|
How to Cite 1. For In-Text Citation (Materials & Methods): 2. For Key Resources Table: |
||
|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. We strive to reply to |
Technical Data
| Formula | C23H19N3O2 |
||||||
| Molecular Weight | 369.42 | CAS No. | 905854-02-6 | ||||
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 74 mg/mL (200.31 mM) | ||||
| Ethanol | 40 mg/mL (108.27 mM) | ||||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Add solvents to the product individually and in order) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
|||||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | Tivantinib is the first non-ATP-competitive c-Met inhibitor with Ki of 0.355 μM in a cell-free assay, little activity to Ron, and no inhibition to EGFR, InsR, PDGFRα or FGFR1/4. This compound induces a G2/M arrest and apoptosis. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||
| In vitro | ARQ-197 has been shown to prevent HGF/c-met induced cellular responses in vitro. This compound possesses antitumor activity; inhibiting proliferation of A549, DBTRG and NCI-H441 cells with IC50 of 0.38, 0.45, 0.29 μM. Treatment with this agent results in a decrease in phosphorylation of the MAPK signaling cascade and prevention of invasion and migration. In addition, ectopic expression of c-Met in NCI-H661, a cell line having no endogenous expression of c-Met, causes it to acquire an invasive phenotype that is also suppressed by this chemical. Although the addition of increasing concentrations of this inhibitor does not significantly affect the Km of ATP, exposure of c-Met to 0.5 μM of this substance decreased the Vmax of c-Met by approximately 3-fold. The ability of this molecule to decrease the Vmax without affecting the Km of ATP confirmed that it inhibits c-Met through a non–ATP-competitive mechanism and may therefore account for its high degree of kinase selectivity. It prevents human recombinant c-Met with a calculated inhibitory constant Ki of approximately 355 nM. Although the highest concentration of ATP used is 200 μM, the potency of this compound against c-Met is not reduced by using concentrations of ATP up to 1 mM. It blocks c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways. This chemical suppresses constitutive and ligand-mediated c-Met autophosphorylation and, by extension, c-Met activity, in turn leading to the inhibition of downstream c-Met effectors. Its induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis is increased in c-Met–expressing human cancer cells including HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells. |
||
| In vivo | All three xenograft models treated with Tivantinib display reductions in tumor growth: 66% in the HT29 model, 45% in the MKN-45 model, and 79% in the MDA-MB-231 model. In these xenograft studies, no significant body weight changes following oral administration of this compound at 200 mg/kg are observed. Pharmacodynamically, the phosphorylation of c-Met in human colon xenograft tumors (HT29) is strongly inhibited by this chemical, as assessed by a dramatic reduction of c-Met autophosphorylation 24 hours after a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg of this agent. This same dosage in mice exhibits that tumor xenografts are exposed to sustained plasma levels of the compound, consistent with the observed pharmacodynamic inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation of c-Met harboring cancer cell lines. Plasma levels of the agent 10 hours after dosing are determined to be 1.3 μM, more than 3-fold above the biochemical inhibitory constant of this substance for c-Met. Therefore, it is able to suppress its target in vivo in the xenografted human tumor tissue. In conclusion, this inhibitor blocks the growth of c-Met-dependent xenografted human tumors. |
||
| Features | The first selective c-Met inhibitor to be advanced into human clinical trials. |
Protocol (from reference)
| Kinase Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Cell Assay: |
|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
|
Customer Product Validation
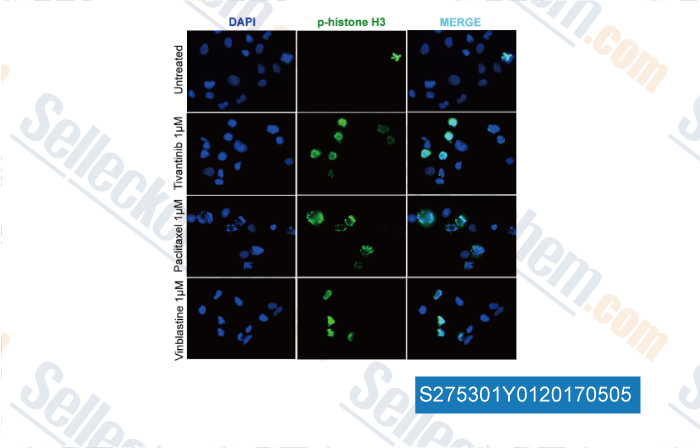
-
, , Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 23(15):4364-4375
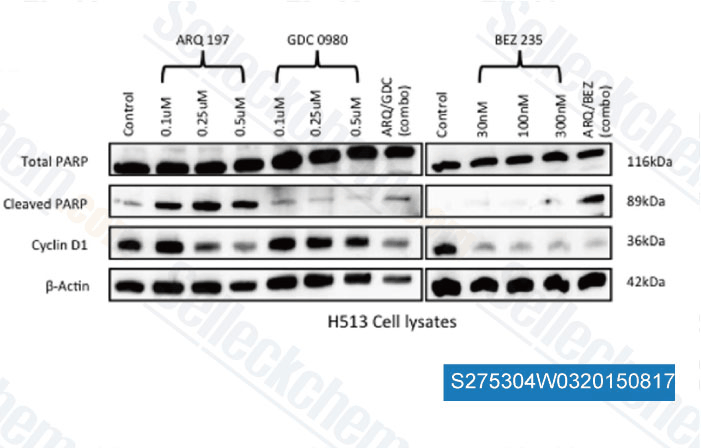
-
Data from [ , , PLoS One, 2014, 9(9): e105919 ]
Selleck's Tivantinib Has Been Cited by 50 Publications
| MET receptor serves as a promising target in melanoma brain metastases [ Acta Neuropathol, 2024, 147(1):44] | PubMed: 38386085 |
| Insulin receptor substrate 1 is a novel member of EGFR signaling in pancreatic cells [ Eur J Cell Biol, 2024, 103(4):151457] | PubMed: 39326351 |
| EZH2/hSULF1 axis mediates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling to shape cartilage tumor progression [ Elife, 2023, 12e79432] | PubMed: 36622753 |
| A community challenge for a pancancer drug mechanism of action inference from perturbational profile data [ Cell Rep Med, 2022, 3(1):100492] | PubMed: 35106508 |
| High-Resolution Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma Identifies Expression Subtypes with Specific Biomarkers and Clinically Relevant Vulnerabilities [ Cancer Res, 2022, 82(21):3917-3931] | PubMed: 36040373 |
| High-resolution profiling of lung adenocarcinoma identifies expression subtypes with specific biomarkers and clinically relevant vulnerabilities [ Cancer Res, 2022, CAN-22-0432] | PubMed: 36040373 |
| Ring Finger Protein 125 Is an Anti-Proliferative Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma [ Cancers (Basel), 2022, 14(11)2589] | PubMed: 35681566 |
| Establishment and Characterization of NCC-PMP1-C1: A Novel Patient-Derived Cell Line of Metastatic Pseudomyxoma Peritonei [ J Pers Med, 2022, 12(2)258] | PubMed: 35207746 |
| MTBP enhances the activation of transcription factor ETS-1 and promotes the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [ Front Oncol, 2022, 12:985082] | PubMed: 36106099 |
| MET Inhibition Sensitizes Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells to NOTCH Signaling Suppression [ Front Oncol, 2022, 12:835642] | PubMed: 35574376 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
