research use only
RITA p53 activator
Cat.No.S2781
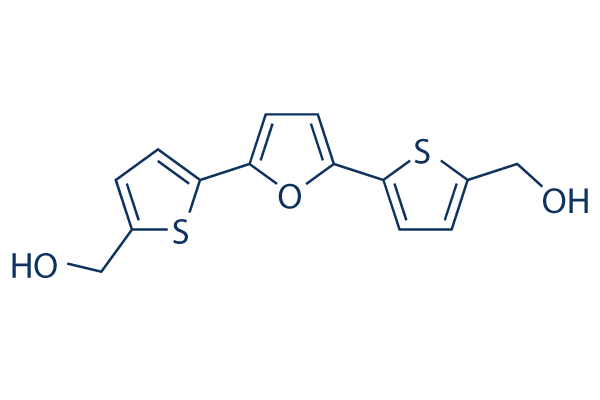
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 292.37
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 58 mg/mL
(198.37 mM)
Ethanol : 8 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 292.37 | Formula | C14H12O3S2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 213261-59-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC 652287 | Smiles | C1=C(SC(=C1)C2=CC=C(O2)C3=CC=C(S3)CO)CO | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Inducer of DNA cross-links, not a DNA intercalator.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Mdm2
p53
|
| In vitro |
RITA shows a highly selective pattern of differential cytotoxic activity in the tumor cell lines, due to cellular accumulation to the cytosolic (S100) fraction. This compound also inhibits the growth of other renal cell lines including ACHN and UO-31 with IC50 of 13 μM and 37 μM, respectively. It (10 nM) causes cell cycle arrest with accumulation of cells at the G2-M phase and induces DNA fragmentation and apoptosis at 100 nM, both with evaluated p53 protein levels. This chemical (30 nM) also induces both DNA-protein and DNA-DNA cross-links in A498 cells. Meanwhile it has no effects on top1-mediated relaxation of supercoiled SV40 DNA. It significantly suppresses the growth of HCT116 cells (97%) but only slightly inhibits the growth of HCT116 TP53-/- cells (13%). This compound is much more efficient at growth suppression in wild-type p53-expressing tumor cell lines than in cell lines lacking p53 and those expressing mutant p53. It binds full-length p53 but not glutathione S-transferase (GST) protein or HDM-2 (a key regulator of p53 is strongly supported by the rescue of embryonic lethality of MDM2). This chemical blocks p53−HDM-2 interaction and p53 ubiquitination. It substantially decreases the amount of HDM-2 that is co-precipitated with p53, although both proteins are upregulated. This compound prevents interactions between the purified GST-p53 and 6XHis-tagged His-HDM-2 proteins. It is shown to induce apoptosis by promoting p53Ser46 phosphorylation. This chemical induces activation of p53 in conjunction with up-regulation of phosphorylated ASK-1, MKK-4 and c-Jun. It induces the activation of JNK signaling. But On the contrary, another results by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) show that it does not block the formation of the complex between p53 (residues 1-312) and the N-terminal p53-binding domain of MDM2 (residues 1-118), which is highly probable that the binding of this compound requires native conformation of p53.
|
| In vivo |
RITA is well tolerated in mice after intraperitoneal administration, with no observable weight loss at doses up to 10 mg/kg during 1 month. After five injections of 0.1 mg/kg of this compound, the growth of the HCT116 tumors is suppressed by 40%, without apparent effects on the HCT116 TP53-/- tumors. At a dose of 1 or 10 mg/kg, it shows strong antitumor activity. Five 1 mg/kg injections of this chemical results in a more than twofold decrease in the growth rate of p53-positive xenografts without any effect on p53-null xenografts. HCT116 tumors are 90% smaller in mice treated with 10 mg/kg of it than in control untreated mice. This compound inhibits the tumor growth in a wild-type p53−dependent manner.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05260203 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma|Solitary Plasmacytoma|Amyloidosis|Chronic Myeloid Leukemia|Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia|T Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma|Lymphocytic Lymphoma|Hodgkin Lymphoma|B-cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma|Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Myelodysplasia|Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorder|Treatment Adherence|Treatment Adherence and Compliance |
Advice Pharma Group srl |
June 4 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05153551 | Completed | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
University of Michigan|Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Foundation |
January 27 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT03806127 | Completed | Irritable Bowel Syndrome |
Urovant Sciences GmbH |
December 31 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00779025 | Completed | Coitus |
Johnson & Johnson Consumer and Personal Products Worldwide |
January 2008 | Not Applicable |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































