research use only
DPI (Diphenyleneiodonium chloride) NADPH-oxidase inhibitor
Cat.No.S8639
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 314.55
Quality Control
| Related Targets | PD-1/PD-L1 CXCR STING AhR Immunology & Inflammation related CD markers Interleukins Anti-infection Antioxidant COX |
|---|---|
| Other NADPH-oxidase Inhibitors | Setanaxib (GKT137831) NAD+ (β-DPN) Apocynin GSK2795039 GLX351322 2-Acetylphenothiazine (ML171) VAS2870 gp91ds-tat Isuzinaxib (APX-115 free base) |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC3T3-E1 | Function assay | 10 μM | 30 min | block ROS generation and NOX expression | 31049140 | |
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 10 μM | 4 days | DPI administration inhibited the effect of RANKL on osteoclast differentiation and reduced the number of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells | 30942408 | |
| VSMC | Function assay | 10 μM | 6 h | diminished PDGF-BB-evoked VSMC dedifferentiation, proliferation and migration | 29175753 | |
| HK-2 | Function assay | inhibited ROS generation in the TZA-induced necroptosis | 28894570 | |||
| mouse neural precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of neurosphere proliferation of mouse neural precursor cells by MTT assay | 17417631 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of LPS-stimulated ROS production in mouse RAW264.7 cells preincubated for 1 hr followed by LPS stimulation after 24 hrs by CMH2DCFDA probe-based fluorescence assay | 28384544 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 13 mg/mL
(41.32 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 314.55 | Formula | C12H8I.Cl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 4673-26-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C3=CC=CC=C3[I+]2.[Cl-] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
NADPH oxidase
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI) inhibits the activity of NADPH oxidase, nitric oxide synthase, xanthine oxidase and NADPH cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. Femtomolar concentrations of this compound exert potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects by inhibiting microglial activation through the inhibition of ERK-regulated PHOX activity. It has frequently been used to inhibit ROS production mediated by various flavoenzymes, including NAD(P)H oxidase, quinone oxidoreductase, cytochrome P450 reductase and nitric oxide synthase. NADPH, NADP+, and 2'5'-ADP blocks its inhibitory action. Treatment with DPI in ARPE-19 cells evoked a dose- and time-dependent growth inhibition, and also induced DNA fragmentation and protein content of the proapoptotic factor Bax. In addition, it significantly induced the expression and phosphorylation of p53, which induces proapoptotic genes in response to DNA damage or irreparable cell cycle arrest. ROS have been implicated as a key factor in the activation of p53 by many chemotherapeutic drugs. |
| In vivo |
Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI), an NADPH oxidase inhibitor, inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6), reduced macrophage infiltration and classical polarization, and induced ROS generation. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
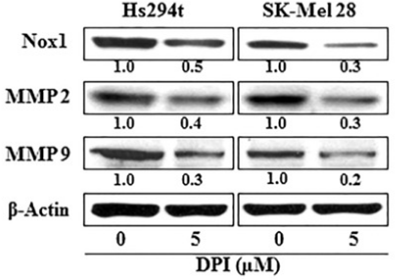
| Western blot | Nox1 / MMP2 / MMP9 |
|
26760964 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06061679 | Not yet recruiting | COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) With Acute Lower Respiratory Infection |
Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS|University of Florence UNIFI University of Florence Florence Italy Florence |
November 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06111664 | Recruiting | Mood Disorders |
University Hospital Strasbourg France |
May 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05706129 | Recruiting | Clear Cell Renal Cell Cancer (ccRCC)|Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC)|Colorectal Cancer (CRC) |
Debiopharm International SA |
March 14 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05764681 | Recruiting | Cerebral Palsy|Chronic Post Surgical Pain |
Chantel Burkitt|National Institutes of Health (NIH)|Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)|University of Minnesota|Nemours Children''s Hospital Delaware|Gillette Children''s Specialty Healthcare |
March 17 2023 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































