research use only
b-AP15 DUB inhibitor
Cat.No.S4920
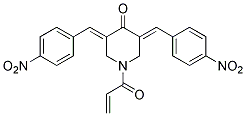
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 419.39
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Proteasome E1 Activating E3 Ligase p97 SUMO E2 conjugating |
|---|---|
| Other DUB Inhibitors | PR-619 P5091 IU1 P22077 ML323 LDN-57444 VLX1570 TCID EOAI3402143 USP25/28 inhibitor AZ1 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P388 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against murine P388 cells, IC50=0.05 μM | ||||
| human HSC2 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human HSC2 by MTT method, CC50=0.094 μM | ||||
| HL60 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human HL60 cells in presence of RPMI1640 containing 10% fetal bovine serum by trypan blue exclusion test, CC50=0.13 μM | ||||
| Molt 4/C8 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human Molt 4/C8 cells, IC50=0.15 μM | ||||
| CEM cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human CEM cells, IC50=0.26 μM | ||||
| L1210 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against murine L1210 cells, IC50=0.42 μM | ||||
| HSC4 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human HSC4 cells by MTT method, CC50=0.56 μM | ||||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 48 mg/mL
(114.45 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 419.39 | Formula | C22H17N3O6 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1009817-63-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC687852 | Smiles | C=CC(=O)N1CC(=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)[N+](=O)[O-])C(=O)C(=CC3=CC=C(C=C3)[N+](=O)[O-])C1 | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Not a general deubiquitinase inhibitor. Has minimal inhibition on recombinant and cytosolic nonproteasomal cysteine deubiquitinases.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
USP14
UCHL5
2.1 μM
|
| In vitro |
b-AP15 inhibits the activity of two 19S regulatory-particle-associated deubiquitinases, ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 5 (UCHL5) and ubiquitin-specific peptidase 14 (USP14), resulting in accumulation of polyubiquitin. This compound results in a dose-dependent accumulation of the UbG76V-YFP reporter with IC50 of 0.8 μM, indicating impaired proteasome degradation. It (1 μM) results in rapid accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins in human colon carcinoma HCT-116 cells. This chemical (2.2 μM) increases the amounts of the cyclin-dependent kinases CDKN1A and CDKNIB and the tumor suppressor TP53 in a dose-dependent manner without altering the amounts of ornithine decarboxylase 1 (ODC1) in HCT-116 cells. It (1 μM) results in G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest in HCT-116 cells, consistent with the accumulation of cell-cycle inhibitors. This compound treatment increases the number of hypodiploid cells and is associated with increased amounts of apoptotic markers, including activated caspase-3, caspase-cleaved poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) and cytokeratin-18 (CK18). It is more toxic to HCT-116 cells as compared to immortalized epithelial cells (hTERT-RPE1) or peripheral blood mononuclear cells. This inhibitor inhibits deubiquitinating activity using a variety of substrates, including Ub-AMC, Ub-GFP22, ubiquitinated p53-binding protein homolog (HDM2), and K48- and K63-linked ubiquitin tetramer chains. It is an inhibitor of the UPS that induced cell death via induction of the lysosomal apoptosis pathway in a cathepsin-D dependent manner. This compound elicits characteristic UPS defects including the accumulation of ubiquitin conjugates and cell cycle inhibitors such as p21, p27 and the tumor suppressor p53. It inhibits the deubiquitinase activity of both cysteine DUBs, with USP14 being slightly more sensitive than UCHL5. This chemical induces apoptosis in cells over-expressing the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and in cells lacking the p53 gene. It (1 μM) inhibits ATP-induced IL-1β release from LPS-primed peritoneal macrophages. This compound (1 μM) reduces the levels of cell death induced by nigericin treatment in THP-1 cells. It (1 μM) significantly reduces the numbers of ASC specks formed after nigericin treatment in LPS-primed THP-1 cells.
|
| In vivo |
b-AP15 (5 mg/kg) shows significant antitumor activity in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice with FaDu squamous carcinoma xenografts. This compound significantly delays tumor onset in mice with HCT-116 colon carcinoma xenografts.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































