research use only
Busulfan Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibitor
Cat.No.S1692
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 246.3
Quality Control
| Related Targets | HDAC PARP ATM/ATR DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase |
|---|---|
| Featured Inhibitors | Y-27632 Dihydrochloride SB431542 CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) RMC-7977 RMC-6236 (Daraxonrasib) MRTX1133 MG132 Z-VAD-FMK VT3989 IAG933 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK-N-SH cells | Proliferation assay | 10-100 μM | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human SK-N-SH cells at 10 to 100 uM after 72 hrs by MTT assay | 24814532 | |
| SiMa cells | Proliferation assay | 10-100 μM | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human SiMa cells at 10 to 100 uM after 72 hrs by MTT assay | 24814532 | |
| Kelly cells | Proliferation assay | 10-100 μM | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human Kelly cells at 10 to 100 uM after 72 hrs by MTT assay | 24814532 | |
| LS cells | Proliferation assay | 10-100 μM | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human LS cells at 10 to 100 uM after 72 hrs by MTT assay | 24814532 | |
| K562 | Apoptosis assay | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in imatinib mesylate-resistant human K562 cells after 48 hrs | 18339455 | ||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 49 mg/mL
(198.94 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 246.3 | Formula | C6H14O6S2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 55-98-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC-750 | Smiles | CS(=O)(=O)OCCCCOS(=O)(=O)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vitro |
Busulfan inhibits the cobblestone area-forming cell frequency but fails to cause a significant increase in apoptosis in hematopoietic stem cell alike cells and progenitors. This compound inhibits the hematopoietic function of HSC alike cells and progenitors via an apoptosis-independent mechanism. It induces bone marrow hematopoietic cell senescence associated with an increased expression of p16Ink4a and p19Arf in a time-dependent manner. This chemical, an alkylating agent that causes DNA damage by cross-linking DNAs and DNA and proteins, induces senescence in normal human diploid WI38 fibroblasts through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) cascade independent of the p53-DNA damage pathway. It induces a transient reduction in GSH but a continuous increase in ROS production. This compound-induced hypophosphorylation of Rb prevents apoptosis of spermatogonial stem cells by inhibiting PCNA expression in testicular cells. |
|---|---|
| In vivo |
Busulfan-treated mice exhibit a marked increase in apoptosis and a decrease in testis weight. This compound is administered at the rate of 40 mg/kg body weight to induce a maximal number of apoptotic cells while minimizing the number of necrotic cells. Its conditioning and irradiation results in comparable sensitivity of HSC detection as evaluated by limiting dilution analysis in NOD/SCID mice. This chemical-transplanted mice has slow and incomplete lymphoid engraftment. It (20 mg/kg to 100 mg/kg) provides dose-dependent congenic lymphoid reconstitution in mice. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
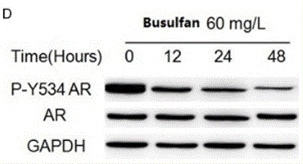
| Western blot | p-Y534 AR / AR Ack1 / Src |
|
27904688 |
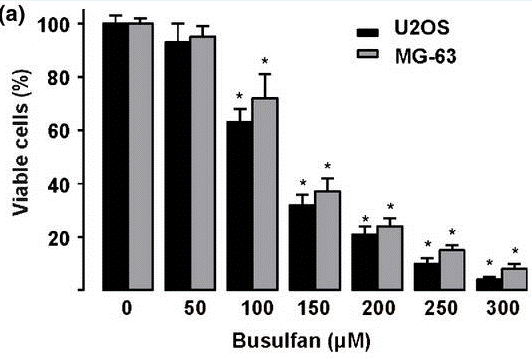
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
24815002 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04451200 | Not yet recruiting | Acute Leukemia|Mielodysplasic Syndrome|Myeloproliferative Neoplasm |
Institut Paoli-Calmettes |
November 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03601286 | Recruiting | Severe Combined Immunodeficiency X-Linked |
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust |
December 21 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03235973 | Unknown status | Leukemia Myeloid Acute|Leukemia Lymphoblastic Acute |
Institut Paoli-Calmettes |
April 28 2018 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
How can I reconstitute it for in vivo studies?
Answer:
This compound also can be dissolved in 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O at 5mg/ml as a clear solution. When preparing the solution, please dissolve it in DMSO clearly first. Then add PEG and Tween. After they mixed well, dilute with water. It in this formulation is not suitable for long-term storage. Please make the fresh solution each time before use.






































