research use only
Volasertib (BI6727) PLK1 inhibitor
Cat.No.S2235
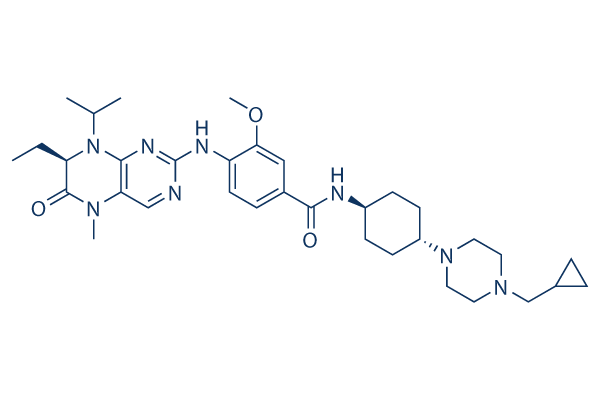
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 618.81
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CDK HSP PD-1/PD-L1 ROCK Wee1 DNA/RNA Synthesis Microtubule Associated Ras KRas Aurora Kinase |
|---|---|
| Other PLK Inhibitors | BI 2536 Rigosertib (ON-01910) GSK461364 Onvansertib (NMS-1286937, NMS-P937) CFI-400945 Ro3280 HMN-214 SBE 13 HCl Centrinone (LCR-263) MLN0905 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KASUMI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=170±51 nM | 25576074 | ||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=150±67 nM | 25576074 | ||
| MOLM-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=57±44 nM | 25576074 | ||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=16±6 nM | 25576074 | ||
| NOMO-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=145±7 nM | 25576074 | ||
| OCI-AML3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=90±51 nM | 25576074 | ||
| SKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=95±52 nM | 25576074 | ||
| THP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=56±39 nM | 25576074 | ||
| MCF7/LTED | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2.5-40 nM | 5 d | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 25480943 | |
| HCC1428/LTED | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2.5-40 nM | 5 d | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 25480943 | |
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-30 nM | 1-4 d | inhibits cell growth in both dose- and time-dependent manner | 23891096 | |
| FaDu | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-1000 nM | 1-4 d | inhibits cell growth in both dose- and time-dependent manner | 23891096 | |
| SF188 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50-150 nM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | 23887645 |
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50-150 nM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | 23887645 |
| DU145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10/50/250 nM | 24 h | IC50<10 nM | 23884428 | |
| LNCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10/50/250 nM | 24 h | IC50<10 nM | 23884428 | |
| PC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10/50/250 nM | 24 h | IC50∼600 nM | 23884428 | |
| RT4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=111.27 nM | 23792639 | ||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=1165.14 nM | 23792639 | ||
| T24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=204.91 nM | 23792639 | ||
| KMCH-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 200 nM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23703673 | |
| Mz-ChA-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 200 nM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23703673 | |
| HUCCT-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 200 nM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23703673 | |
| HCT 116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 23 nM | 19383823 | |||
| NCI-H460 | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 21 nM | 19383823 | |||
| BRO | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 11 nM | 19383823 | |||
| GRANTA-519 | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 15 nM | 19383823 | |||
| HL-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 32 nM | 19383823 | |||
| THP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 36 nM | 19383823 | |||
| Raji | Growth Inhibition Assay | EC50 = 37 nM | 19383823 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SKBR3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human SKBR3 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay | 29288948 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay | 29288948 | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-468 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay | 29288948 | ||
| BT474 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human BT474 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay | 29288948 | ||
| ZR-75-1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human ZR-75-1 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay | 29288948 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 35 mg/mL
(56.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 618.81 | Formula | C34H50N8O3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 755038-65-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | BI 6727 | Smiles | CCC1C(=O)N(C2=CN=C(N=C2N1C(C)C)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)C(=O)NC4CCC(CC4)N5CCN(CC5)CC6CC6)OC)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
A high volume of distribution, indicating good tissue penetration, and a long terminal half-life.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PLK1
(Cell-free assay) 0.87 nM
|
| In vitro |
Like BI2536, BI6727 is an ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor from the dihydropteridinone class of compounds. In addition to Plk1, this compound also potently inhibits two closely related kinases Plk2 and Plk3 with IC50 of 5 nM and 56 nM, respectively. This chemical at concentrations up to 10 μM displays no inhibitory activity against a panel of >50 other kinases. It inhibits the proliferation of multiple cell lines derived from various cancer tissues, including HCT116, NCI-H460, BRO, GRANTA-519, HL-60, THP-1, and Raji cells with EC50 of 23 nM, 21 nM, 11 nM, 15 nM, 32 nM, 36 nM, and 37 nM, respectively. This compound treatment (100 nM) in NCI-H460 cells induces an accumulation of mitotic cells with monopolar spindles and positive staining for histone H3 phosphoserine 10, confirming that cells are arrested early in the M phase, followed by induction of apoptosis. Low nanomolar concentrations of this inhibitor display potent inhibitory activity against neuroblastoma (NB) tumor-initiating cells (NB TIC) with EC50 of 21 nM, whereas only micromolar concentrations of it are cytotoxic for normal pediatric neural stem cells. It induces growth arrest of Daoy and ONS-76 medulloblastoma cells similar to BI 2536. |
| Kinase Assay |
In vitro kinase assays
|
|
Recombinant human Plk1 (residues 1-603) is expressed as NH2-terminal, GST-tagged fusion protein using a baculoviral expression system and purified by affinity chromatography using glutathione-agarose. Enzyme activity assays for Plk1 are done in the presence of serially diluted this compound using 20 ng of recombinant kinase and 10 μg casein from bovine milk as substrate. Kinase reactions are done in a final volume of 60 μL for 45 minutes at 30 °C [15 mM MgCl2, 25 mM MOPS (pH 7.0), 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO, 7.5 μM ATP, 0.3 μCi γ-32P-ATP]. Reactions are terminated by the addition of 125 μL of ice-cold 5% TCA. After transferring the precipitates to MultiScreen mixed ester cellulose filter plates, plates are washed with 1% TCA and quantified radiometrically. Dose-response curves are used for calculating IC50 value.
|
|
| In vivo |
Administration of BI6727 significantly inhibits the growth of multiple human carcinoma xenografts including HCT116, NCI-H460, and taxane-resistant CXB1 colon carcinoma, accompanied by an increase in the mitotic index as well as an increase in apoptosis. In in vivo studies, this compound shows better toxicity and pharmacokinetic profile compared to BI2536. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-PLK1 / PLK1 p-AKT / AKT / p-MAPK / MAPK PARP / c-myc p-c-Met / c-Met / p-FAK / FAK / p-Src / Src Fibronectin / β-integrin / p-vimentin / Vimentin / p-HH3 |
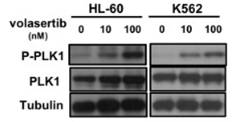
|
29108241 |
| Immunofluorescence | PLK1 / Wee1 |
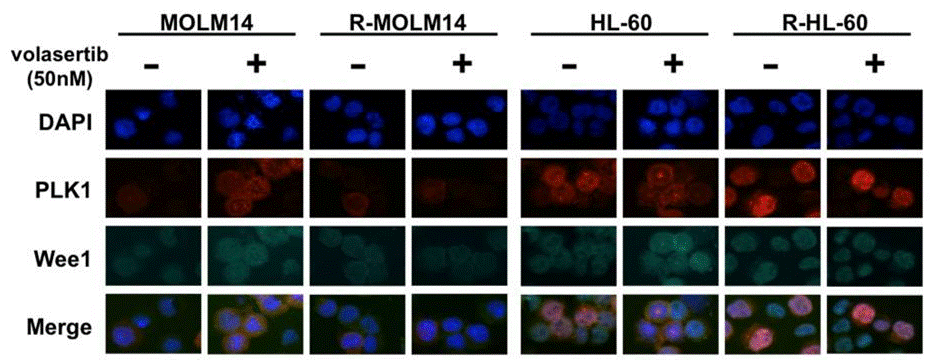
|
29108241 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
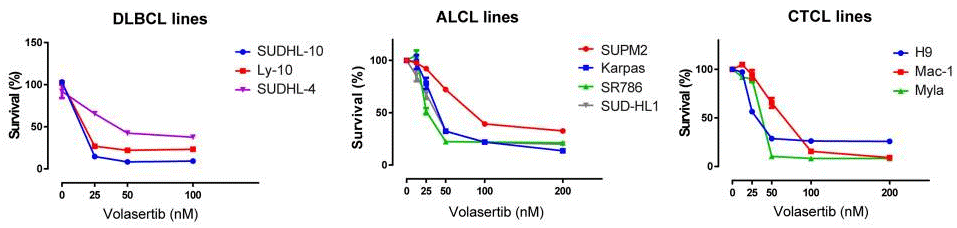
|
29383095 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02722135 | Withdrawn | Leukemia Myeloid Acute |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
November 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02721875 | Terminated | Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
April 28 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02201329 | Completed | Myelodysplastic Syndromes|Leukemia Myelomonocytic Chronic |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
August 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01971476 | Completed | Leukemia|Neoplasms |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
October 22 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01772563 | Completed | Neoplasms |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
February 4 2013 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01662505 | Completed | Leukemia Myeloid Acute |
Boehringer Ingelheim |
August 2012 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
I wonder how to reconstitute it for in vivo studies?
Answer:
It can be dissolved in 4% DMSO+Corn oil at 2mg/ml for i.p. injection in mice. For oral administration, this compound can be formulated in hydrochloric acid (0.1 N), and diluted with 0.9% NaCl, or suspended in 0.5% Natrosol 250 hydroxyethyl-cellulose as indicated in the publications. We also suggest the vehicle 30% PEG400/0.5% Tween80/5% propylene glycol for a suspension which we tested in house.






































