research use only
Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1) V-ATPase inhibitor
Cat.No.S1413
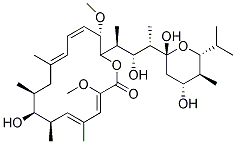
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 622.83
Quality Control
Products Often Used Together with Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1)
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Sodium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor TRP Channel ATPase |
|---|---|
| Other Proton Pump Inhibitors | Ilaprazole Tenatoprazole Ilaprazole sodium Revaprazan Hydrochloride PF-3716556 Ufiprazole |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human H4 cells | Function assay | 0.4 μM | 24 h | Induction of light chain 3-GFP level in human H4 cells at 0.4 uM after 24 hrs by high throughput fluorescence microscopy relative to control | 18024584 | |
| RAW 264.7 cells | Function assay | 100 nM | Antimicrobial activity against Salmonella enterica Typhimurium 14028 infected in RAW 264.7 cells assessed as increased nitric oxide production in infected cells at 100 nM | 19307359 | ||
| mouse RAW264.7 cells | Apoptosis assay | 100 nM | 16 h | Induction of apoptosis in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as late apoptotic cells at 100 nM after 16 hrs using annexin V-propidium iodide staining by flow cytometry | 19307359 | |
| human HeLa cells | Function assay | 400 nM | Induction of autophagy in human HeLa cells expressing EGFP-LC3 assessed as increase in LC3-2 level at 400 nM | 18391949 | ||
| human MCF7 cells | Function assay | 4 h | Inhibition of rapamycin-induced autophagy in human MCF7 cells expressing EGFP-LC3 assessed as decrease in EGFP levels at 100 nM after 4 hrs by Western blotting relative to control | 20028134 | ||
| RAW 264.7 cells | Bactericidal activity assay | 100 nM | 16 h | Bactericidal activity against Salmonella enterica Typhimurium 14028 infected in RAW 264.7 cells assessed as decrease in bacterial growth yield at 100 nM after 16 hrs postinfection by flow cytometry in presence of 10 ug/ml of intracellular replication inhi | 19307359 | |
| RAW 264.7 cells | Antimicrobial activity assay | 100 nM | Antimicrobial activity against Salmonella enterica Typhimurium 14028 infected in RAW 264.7 cells assessed as increased nitric oxide production in infected cells at 100 nM | 19307359 | ||
| RAW 264.7 cells | Antimicrobial activity assay | 100 nM | 30 mins | Antimicrobial activity against Salmonella enterica Typhimurium 14028 infected in RAW 264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of bacterial replication at 100 nM treated 30 mins before infection measured after 2 to 16 hrs postinfection by flow cytometry | 19307359 | |
| rat 3Y1 cells | Function assay | Induction of morphological changes in rat 3Y1 cells assessed as elongation of cells | 29701963 | |||
| human Huh7.5.1 cells | Antiviral activity | 3 h | Antiviral activity against HCV genotype 2a JFH-1 in human Huh7.5.1 cells assessed as reduction of viral entry up to 3 hrs by luciferase assay | 26396683 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
|
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 622.83 | Formula | C35H58O9 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 88899-55-2 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1CC(=CC=CC(C(OC(=O)C(=CC(=CC(C1O)C)C)OC)C(C)C(C(C)C2(CC(C(C(O2)C(C)C)C)O)O)O)OC)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
H+-ATPase
(Cell-free assay) 0.44 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1) is a toxic macrolide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces griseus, which inhibits the short circuit current induced by the outer mantle epithelium (OME). The IC50 and maximum inhibition dose of this compound are 0.17 μM and 0.5 μM, respectively. In addition, it inhibits the acid influx with an IC50 value of 0.4 nM. It also inhibits the acidification dose-dependently resulting in a lower quenching, and thus a higher fluorescence. This compound prevents the vacuolization of Hela cells induced by H. pylori, with an inhibitory concentration giving 50% of maximal (ID50) of 4 nM, and is very efficient in restoring vacuolated cells to a normal appearance. It also affects the transport of endocytosed material from early to late endocytic compartments, not only dissipating the low endosomal pH but also blocking transport from early to late endosomes in HeLa cells. At doses of 0.1-1 μM, it completely inhibits the acidification of lysosomes revealed by the incubation with acridine orange in BNL CL.2 and A431 cells. When added to Hanks' balanced salt solution, endogenous protein degradation is strongly inhibited and numerous autophagosomes accumulated in H-4-II-E cells. It also prevents the appearance of endocytosed HRP in autophagic vacuoles.
|
| Kinase Assay |
ATPase enzyme activity assays
|
|
The ATPase enzyme assay medium contains 6 mM MgSO4, 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 200 mM Na2SO3 (V-ATPase activator), 0.5 mM sodium ortho-vanadate (P-ATPase inhibitor), 0.5 mM sodium azide (F-ATPase inhibitor) and 3 mM Na2ATP. This medium (1.0 mL), with or without the addition of the V-type ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1), is incubated with the filtered homogenate (0.1 mL) for 60 minutes at 23–25 °C. The reaction is stopped by the addition of 1 mL of TCA 3%. Spectrometric blanks are prepared as for the enzyme assay with the exception that the tissue sample is added after the acid. Phosphate analysis is accomplished by adding 2 mL of 1-butanol and 0.2 mL molybdate solution (5 g ammonium molybdate, 22 mL H2SO4 to 100 mL). After vortexing for 15 seconds the solution is neutralised with 0.5 mL citrate solution (100 g/500 mL, pH 7.0) and again vortexed for 15 seconds. The solution is then centrifuged (2000 × g; 3 minutes) to separate the butanol phase and the absorbance of this phase is read at 400 nm. Standards of orthophosphate are prepared (0.1 μM–2.0 μM) and treated in the same way as the enzyme activity assays. Enzyme activity is expressed in μmol of orthophosphate liberated per hour and per milligram of protein. V-ATPase activity is considered to be the difference between the total ATPase activity measured in the presence of Na2SO3, sodium orthovanadate and sodium azide and the ATPase activity measured in the presence of these reagents and of this compound.
|
|
| In vivo |
Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1) (1 μM and 0.1 μM) completely inhibits the resorptive activity of cultured osteoclasts. This compound dose-dependently inhibits the rate of Na+ uptake in young tilapia with a Ki of 0.16 μM.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | Ret / EGFR / p75 NGFR |
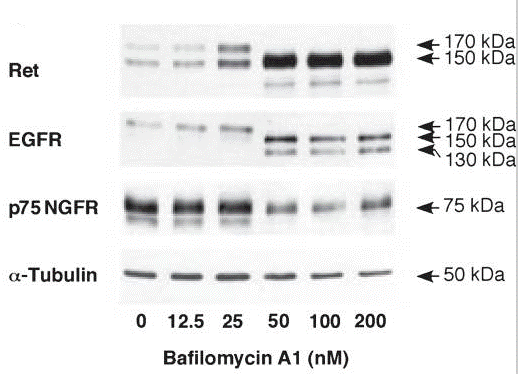
|
21559479 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
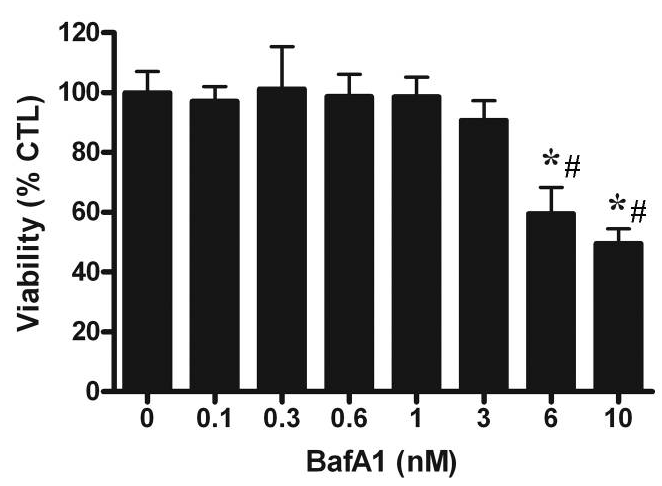
|
20534000 |
| Immunofluorescence | AIF LC3 |
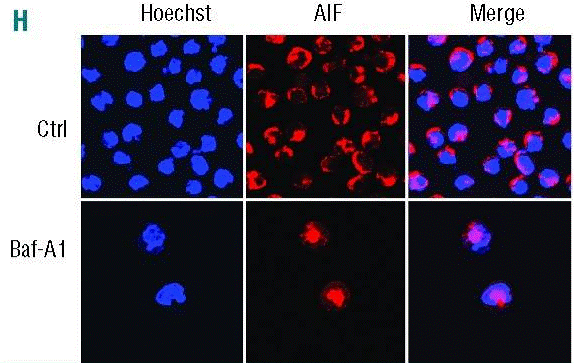
|
25512644 |
| ELISA | TNF-alpha |
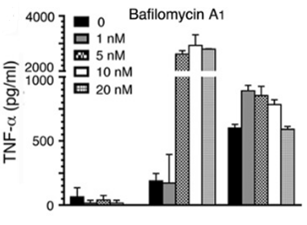
|
26240140 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
How to dissolve it?
Answer:
S1413 is soluble in DMSO at 6 mg/ml. Please do not use alcohols as solvent, because this compound will degrade in alcohols.






































