research use only
Aprepitant Neurokinin Receptor antagonist
Cat.No.S1189
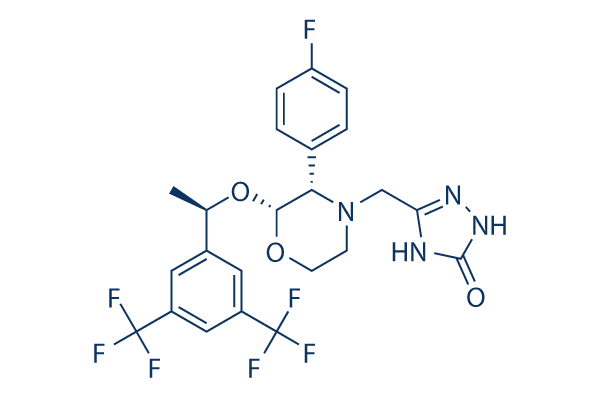
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 534.43
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor COX Calcium Channel Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) |
|---|---|
| Other Neurokinin Receptor Inhibitors | Tradipitant L-732138 Fezolinetant Substance P Asparagus Extract Maropitant citrate |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHO cells | Function assay | Displacement of [125I]SP from human NK1 receptor expressed in CHO cells, IC50=9e-05 μM | ||||
| HEK293 cell | Function assay | Displacement of [125I]-substance P from gerbil NK1 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes incubated for 30 mins by liquid scintillation counting method, IC50=9e-05 μM | ||||
| HEK293 cell | Function assay | Noncompetitive inhibition of wild type human NK1 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as decrease in SP1-induced [3H]IP accumulation after 20 mins | ||||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 107 mg/mL
(200.21 mM)
Ethanol : 15 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 534.43 | Formula | C23H21F7N4O3 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 170729-80-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | MK-0869, L-754030 | Smiles | CC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)OC2C(N(CCO2)CC3=NNC(=O)N3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
G-CSF
IL-6
IL-8
TNFα
Neurokinin-1 receptor
(Cell-free assay) 0.1 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Aprepitant antagonizes the effects of substance P by binding to NK-1 receptors primarily in the CNS, but also in the periphery. This compound, at concentrations of 0.1 nM displaces 50% of substance P from hNK1 receptors transfected in CHO or COS cells. In radioligand binding assays, it is 3000-fold selective for the human cloned NK1 receptor versus the human cloned NK3 receptor and >50,000-fold selective over the human cloned NK2 receptor. In a range of assays at other human cloned G–protein coupled receptors, this chemical retains >50,000-fold selectivity for the human cloned NK1 receptor. It is inactive in human monoamine oxidase A and B assays and at human serotonin 5–HT1A, 5–HT2A, 5–HT2c, 5–HT3, 5–HT5, 5–HT6, and 5–HT7 receptors (IC50>3 μM). In the PANLABS panel of radioligand binding screens using native animal tissues, this compound inhibits [3H]substance P binding to native NK1 receptors in rat submaxillary gland; there are no significant interactions of it with any other native animal G–protein coupled receptors or ion channels examined in the PANLABS screen. It is inactive in monoamine uptake site (NE, 5–HT, DA) counterscreens using human and animal tissues (IC50> 3 μM) |
| In vivo |
Aprepitant crosses the blood–brain barrier and occupied NK-1 receptors in the brain. This compound has been shown to inhibit both acute and delayed emesis induced by cytotoxic chemotherapeutic such as cisplatin by blocking substance P. It (3 mg/kg i.v. or p.o.) inhibits the emetic response to cisplatin (10 mg/kg i.v.). The anti-emetic protection afforded by this chemical (0.1 mg/kg i.v.) is enhanced by combined treatment with either dexamethasone (20 mg/kg i.v.) or the 5–HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron (0.1 mg/kg i.v.). In a model of acute and delayed emesis, ferrets are dosed with cisplatin (5 mg/kg i.p.) and the retching and vomiting response recorded for 72 h. Pretreatment with it (4–16 mg/kg p.o.) dose-dependently inhibits the emetic response to cisplatin. Once daily treatment with this compound (2 and 4 mg/kg p.o.) completely prevents retching and vomiting in all ferrets tested. Further when daily dosing began at 24 h after cisplatin injection, when the acute phase of emesis had already become established, it (4 mg/kg p.o. at 24 and 48 h after cisplatin) prevents retching and vomiting in three out of four ferrets. This chemical also plays a key part in transmission of pain impulses from the peripheral receptors to the CNS and is involved in various behavioural, neurochemical and cardiovascular responses to stress. |
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05755659 | Recruiting | Neoplasms |
Xijing Hospital |
July 15 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04075955 | Completed | Chemotherapy-induced Nausea and Vomiting |
CR-CSSS Champlain-Charles-Le Moyne |
April 29 2019 | Phase 3 |
| NCT03683225 | Active not recruiting | Idiopathic Parkinson Disease |
Chase Therapeutics Corporation |
April 1 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03889366 | Completed | Healthy |
Nuformix Technologies Limited |
March 20 2019 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































