research use only
Eprenetapopt (APR-246) p53 activator
Cat.No.S7724
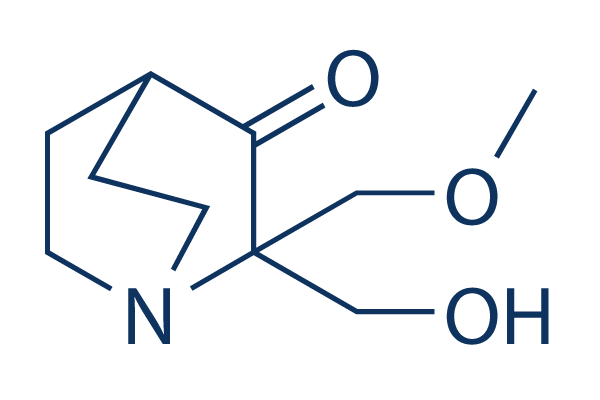
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 199.25
Quality Control
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NALM-6 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| UoCB-6 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| EU-3 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| MUTZ-5 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| KOPN-8 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| RS4;11 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| SKBR3 | Cell cycle assay | 5 µM | 2 weeks | lapatinib in combination with APR-246 caused a lower level of G1 arrest and an increase in the sub-G1 fraction | 30743996 | |
| BT549 | Cell viability assay | IC50=3.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-468 | Cell viability assay | IC50=5 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cell viability assay | IC50=4.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| HCC1143 | Cell viability assay | IC50=6.8 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-453 | Cell viability assay | IC50=0.9 μM | 30196236 | |||
| SKBR3 | Cell viability assay | IC50=5.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| UACC812 | Cell viability assay | IC50=11.3 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MCF7 | Cell viability assay | IC50=31.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MCF10A | Cell viability assay | IC50=5.2 μM | 30196236 | |||
| UMSCC10A | Cell viability assay | 0-50 μM | 72 h | suppressed cell survival and bore a modest effect on the killing of HNSCC cells | 29348462 | |
| FaDu | Cell viability assay | 0-50 μM | 72 h | suppressed cell survival and bore a modest effect on the killing of HNSCC cells | 29348462 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(200.75 mM)
Water : 40 mg/mL Ethanol : 40 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 199.25 | Formula | C10H17NO3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 5291-32-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | PRIMA-1MET | Smiles | COCC1(C(=O)C2CCN1CC2)CO | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Mutant p53
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Eprenetapopt (APR-246), also known as PRIMA-1MET, is the first clinical-stage compound that reactivates mutant p53 and induces apoptosis. It is a prodrug that is converted to the active compound methylene quinuclidinone (MQ), a Michael acceptor that binds to cysteine residues in mutant p53 and restores its wild-type conformation. This compound not only reactivates p53 but also decreases intracellular glutathione levels in a dose-dependent manner. It can trigger apoptosis in a p53-independent manner by inducing ROS and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and by inhibiting thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1). It was also reported that APR-246 induces cell death in myeloma cells independently of p53 status by impairing the GSH/ROS balance. PRIMA-1Met/APR-246 efficiently inhibited the growth of the SCLC cell lines expressing mutant p53 in vitro and induced apoptosis, associated with increased fraction of cells with fragmented DNA, caspase-3 activation, PARP cleavage, Bax and Noxa upregulation and Bcl-2 downregulation in the cells. |
| In vivo |
In a Phase I/II clinical dose-finding study on hematological malignancies and prostate cancer, Eprenetapopt (APR-246) showed a good safety profile, and both clinical and p53-dependent biological responses were observed. It is well tolerated in animal studies, and single treatment with this compound inhibits tumor growth by 21% in mice bearing the aggressively growing A2780-CP20 tumor xenografts. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | FL-PARP / Cleaved PARP p-p53 |
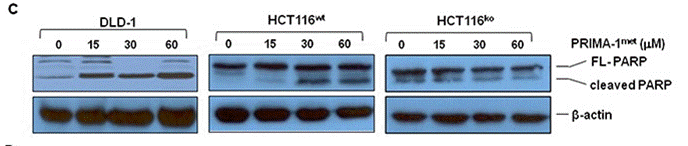
|
26452133 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
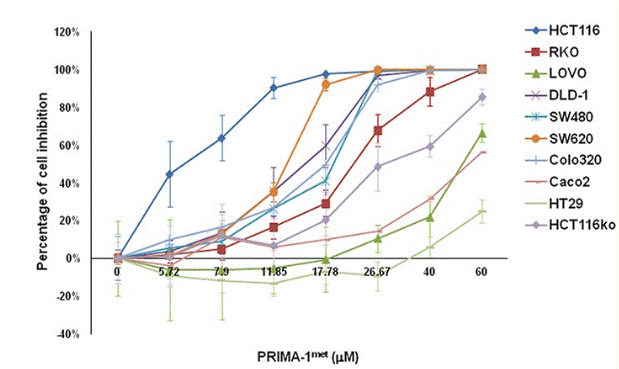
|
26452133 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04383938 | Completed | Bladder Cancer|Gastric Cancer|Non Small Cell Lung Cancer|NSCLC|Urothelial Carcinoma|Advanced Solid Tumor |
Aprea Therapeutics |
June 25 2020 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04214860 | Completed | Myeloid Malignancy |
Aprea Therapeutics |
December 13 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03391050 | Terminated | Melanoma |
Aprea Therapeutics|Jules Bordet Institute |
January 18 2018 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT02999893 | Terminated | Oesophageal Carcinoma |
Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Australia |
April 11 2017 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































