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.37 nM | SANGER | |||
| IGR-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.42 nM | SANGER | |||
| TK10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.49 nM | SANGER | |||
| REH | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.51 nM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.59 nM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 14.97 nM | SANGER | |||
| PANC-10-05 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 15.38 nM | SANGER | |||
| HL-60 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 15.69 nM | SANGER | |||
| T84 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 15.96 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.02 nM | SANGER | |||
| UM-UC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| TE-10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.21 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-148 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.23 nM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.27 nM | SANGER | |||
| Calu-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.29 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-2650 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.59 nM | SANGER | |||
| MKN45 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.73 nM | SANGER | |||
| NUGC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 18.34 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H520 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 18.77 nM | SANGER | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 18.85 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2405 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 19.1 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES7 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 19.76 nM | SANGER | |||
| BPH-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.28 nM | SANGER | |||
| SAS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.5 nM | SANGER | |||
| HuCCT1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.58 nM | SANGER | |||
| LOUCY | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.66 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H292 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.79 nM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.07 nM | SANGER | |||
| M059J | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.08 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1651 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.11 nM | SANGER | |||
| KALS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.39 nM | SANGER | |||
| DJM-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.59 nM | SANGER | |||
| AU565 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.83 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCC38 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.95 nM | SANGER | |||
| U251 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 22.27 nM | SANGER | |||
| ABC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 22.65 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 22.93 nM | SANGER | |||
| CESS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.19 nM | SANGER | |||
| MIA-PaCa-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.36 nM | SANGER | |||
| SUP-T1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.47 nM | SANGER | |||
| L-428 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.62 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW954 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.68 nM | SANGER | |||
| HO-1-N-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 23.77 nM | SANGER | |||
| CHP-126 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.34 nM | SANGER | |||
| NB10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.37 nM | SANGER | |||
| A172 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.71 nM | SANGER | |||
| MONO-MAC-6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.84 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1650 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 25.4 nM | SANGER | |||
| NH-12 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 25.5 nM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 25.74 nM | SANGER | |||
| MZ2-MEL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 26.22 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 26.41 nM | SANGER | |||
| HuP-T4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.3 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW837 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.62 nM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.78 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-140 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.91 nM | SANGER | |||
| NOMO-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 28.68 nM | SANGER | |||
| GP5d | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 28.72 nM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L105 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 29.42 nM | SANGER | |||
| LS-411N | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 29.88 nM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 30.18 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2030 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 30.45 nM | SANGER | |||
| CCF-STTG1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 31.42 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1703 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 31.78 nM | SANGER | |||
| TUR | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 32.03 nM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 32.44 nM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 32.83 nM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-103H | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 33.25 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H510A | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 33.27 nM | SANGER | |||
| BC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 33.77 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-CO-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 34.01 nM | SANGER | |||
| A673 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 34.17 nM | SANGER | |||
| VM-CUB-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 34.69 nM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 35.06 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-27 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 35.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| NEC8 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 35.37 nM | SANGER | |||
| BxPC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 36.91 nM | SANGER | |||
| SNB75 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 37.24 nM | SANGER | |||
| NB13 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 38.23 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-OV-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 38.74 nM | SANGER | |||
| ME-180 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 38.8 nM | SANGER | |||
| JiyoyeP-2003 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 39.38 nM | SANGER | |||
| LU-134-A | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 40.02 nM | SANGER | |||
| LS-123 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 40.28 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-800 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 40.56 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB831-BLC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 41.85 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H747 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 42.28 nM | SANGER | |||
| MZ7-mel | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 42.66 nM | SANGER | |||
| GT3TKB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 42.72 nM | SANGER | |||
| 23132-87 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 43.05 nM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-16 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 43.05 nM | SANGER | |||
| PF-382 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 44.22 nM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 44.6 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW756 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 45.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| OAW-28 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 45.36 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8402 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 45.93 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1693 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 46.09 nM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 46.34 nM | SANGER | |||
| WSU-NHL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 50.35 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCT-116 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 50.83 nM | SANGER | |||
| SF295 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 51.12 nM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-296 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 51.35 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 52.07 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW962 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 52.41 nM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 53.39 nM | SANGER | |||
| EFO-21 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 53.66 nM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 53.78 nM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L279 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 53.91 nM | SANGER | |||
| HN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 54.09 nM | SANGER | |||
| Caov-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 54.13 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1770 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 55.04 nM | SANGER | |||
| G-401 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 55.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-410 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 55.87 nM | SANGER | |||
| OE33 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 61.17 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1694 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 61.29 nM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 62.2 nM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-423 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 62.48 nM | SANGER | |||
| GDM-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 62.54 nM | SANGER | |||
| SU-DHL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 62.66 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 64.52 nM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 65.09 nM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 65.28 nM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 67.18 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1599 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 70.22 nM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 72.64 nM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 72.75 nM | SANGER | |||
| LC4-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 74.74 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-680N | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 75.49 nM | SANGER | |||
| MKN1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 78.37 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCT-15 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 82.16 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1882 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 82.45 nM | SANGER | |||
| IMR-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 82.96 nM | SANGER | |||
| DB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 84.4 nM | SANGER | |||
| P12-ICHIKAWA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 84.7 nM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-422 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 85.79 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-DZ | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 86.56 nM | SANGER | |||
| FTC-133 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 87.49 nM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 89.64 nM | SANGER | |||
| KM12 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 91.49 nM | SANGER | |||
| OAW-42 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 92.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| GCIY | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 92.69 nM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-520 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 92.84 nM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8866 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 95.23 nM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 95.5 nM | SANGER | |||
| 22RV1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 96.48 nM | SANGER | |||
| DSH1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 96.5 nM | SANGER | |||
| A253 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 102.28 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H661 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 104.02 nM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 105.1 nM | SANGER | |||
| FADU | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 105.45 nM | SANGER | |||
| SJRH30 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 106.41 nM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1569 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 109.36 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 109.88 nM | SANGER | |||
| BL-70 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 110.97 nM | SANGER | |||
| SW1990 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 113.07 nM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 115.04 nM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-741 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 120.12 nM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-15 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 121.13 nM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 121.82 nM | SANGER | |||
| HEC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 123.63 nM | SANGER | |||
| D-283MED | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 126.98 nM | SANGER | |||
| RD | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 130.11 nM | SANGER | |||
| K052 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 136.71 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-85-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 144.63 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2052 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 144.82 nM | SANGER | |||
| BFTC-909 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 145.6 nM | SANGER | |||
| HuP-T3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 145.65 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H64 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 150.93 nM | SANGER | |||
| C-4-II | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 152.37 nM | SANGER | |||
| KMOE-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 154.93 nM | SANGER | |||
| NB12 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 155.15 nM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 159.9 nM | SANGER | |||
| SIMA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 161.25 nM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 165.57 nM | SANGER | |||
| KS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 166.52 nM | SANGER | |||
| no-10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 173.76 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCCIT | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 176.26 nM | SANGER | |||
| RERF-LC-MS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 176.69 nM | SANGER | |||
| BT-20 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 181.74 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1623 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 187.08 nM | SANGER | |||
| TE-9 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 189.63 nM | SANGER | |||
| U-87-MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 190.57 nM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-51 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 191.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| 639-V | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 193.14 nM | SANGER | |||
| SJSA-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 195.01 nM | SANGER | |||
| DOHH-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 195.64 nM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 197.47 nM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1618 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 197.56 nM | SANGER | |||
| TGW | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 199.64 nM | SANGER | |||
| HT-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.20054 μM | SANGER | |||
| AN3-CA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.20329 μM | SANGER | |||
| PC-14 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.20331 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.21039 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.21106 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.21185 μM | SANGER | |||
| EGI-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.21386 μM | SANGER | |||
| Calu-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22003 μM | SANGER | |||
| BC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22065 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22258 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22363 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-320-HSR | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22408 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H596 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22513 μM | SANGER | |||
| EHEB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.22651 μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.23791 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.24804 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.25035 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.252 μM | SANGER | |||
| BOKU | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.25433 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ1-PC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.25435 μM | SANGER | |||
| IPC-298 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.25477 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1792 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.25904 μM | SANGER | |||
| KM-H2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.26068 μM | SANGER | |||
| Becker | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.26704 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H446 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.26911 μM | SANGER | |||
| MLMA | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.27156 μM | SANGER | |||
| JEG-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.27669 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-25 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.28928 μM | SANGER | |||
| CA46 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.29339 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-54 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.29759 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-70 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.29969 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-65 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.30381 μM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.30577 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2081 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.31077 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H226 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.31696 μM | SANGER | |||
| A427 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.32398 μM | SANGER | |||
| CPC-N | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.329 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW13 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.33037 μM | SANGER | |||
| K-562 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.33298 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-N87 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.33304 μM | SANGER | |||
| U-698-M | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.34453 μM | SANGER | |||
| IM-9 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.34691 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H748 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.35458 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.36412 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.36895 μM | SANGER | |||
| GAK | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.37294 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.37297 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.38454 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-NB-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.38597 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAMA-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.3958 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.4051 μM | SANGER | |||
| HPAF-II | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.42847 μM | SANGER | |||
| Raji | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.43145 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.43352 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1573 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.45733 μM | SANGER | |||
| KLE | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.45942 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H69 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.45948 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-361 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.46064 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW48 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.46259 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.47912 μM | SANGER | |||
| MC116 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.48166 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.48753 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.48828 μM | SANGER | |||
| SN12C | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.49734 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H838 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.49875 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1463 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.51017 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.51081 μM | SANGER | |||
| M14 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.51466 μM | SANGER | |||
| T98G | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.53948 μM | SANGER | |||
| CaR-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.55122 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H650 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.56569 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuH-7 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.56861 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daudi | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.56949 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-120 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.57588 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.57956 μM | SANGER | |||
| OMC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.58333 μM | SANGER | |||
| U-266 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.60794 μM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.62523 μM | SANGER | |||
| RCC10RGB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.63374 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2141 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.64404 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.66087 μM | SANGER | |||
| THP-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6642 μM | SANGER | |||
| RCM-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.66478 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.68269 μM | SANGER | |||
| MPP-89 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.69228 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.6956 μM | SANGER | |||
| OE19 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.70216 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1755 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.71816 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-42 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.73582 μM | SANGER | |||
| no-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.73668 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MES1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.77354 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2347 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.79201 μM | SANGER | |||
| SKG-IIIa | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.80972 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-62 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.8126 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-387 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.82744 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-513 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.88761 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H719 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.89157 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.95075 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.95508 μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.9965 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-392MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.02288 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-CALL-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.02319 μM | SANGER | |||
| DMS-53 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.03815 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC24TKB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.04183 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1417 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.07075 μM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.0739 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.1432 μM | SANGER | |||
| MKN28 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.15124 μM | SANGER | |||
| MSTO-211H | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.15257 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2126 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.15799 μM | SANGER | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.16785 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.17366 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1581 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.17372 μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.20277 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H28 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.2149 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-81-FD | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.23463 μM | SANGER | |||
| YT | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.28559 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.32585 μM | SANGER | |||
| U-118-MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.35159 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-1034 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.3845 μM | SANGER | |||
| PANC-08-13 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.39613 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-205 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.47181 μM | SANGER | |||
| KURAMOCHI | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.49739 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-C2B | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.54777 μM | SANGER | |||
| HDLM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.63327 μM | SANGER | |||
| PFSK-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.64794 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1088 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.66167 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB373-MEL-D | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.66495 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.76425 μM | SANGER | |||
| MMAC-SF | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1.7766 μM | SANGER | |||
| T-24 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.07629 μM | SANGER | |||
| LK-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.08563 μM | SANGER | |||
| 5637 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.10298 μM | SANGER | |||
| GI-ME-N | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.10851 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2196 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.31034 μM | SANGER | |||
| KOSC-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.35338 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.43457 μM | SANGER | |||
| AsPC-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.50301 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-175-VII | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.51493 μM | SANGER | |||
| DG-75 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.5612 μM | SANGER | |||
| LNCaP-Clone-FGC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.65415 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCLC-21H | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.77414 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFE-184 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.79042 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.80678 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1573 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.80723 μM | SANGER | |||
| PC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.83163 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.8814 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.92765 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-AS | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 2.96758 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.2819 μM | SANGER | |||
| KMS-12-PE | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.55998 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2171 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 3.76535 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.09997 μM | SANGER | |||
| DMS-153 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.10246 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.11559 μM | SANGER | |||
| RO82-W-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 4.42356 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.86741 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-280 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.90388 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 5.93153 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1963 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.26713 μM | SANGER | |||
| S-117 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.30327 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC1TKB | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.51712 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1522 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.53336 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-441-T | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.5501 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-893 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.55203 μM | SANGER | |||
| SHP-77 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 6.85463 μM | SANGER | |||
| TALL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.00001 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.00094 μM | SANGER | |||
| Capan-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.09987 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.13094 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1092 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.15535 μM | SANGER | |||
| LP-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.30969 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H889 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.57024 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2452 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 7.63456 μM | SANGER | |||
| UMC-11 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.35939 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-165 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.41085 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mewo | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.43715 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.43927 μM | SANGER | |||
| DV-90 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.45559 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1417 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.63434 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H187 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 8.85234 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-99A | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.13742 μM | SANGER | |||
| DMS-79 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.4013 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-415 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.95336 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1954 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 9.97404 μM | SANGER | |||
| EB-3 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.1641 μM | SANGER | |||
| CW-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.2237 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L88 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.4887 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP50-MEL-B | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.567 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.8448 μM | SANGER | |||
| EVSA-T | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 11.9609 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 12.0511 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-812 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.3687 μM | SANGER | |||
| LC-1F | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.4575 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1419 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.5715 μM | SANGER | |||
| C2BBe1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.6612 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-678 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.7484 μM | SANGER | |||
| RT4 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 13.8428 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H524 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 15.3769 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1143 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.3541 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT55 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.4103 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-39 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.6227 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU-19-19 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.8123 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB771-HNC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 16.9876 μM | SANGER | |||
| OPM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 17.6337 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAKI-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 18.0406 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YN | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 18.8885 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW948 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.4975 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20.6083 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1563 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.5347 μM | SANGER | |||
| GMS-10 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 21.6061 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-453 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 22.2184 μM | SANGER | |||
| PLC-PRF-5 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 22.8813 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFM-19 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 24.2029 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-FI | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 25.1429 μM | SANGER | |||
| Saos-2 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 26.765 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.5648 μM | SANGER | |||
| EKVX | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 27.7875 μM | SANGER | |||
| KINGS-1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 30.879 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2227 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 31.2813 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-542MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 32.2968 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-263MG | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 33.5726 μM | SANGER | |||
| A498 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 38.4491 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-157 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 38.5533 μM | SANGER | |||
| RMG-I | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 42.9009 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-792 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 43.2931 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 43.4294 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-475 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 44.5002 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 46.3321 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAN-6 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 46.6441 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 46.7503 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB49-HNC | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 47.6209 μM | SANGER | |||
| TT | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 49.8459 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | EC50 = 0.00003 μM | 27032331 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | GI50 = 0.000251 μM | 29301085 | |||
| Colo-357 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.00036 μM | 20930123 | |||
| SW620 | Antiproliferative assay | GI50 = 0.00084 μM | 29301085 | |||
| BV173 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.001 μM | 21711054 | ||
| PANC1 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.001 μM | 20930123 | |||
| RT112 | Cytotoxicity assay | EC50 = 0.0014 μM | 24471998 | |||
| A2780 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.0015 μM | 17602464 | |||
| T3M4 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0015 μM | 20930123 | |||
| NCI-H23 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | GI50 = 0.002 μM | 19929004 | ||
| H460 | Antiproliferative assay | GI50 = 0.002085 μM | 29301085 | |||
| OVCAR8 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0026 μM | 18469809 | ||
| PC3 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0026 μM | 18469809 | ||
| A2780/E6 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0026 μM | 18469809 | ||
| Patu-T | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0028 μM | 20930123 | |||
| HCT15 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | GI50 = 0.003 μM | 19929004 | ||
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.003 μM | 11728191 | |||
| OVCAR8 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.003 μM | 20873740 | ||
| C3 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.003 μM | 20873740 | ||
| Patu-S | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0032 μM | 20930123 | |||
| Patu-02 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0034 μM | 20930123 | |||
| DAN-G | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0034 μM | 20930123 | |||
| DU145 | Antiproliferative assay | IC50 = 0.0035 μM | 17887663 | |||
| BxPC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.00364 μM | 23094992 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.0039 μM | 25874330 | ||
| BT549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | GI50 = 0.004 μM | 19929004 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.004 μM | 24786915 | ||
| Aspc-1 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.004 μM | 20930123 | |||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.005 μM | 19691349 | |||
| MES-SA | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.005 μM | 21711054 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.005 μM | 24786915 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.005 μM | 24786915 | ||
| PC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | GI50 = 0.006 μM | 19929004 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.006 μM | 20873740 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.006 μM | 21711054 | ||
| CT26 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.006 μM | 21711054 | ||
| BxPC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 96 hrs | IC50 = 0.006 μM | 29356532 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0063 μM | 25874330 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0068 μM | 25874330 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.0068 μM | 25874330 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0069 μM | 25874330 | ||
| EL4 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.007 μM | 21711054 | ||
| L1210 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.007 μM | 21711054 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 2 days | IC50 = 0.0072 μM | 24341356 | ||
| NCI-H460 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0078 μM | 11728191 | |||
| BT549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.008 μM | 21711054 | ||
| MOLT4 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.008 μM | 24786915 | ||
| BxPC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | LC50 = 0.00871 μM | 23094992 | ||
| DMS53 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.009 μM | 22861499 | ||
| MES-SA | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0092 μM | 11728191 | |||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0097 μM | 18469809 | ||
| HCT15 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0099 μM | 18469809 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 4 days | IC50 = 0.0099 μM | 24341356 | ||
| H460 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.01 μM | 17602464 | |||
| MCF7 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.01 μM | 18588281 | ||
| SF268 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.01 μM | 20873740 | ||
| HCT15 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.01 μM | 20873740 | ||
| BxPC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | EC50 = 0.01 μM | 24867590 | ||
| SF268 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0103 μM | 18469809 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | IC50 = 0.0114 μM | 17887663 | |||
| Jurkat | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.012 μM | 24786915 | ||
| H292 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.013 μM | 17602464 | |||
| L1210 | Cytotoxicity assay | 2 days | IC50 = 0.013 μM | 24341356 | ||
| L1210 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.013 μM | 24471998 | ||
| SW480 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0136 μM | 18469809 | ||
| A549 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.014 μM | 17602464 | |||
| A2780 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.015 μM | 17602464 | |||
| SW1573 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.016 μM | 17602464 | |||
| A2780 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0166 μM | 18469809 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.017 μM | 25874330 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.018 μM | 25874330 | ||
| P388D1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.019 μM | 21711054 | ||
| Capan1 | Growth inhibition assay | 96 hrs | IC50 = 0.019 μM | 29356532 | ||
| SF539 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0198 μM | 18469809 | ||
| SF539 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.02 μM | 20873740 | ||
| A549 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.02 μM | 22861499 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.02 μM | 28221790 | ||
| MRC5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.0216 μM | 25874330 | ||
| CEM-DNR-bulk | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.022 μM | 21711054 | ||
| Jurkat | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | EC50 = 0.023 μM | 27032331 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | LD50 = 0.023 μM | 24786915 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.025 μM | 25350923 | ||
| U373-MAGI | Antiviral assay | 2 hrs | EC50 = 0.0275 μM | 24120088 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.029 μM | 25874330 | ||
| HT29 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.03 μM | 18588281 | ||
| Jurkat | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.03 μM | 20873740 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.03 μM | 28221790 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.03 μM | 29253340 | ||
| HCT116 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.03 μM | 29253340 | ||
| A2780 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.035 μM | 20873740 | ||
| DU-145 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.0356 μM | 11728191 | |||
| MIAPaCa2 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.03583 μM | 23094992 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.0364 μM | 29795767 | ||
| PC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.04 μM | 19691349 | |||
| Jurkat | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0453 μM | 18469809 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.05 μM | 22944119 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.05 μM | 24631359 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.05 μM | 28221790 | ||
| K562-TAX | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.05 μM | 28221790 | ||
| COLO205 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0514 μM | 18469809 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.06 μM | 22944119 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.06 μM | 22944119 | ||
| PC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | EC50 = 0.065 μM | 27032331 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.069 μM | 24341356 | ||
| HPAC | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.073 μM | 21711054 | ||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.08 μM | 20873740 | ||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0803 μM | 18469809 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.086 μM | 24471998 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 0.09 μM | 19691349 | |||
| U2OS | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.0907 μM | 18469809 | ||
| HuH7 | Cytotoxicity assay | CC50 = 0.1 μM | 20580554 | |||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.1 μM | 28221790 | ||
| CEM-DNR-bulk | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.1 μM | 28221790 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | LC50 = 0.1 μM | 23094992 | ||
| H460 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.103 μM | 17602464 | |||
| RT112 | Cytotoxicity assay | EC50 = 0.1049 μM | 24471998 | |||
| PANC1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.11 μM | 22342146 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.11 μM | 29328656 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Antiproliferative assay | 70 hrs | IC50 = 0.12 μM | 29471119 | ||
| CEM | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.13 μM | 17602464 | |||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.149 μM | 21711054 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.15 μM | 26025875 | ||
| CaCo2 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.18 μM | 18588281 | ||
| U2OS | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.18 μM | 20873740 | ||
| U2OS | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.18 μM | 28221790 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.19 μM | 25703296 | ||
| H292 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.21 μM | 17602464 | |||
| A549 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.225 μM | 17602464 | |||
| NCI-H460 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.23 μM | 22342146 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.245 μM | 21711054 | ||
| SW1573 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 0.275 μM | 17602464 | |||
| A2780 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.31 μM | 19362474 | ||
| K562 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 0.32 μM | 18588281 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.32 μM | 22342146 | ||
| CFPAC-1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 96 hrs | IC50 = 0.35 μM | 24631359 | ||
| PANC1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.4 μM | 29656202 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.41 μM | 28221790 | ||
| CFPAC-1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.47 μM | 24631359 | ||
| ACHN | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.48 μM | 22342146 | ||
| HCT116-E6 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.5 μM | 20873740 | ||
| C6 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.504 μM | 21711054 | ||
| LNCAP | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.512 μM | 21711054 | ||
| Calu1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 0.52 μM | 22342146 | ||
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.52 μM | 26025875 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.57 μM | 28075592 | ||
| K562 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.6 μM | 20873740 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 0.6 μM | 25703296 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.65 μM | 26025875 | ||
| BxPC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.67 μM | 24471998 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 0.718 μM | 21711054 | ||
| K562 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.7459 μM | 18469809 | ||
| Bel7402 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.84 μM | 19362474 | ||
| HCT116/E6 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 0.8965 μM | 18469809 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 96 hrs | IC50 = 0.9 μM | 24631359 | ||
| CEM | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 1 μM | 17602464 | |||
| HB-1 | Antiviral assay | 24 hrs | EC50 = 1 μM | 20580554 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.04 μM | 24471998 | ||
| SK-N-AS | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 1.1 μM | 21711054 | ||
| SW1990 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.2 μM | 19362474 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.4 μM | 19362474 | ||
| HepG2 | Function assay | Km = 1.4 μM | 17101674 | |||
| BL21(DE3) | Function assay | Km = 1.43 μM | 23230131 | |||
| U87MG | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 1.49 μM | 21711054 | ||
| BL21(DE3) | Function assay | Km = 1.52 μM | 23230131 | |||
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 1.53 μM | 21711054 | ||
| SW1990 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 1.6 μM | 24195466 | |||
| Capan2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.7 μM | 19362474 | ||
| SW480 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.7 μM | 20873740 | ||
| PANC1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.7 μM | 29656202 | ||
| HCT8 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 1.74 μM | 19362474 | ||
| BL21(DE3) | Function assay | Km = 1.75 μM | 23230131 | |||
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 1.95 μM | 23968824 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | EC50 = 2 μM | 24867590 | ||
| BL21(DE3) | Function assay | 1 min | Km = 2.15 μM | 23230131 | ||
| SW1990 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 2.2 μM | 25105722 | |||
| SW1990 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 2.3 μM | 27966950 | ||
| NCI-H146 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 2.78 μM | 21711054 | ||
| BxPC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 2.9 μM | 19362474 | ||
| p53 deficient COLO205 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 3 μM | 20873740 | ||
| MiaPaCa | Cytotoxicity assay | 6 days | IC50 = 3 μM | 23360104 | ||
| COLO205 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 3.24 μM | 23968824 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 3.28 μM | 19362474 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 3.3 μM | 29328656 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 3.3 μM | 25703296 | ||
| FTC-133 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 3.36 μM | 24436994 | ||
| BxPC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 3.64 μM | 22512908 | ||
| COLO320DM | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | IC50 = 3.92 μM | 23968824 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 4.12 μM | 21711054 | ||
| 8305C | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 4.53 μM | 24436994 | ||
| PANC1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 5.6 μM | 19362474 | ||
| PANC1 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | GI50 = 5.8 μM | 28495081 | ||
| SK-MEL-2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 7.11 μM | 21711054 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 7.6 μM | 24341356 | ||
| SW1573 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 8.3 μM | 17419604 | ||
| BxPC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | LC50 = 8.71 μM | 22512908 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 8.9 μM | 28075592 | ||
| BJ | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | IC50 = 9.88 μM | 21711054 | ||
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 10 μM | 24631359 | ||
| B16-F10-Luc-G5 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | IC50 = 11 μM | 27349332 | ||
| HCT15 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 11.8 μM | 18186604 | |||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 13.1 μM | 17419604 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | IC50 = 14.3 μM | 18186604 | |||
| MiaPaCa | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 17.1 μM | 23489626 | ||
| AG6000 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20 μM | 17602464 | |||
| AG6000 | Growth inhibition assay | IC50 = 20 μM | 17602464 | |||
| BxPC3 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 20.2 μM | 28576633 | ||
| CV1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 21.9 μM | 23489626 | ||
| AsPC1 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 26.8 μM | 28576633 | ||
| PANC1 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | IC50 = 30.4 μM | 28576633 | ||
| MIAPaCa2 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | GI50 = 35.83 μM | 22512908 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Mechanism of Action
| Features | Gemcitabine has been used to treat pancreatic cancer and has demonstrated effective anti-tumor activity. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
In vitro |
||||
| In vitro | Gemcitabine induced NF-κB activity in BxPC-3, PANC-1, and MIA PaCa-2 cells and decreased the level of the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα in BxPC-3 and PANC-1 cells. Treatment of BxPC-3 cells with low dose Gemcitabine for 48 hours results in a dose-dependent increase in NF-κB binding. In contrast, NF-κB DNA binding is decreased in BxPC-3 cells treated with the higher Gemcitabine doses for 48 h; however, 24-h treatment with these higher doses increases NF-κB binding in BxPC-3 cells [2] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Research | Cell lines | BxPC-3, MIA PaCa-2, and PANC-1 cells | ||
| Concentrations | 0.2 μM | |||
| Incubation Time | 24 hours or 48 hours | |||
| Method | BxPC-3, MIA PaCa-2, and PANC-1 cells are seeded in a 96-well plate. After 24 hours, cells are treated with vehicle, DMAPT and/or Gemcitabine for an additional 24 hours or 48 hours. Apoptosis is quantified using the Cell Death Detection ELISA to detect the amount of cytoplasmic histone-associated DNA fragments and expressed relative to vehicle-treated cells. | |||
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | p-JNK / JNK / p-ATF2 / p-c-Jun caspase-3 / caspase-8 / caspase-9 pS-ERα / ERα / pERK / ERK LC3-I / LC3-II p70S6K1 / p-S6 / HIF-1α |
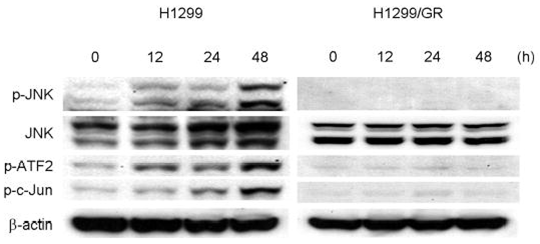
|
16307741 | |
| Immunofluorescence | BMI1 |
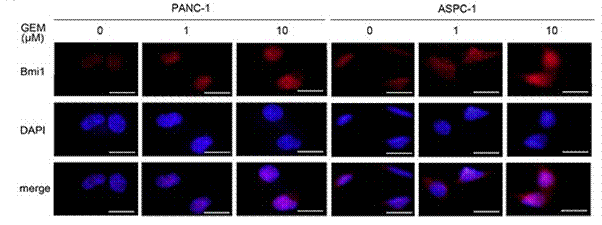
|
27177084 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
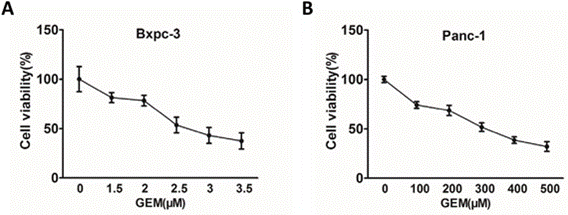
|
27765914 | |
In Vivo |
||
| In vivo | Intratumoral NF-κB activity is significantly elevated (1.3- to 1.8-fold) in the Gemcitabine-treated mice compared to the PBS-treated mice, suggesting that Gemcitabine also induces NF-κB activation. [2] | |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Research | Animal Models | Athymic nude mice with MIA PaCa-2 cells |
| Dosages | 50 mg/kg or 100 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Administered via i.p. | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06320301 | Recruiting | Biliary Tract Cancer|Gemox Chemotherapy |
Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University|Suzhou Suncadia Biopharmaceuticals Co. Ltd. |
April 1 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06046794 | Not yet recruiting | Cancer Of Pancreas |
Institut Paoli-Calmettes |
February 1 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06199466 | Recruiting | Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center|280Bio Inc |
January 22 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT06055348 | Not yet recruiting | Serous Ovarian Cancer|Advanced Ovarian Cancer |
Biocity Biopharmaceutics Co. Ltd. |
October 30 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
References |
|
Chemical Information
| Molecular Weight | 299.66 | Formula | C9H11F2N3O4.HCI |
| CAS No. | 122111-03-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| Synonyms | NSC 613327 HCl,LY-188011 HCl | ||
| Smiles | C1=CN(C(=O)N=C1N)C2C(C(C(O2)CO)O)(F)F.Cl | ||
Storage and Stability
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
Water : 59 mg/mL DMSO : Insoluble ( Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
|||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
What’s the difference between S1714 and S1149 and which one is better?
Answer:
They have the same biological activities. The free base(S1714) dissolves better in DMSO, and it dissolves better in water.