
- Inhibitors
- By product type
- Natural Products
- Inducing Agents
- Peptides
- Antibiotics
- Antibody-drug Conjugates(ADC)
- PROTAC
- Hydrotropic Agents
- Dyes
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
By research - Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- Featured Products
- MRTX1133
- Nab-Paclitaxel
- KP-457
- IAG933
- RMC-6236 (Daraxonrasib)
- RMC-7977
- Zoldonrasib (RMC-9805)
- GsMTx4
- Navitoclax (ABT-263)
- TSA (Trichostatin A)
- Y-27632 Dihydrochloride
- SB431542
- SB202190
- MK-2206 Dihydrochloride
- LY294002
- Alisertib (MLN8237)
- XAV-939
- CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib)
- Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1)
- Thiazovivin (TZV)
- CP-673451
- Verteporfin
- DAPT
- Galunisertib (LY2157299)
- MG132
- SBE-β-CD
- Tween 80
- Bavdegalutamide (ARV-110)
- Z-VAD-FMK
- Wnt-C59 (C59)
- IWR-1-endo
- (+)-JQ1
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) Hydrochloride
- RepSox (E-616452)
- Erastin
- Q-VD-Oph
- Puromycin Dihydrochloride
- Cycloheximide
- Telaglenastat (CB-839)
- A-83-01
- Ceralasertib (AZD6738)
- Liproxstatin-1
- Emricasan (IDN-6556)
- PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)
- Dibutyryl cAMP (Bucladesine) sodium
- Nedisertib (M3814)
- PLX5622
- IKE (Imidazole Ketone Erastin)
- STM2457
- Saruparib (AZD5305)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Marbofloxacin Topoisomerase inhibitor
Cat.No.S1464
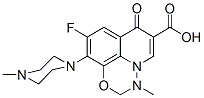
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 362.36
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.97%
99.97
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 362.36 | Formula | C17H19FN4O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 115550-35-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CN1CCN(CC1)C2=C(C=C3C4=C2OCN(N4C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C)F | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 3 mg/mL
(8.27 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki | |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Marbofloxacin is a fluorofloxacin antimicrobial agent developed exclusively for veterinary use. This compound exhibits high bactericidal activity against a broad spectrum of aerobic Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria, as well as Mycoplasma spp. As the third generation fluorofloxacin, it also mainly targets replication and transcription enzymes such as DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are both essential for bacterial viability. This agent has a mycoplasmacidal effect during the exponential phase but not during the lag phase, in both the M. hyopneumoniae 116 wild-type strain and a clone isolated 4 days post-marbofloxacin treatment in vivo at the therapeutic dose. [1] It significantly kills Leishmania promastigotes and intracellular amastigotes in a dose-dependent manner, more efficient than meglumine antimoniate and sodium stibogluconate. After treatment with this compound, macrophages acquire resistance to infection and enhanced antileishmanial activity through the NO synthase pathway. [2]
|
| In vivo |
Marbofloxacin treatment at the therapeutic dose does not eliminate M. hyopneumoniae, with 87.5 to 100% of the pigs still positive at the end of the assays, and is not effective in significantly reducing clinical signs. Nevertheless, this compound seems to decrease the lung lesion scores. [1] Administration of this compound at 6 mg/kg once daily for 7 days in a Staphylococcus aureus infection in tissue cages in ponies is not effective for the elimination of S. aureus infections from secluded sites. [3]
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































