research use only
Tivantinib c-Met inhibitor
Cat.No.S2753
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 369.42
Quality Control
| Related Targets | EGFR VEGFR PDGFR FGFR Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 c-Kit |
|---|---|
| Other c-Met Inhibitors | Tepotinib Dihexa SGX-523 PHA-665752 Foretinib SU11274 BMS-777607 JNJ-38877605 PF-04217903 Savolitinib (AZD6094) |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNK-45 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| HT29 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| NCI-H441 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | |||
| NCI-H661 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | |||
| NCI-H446 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=7 μM | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.55 μM | |||
| DLD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.53 μM | |||
| A549 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.59 μM | |||
| SK-OV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.66 μM | |||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.6 μM | |||
| A375 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.42 μM | |||
| NCI-H441 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.3 μM | |||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.49 μM | |||
| MKN-45 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.58 μM | |||
| HT29 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | |||
| MKN-45 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | modestly induces apoptosis by 35%. | |||
| MDA-MB-231/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=1.2 μM | |||
| 1833/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=3.7 μM | |||
| EBC1 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | |||
| SNU638 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | |||
| A549 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| H460 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| HCC827 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | |||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | |||
| EBC1 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | |||
| H460 | Function assay | 10 μM | inhibits tubulin polymerization | |||
| K562/VCR | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | |||
| CEM/VBL | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | |||
| U266 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.1 μM | |||
| OPM-2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.8 μM | |||
| MM.1S | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.6 μM | |||
| MM.1R | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 49% | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=0.9 μM | |||
| ANBL-6 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| ANLB-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/1 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| KAS-6/R10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | |||
| 8226/S | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | |||
| 8226/LR-5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | |||
| Huh7 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=9.9 nM | ||
| Hep3B | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=139.77 nM | ||
| Chang | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | DMSO | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Hep3B | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| HepG2 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Chang | Function assay | 1.6 μM | DMSO | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| MHCC97L | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=315 nM | ||
| MHCC97H | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=368 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=265 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=392 nM | ||
| MHCC97L | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| MHCC97L | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| Huh7 | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts | Kinase assay | 25 μM | DMSO | reduces Histone H3 and H4 acetylation levels | ||
| H23 | Growth inhibitory assay | 25 μM | DMSO | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| WM35 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| NIH 3T3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H838 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H1395 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| Quiescent S2 | Kinase assay | 30 μM | DMSO | completely abrogates TSA-induced hyperacetylation of H3K4me3 histones | ||
| PC3 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| Du145 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LAPC-4 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Function assay | 20 μM | DMSO | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| LAPC-4 | Function assay | 20 μM | DMSO | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| SKNO-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| SKNO-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | enhances mitotic catastrophe | ||
| NRK-52E | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits Ang II-induced STAT3 nuclear translocation and the expression of TGF-β1, collagen IV and fibronectin | ||
| PC12 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~12.5 μM | DMSO | prevents TSA-induced neurite formation | ||
| HPMCs | Function assay | reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human peritoneal mesothelial cells | ||||
| A549 | Function assay | ~50 μM | DMSO | affects the viral life cycle and host response | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | ~30 μM | DMSO | reduces pro-inflammatory gene expression | ||
| MEMM | Kinase assay | 15 µM | DMSO | decreases acetylation of histone H3 | ||
| MEMM | Growth inhibitory assay | ~20 µM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| MEMM | Apoptosis assay | 15 µM | DMSO | induces the presence of the apoptosis protein, cleaved Caspase-3 | ||
| T47D | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=72 nM | ||
| ZR-75-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=79 nM | ||
| BT474 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=86 nM | ||
| HCC1954 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=119 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-453 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=975 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3208 nM | ||
| SkBr3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HCT116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=5836 nM | ||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HFF | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=7615 nM | ||
| HN5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=4009 nM | ||
| H157 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2642 nM | ||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>2,500 nM | ||
| SKOV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2126 nM | ||
| OVCAR-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2918 nM | ||
| BXPC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3141 nM | ||
| MiaPaCa | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=5433 nM | ||
| PANC-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=8681 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=147 nM | ||
| DU145 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50=3812 nM | ||
| PC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| BT474 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 160 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 150 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 43 nM | ||
| PC3 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | DMSO | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 49 nM | ||
| KARPAS-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=41 nM | ||
| CCRFSB | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=155 nM | ||
| SUP B15 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=197 nM | ||
| SD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=320 nM | ||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=654 nM | ||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=3602 nM | ||
| Tanoue | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=4517 nM | ||
| RCH-ACV | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=152 nM | ||
| SEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=202 nM | ||
| KASUMI-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=225 nM | ||
| REH | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=288 nM | ||
| 697 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=338 nM | ||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=421 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=812 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=2114 nM | ||
| J.GAMMA-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=65 nM | ||
| JR45.01 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=68 nM | ||
| A3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=69 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=73 nM | ||
| MOLT-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=74 nM | ||
| P116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=78 nM | ||
| J.Cam1.6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=79 nM | ||
| I 9.2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=80 nM | ||
| LOUCY | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=117 nM | ||
| J.RT3-T3.5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=123 nM | ||
| 800000 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=163 nM | ||
| Jurkat | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=225 nM | ||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=232 nM | ||
| Molt-16 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=241 nM | ||
| CEM/C3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=257 nM | ||
| CEM/C2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=271 nM | ||
| CCRFCEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=327 nM | ||
| CEM/C1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=382 nM | ||
| SUPTI[VB] | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=619 nM | ||
| CCRF–HSB-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | DMSO | EC50=2117 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| I 9.2 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| A3 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | ||
| RD | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| Rh41 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=33.8 nM | |||
| Rh18 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=303 nM | |||
| Rh30 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=4.81 μM | |||
| BT-12 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-266 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.22 μM | |||
| TC-71 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.52 μM | |||
| CHLA-9 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=591 nM | |||
| CHLA-10 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=102 nM | |||
| CHLA-258 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.05 μM | |||
| GBM2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=9.15 μM | |||
| NB-1643 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=5.4 μM | |||
| NB-Ebc1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-90 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| CHLA-136 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=265 nM | |||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=6.49 nM | |||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=147 nM | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=40 nM | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=268 nM | |||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=107 nM | |||
| Karpas-299 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.93 μM | |||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=7.35 μM | |||
| H1299 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits IKBKE-induced Akt Activation | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 73 mg/mL
(197.6 mM)
Ethanol : 35 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 369.42 | Formula | C23H19N3O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 905854-02-6 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | ARQ 197 | Smiles | C1CC2=C3C(=CC=C2)C(=CN3C1)C4C(C(=O)NC4=O)C5=CNC6=CC=CC=C65 | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
The first selective c-Met inhibitor to be advanced into human clinical trials.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
c-Met
(Cell-free assay) 0.355 μM(Ki)
|
| In vitro |
ARQ-197 has been shown to prevent HGF/c-met induced cellular responses in vitro. This compound possesses antitumor activity; inhibiting proliferation of A549, DBTRG and NCI-H441 cells with IC50 of 0.38, 0.45, 0.29 μM. Treatment with this agent results in a decrease in phosphorylation of the MAPK signaling cascade and prevention of invasion and migration. In addition, ectopic expression of c-Met in NCI-H661, a cell line having no endogenous expression of c-Met, causes it to acquire an invasive phenotype that is also suppressed by this chemical. Although the addition of increasing concentrations of this inhibitor does not significantly affect the Km of ATP, exposure of c-Met to 0.5 μM of this substance decreased the Vmax of c-Met by approximately 3-fold. The ability of this molecule to decrease the Vmax without affecting the Km of ATP confirmed that it inhibits c-Met through a non–ATP-competitive mechanism and may therefore account for its high degree of kinase selectivity. It prevents human recombinant c-Met with a calculated inhibitory constant Ki of approximately 355 nM. Although the highest concentration of ATP used is 200 μM, the potency of this compound against c-Met is not reduced by using concentrations of ATP up to 1 mM. It blocks c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways. This chemical suppresses constitutive and ligand-mediated c-Met autophosphorylation and, by extension, c-Met activity, in turn leading to the inhibition of downstream c-Met effectors. Its induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis is increased in c-Met–expressing human cancer cells including HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells. |
| Kinase Assay |
c-Met SDS-PAGE in vitro kinase assay
|
|
Recombinant c-Met protein (100 ng) is preincubated with increasing concentrations of this compound for 30 minutes at room temperature. Following preincubation, 100 μM of poly-Glu-Tyr substrate and various concentrations of ATP containing 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP are added to the reaction mixture. The reaction is incubated for 5 minutes at room temperature and then stopped by the addition of 5 μL of SDS-polyacrylamide gel, reducing sample buffer. The samples are then loaded onto a 7.5% acrylamide gel and SDS-PAGE is performed. The phosphorylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrates are ultimately visualized by autoradiography. c-Met activity is quantified by densitometry.
|
|
| In vivo |
All three xenograft models treated with Tivantinib display reductions in tumor growth: 66% in the HT29 model, 45% in the MKN-45 model, and 79% in the MDA-MB-231 model. In these xenograft studies, no significant body weight changes following oral administration of this compound at 200 mg/kg are observed. Pharmacodynamically, the phosphorylation of c-Met in human colon xenograft tumors (HT29) is strongly inhibited by this chemical, as assessed by a dramatic reduction of c-Met autophosphorylation 24 hours after a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg of this agent. This same dosage in mice exhibits that tumor xenografts are exposed to sustained plasma levels of the compound, consistent with the observed pharmacodynamic inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation of c-Met harboring cancer cell lines. Plasma levels of the agent 10 hours after dosing are determined to be 1.3 μM, more than 3-fold above the biochemical inhibitory constant of this substance for c-Met. Therefore, it is able to suppress its target in vivo in the xenografted human tumor tissue. In conclusion, this inhibitor blocks the growth of c-Met-dependent xenografted human tumors. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | cMET / p-cMET / p-AKT / p-ERK / p-rpS6 |
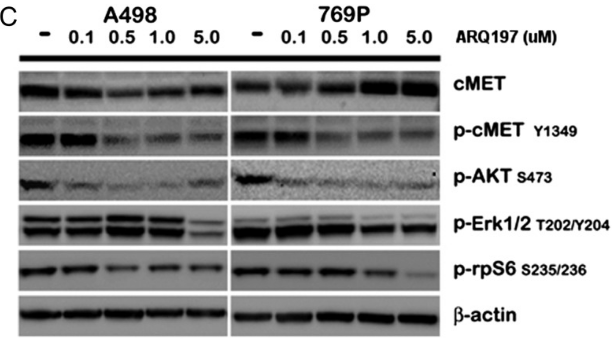
|
23022995 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
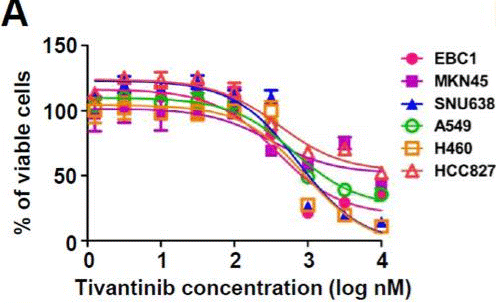
|
23598276 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02150733 | Completed | Hepatic Impairment|Solid Tumor|Cancer |
Daiichi Sankyo|Medpace Inc. |
April 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01892527 | Completed | Colorectal Cancer Metastatic|C-met Overexpression |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
March 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02049060 | Completed | Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma|Nonsquamous Nonsmall Cell Neoplasm of Lung |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
January 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT01755767 | Completed | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
Daiichi Sankyo|ArQule Inc. a subsidiary of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC a subsidiary of Merck & Co. Inc. (Rahway NJ USA) |
December 27 2012 | Phase 3 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
Are there any other solutions (apart from DMSO) I can dissolve it for in vivo experiment?
Answer:
S2753 This compound (ARQ 197) can be dissolved in 1% methylcellulose at 15 mg/ml as a suspension.






































