research use only
BMS-345541 IKK-1/IKK-2 Inhibitor
Cat.No.S8044
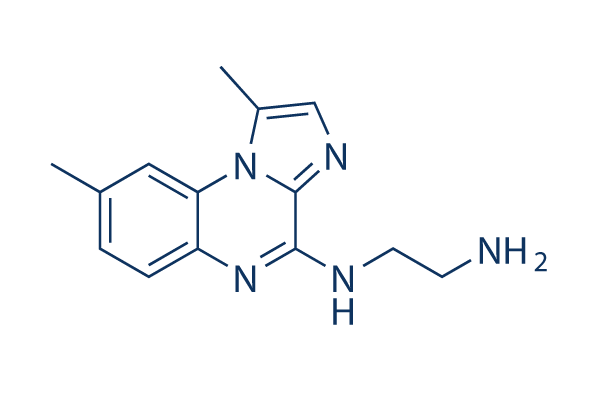
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 255.32
Quality Control
| Related Targets | NF-κB HDAC Antioxidant ROS Nrf2 AP-1 MALT NOD |
|---|---|
| Other IκB/IKK Inhibitors | TBK1/IKKε-IN-5 Wedelolactone IKK-16 TPCA-1 Bay 11-7085 IMD 0354 MRT67307 HCl SC-514 LY2409881 PS-1145 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THP1 cells | Function assay | Inhibition of LPS-induced TNFalpha secretion in THP1 cells, IC50=4 μM | 17197177 | |||
| SF9 cells | Function assay | 20 μM | Inhibition of purified recombinant histidine-HA-tagged IKK-beta expressed in SF9 cells at 20 uM | 18702457 | ||
| H460 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human H460 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 2.8 μM. | 29655083 | ||
| LLC | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse LLC cells measured after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 4.8 μM. | 27886548 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells measured after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 5.6 μM. | 27886548 | ||
| NCI-H1975 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human NCI-H1975 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 8 μM. | 29655083 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 8.6 μM. | 29655083 | ||
| NCI-H1650 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human NCI-H1650 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 9.3 μM. | 29655083 | ||
| Jurkat | Function assay | Inhibition of LPS-induced TNFalpha production in Jurkat cells, EC50 = 13.3 μM. | 17540562 | |||
| HL7702 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HL7702 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 15.3 μM. | 29655083 | ||
| NCI-H1650 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human NCI-H1650 cells measured after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 19.9 μM. | 27886548 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 58 mg/mL
DMSO
: 9 mg/mL
(35.24 mM)
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 255.32 | Formula | C14H17N5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 445430-58-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(C3=NC=C(N23)C)NCCN | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Allosteric IKK inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
IKK2
(Cell-free assay) 0.3 μM
IKK1
(Cell-free assay) 4 μM
|
| In vitro |
BMS-345541 dose-dependently inhibits the TNF-α-stimulated phosphorylation of IκBα in THP-1 monocytic cells with an IC50 of ~4 μM. This compound inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factorα, interleukin-1β, interleukin-8, and interleukin-6 in THP-1 cells with IC50 values in the 1- to 5 μM range. It binds in a mutually exclusive manner with respect to a peptide inhibitor corresponding to amino acids 26 - 42 of IκBα with Ser-32 and Ser-36 changed to aspartates and in a non-mutually exclusive manner with respect to ADP. This chemical binds to similar allosteric sites on IKK-1 and IKK-2, which then affects the active sites of the subunits differently. It affects several mitotic cell cycle transitions, including mitotic entry, prometaphase to anaphase progression and cytokinesis. Adding this compound to the cells released form arrest in G-phase blocks the activation of Aurora A, B, and C, Cdk1 activation and histone H3 phosphorylation. Treatment of the mitotic cells with this chemical results in precocious cyclin B1 and securin degradation, defective chromosome separation and improper cytokinesis. It is also found to override the spindle checkpoint in nocodazole-arrested cells. These effects are not primarily due to a direct inhibitory effect of this compound on mitotic kinases such as Cdk1, Aurora A or B, Plk1 or NEK2. This compound (10 μM) inhibits growth of Normal human epidermal melanocytes, and metastatic melanoma cells (SK-MEL-5, A375, and Hs 294T) by 96% and 99% at 72h, respectively. Application of 100 μM of it to SK-MEL-5 cell culture results in 87% apoptotic cells at 24 h through caspase-independent and AIF-dependent mitochondria-mediated manner. Treatment with this chemical (10 μM) results in 76% and 95% reduction in IKK activities and NF-kB activity, as well as CXCL1 production. It inhibits the growth of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cells line BE-13, RPMI-8402 and DND-41, all three harboring a Notch1 mutation, and T-ALL primary cells from pediatric patients, with IC50 of 2-6 μM. 5 μM of this compound induces an arrest in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle in BE-13 and DND-41 cells, and sub-G1 peak increase in RPMI-8402 cells. 5 μM of it treated for 16 h leads to an increase in apoptotic cells in all these cell, accompanied by a time-dependent cleavage of procaspase-8, procaspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). This chemical (5 μM) induces a time dependent dephosphorylation of IκBα and p65. T-ALL cells treated with it displays nuclear translocation of FOXO3a and restoration of its functions, including control of p21Cip1 expression levels. It inhibits the TNFα-induced expression of both ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells with IC50 of 5 μM. |
| Kinase Assay |
Enzyme Assays
|
|
Assays measuring the enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation of GST-IκBα are performed by adding enzyme (a final concentration of 0.5 μg/mL) at 30 ℃ to solutions of 100 μg/mL GST- IκBα and 5 μM [33P]ATP in 40 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.5, containing 4 mM MgCl2, 34mM sodium phosphate, 3 mM NaCl, 0.6 mM potassium phosphate, 1 mM KCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 3% (w/v) glycerol, and 250 μg/mL bovine serum albumin. The specific activity of [33P]ATP used in the assay is 100 Ci/mmol. After 5 min, the kinase reactions are stopped by the addition of 2× Laemmli sample buffer and heat-treated at 90 ℃ for 1 min. The samples are then loaded on to NuPAGE 10% BisTris gels. After completion of SDS-PAGE, gels are dried on a slab gel dryer. The bands are then detected using a 445Si PhosphorImager, and the radioactivity is quantified using ImageQuant software. Under these conditions, the degree of phosphorylation of GST-IκBα is linear with time and concentration of enzyme.
|
|
| In vivo |
BMS-345541 effectively inhibits melanoma tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner. Tumor-bearing mice treated with 75 mg/kg of this compound shows effective inhibition of growth of SK-MEL-5, A375, and Hs 294T tumors by 86 %, 69% and 67%, respectively, when compared with control animals treated with vehicle alone. This compound administered orally at doses of 100 mg/kg, reduces the severity of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice with weight ratio, clinical scoring of colons, mean injury score and mean inflammation score of 0.86 (vs 0.77 of vehicle group), 1.0 (vs 2.5 of vehicle group), 5.66 (vs 8.52 of vehicle group), 6.82 (vs 12.33 of vehicle group), respectively. This chemical (100 mg/kg), when administered by oral gavage in water once daily beginning at the time of the first collagen immunization, inhibits clinical signs of disease in the murine CIA model (0 vs ~8 of vehicle group), accompanied by reduced paw swelling. It reduces cumulative arthritis injury score from 4.4 to 0, accompanied by lower degrade of tibiotarsal joints and severity of inflammation, synovial hyperplasia, bone resorption, and cartilage erosion. No discernible injury is observed in the joints of animals, which is histologically indistinguishable from those from age-matched, disease-free control animals. This compound dose-dependently inhibits IL-1β message, with animals in the 100 mg/kg dose group showing levels comparable with those of disease-free control animals. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | caspase-3 (p17) / PARP / cleaved PARP IkB / p-IkB / p65 / p-p65 / p50 / p52 / Tax |
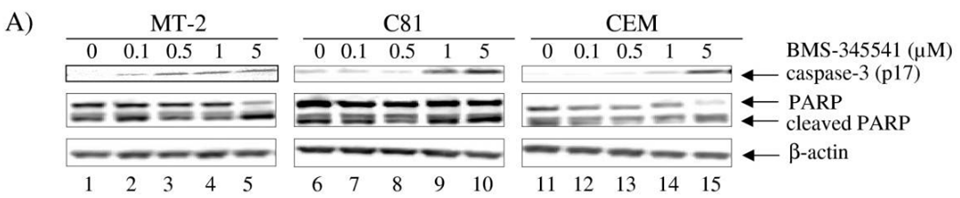
|
18544167 |
| Immunofluorescence | NF-κB-p65 Cyclin D1 / p-Cyclin D1 |
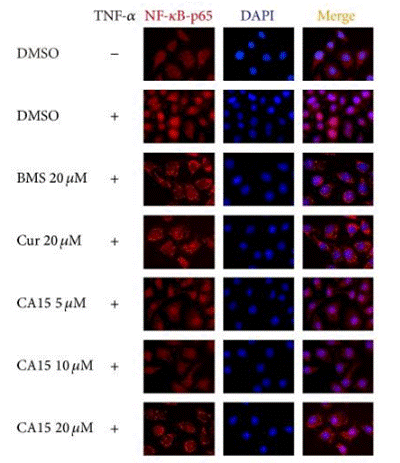
|
28409156 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































