research use only
Moclobemide (Ro 111163) MAO inhibitor
Cat.No.S3212
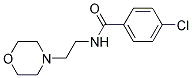
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 268.74
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Other MAO Inhibitors | Sennoside A Paeonol J147 Isatin Iproniazid Norharmane Hypericin Myristicin TB5 Minaprine dihydrochloride |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 53 mg/mL
(197.21 mM)
Ethanol : 10 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 268.74 | Formula | C13H17ClN2O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 71320-77-9 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | C1COCCN1CCNC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
MAO-A (5-HT)
6.1 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Moclobemide (Ro 111163), when orally administered 2 hours before decapitation, preferentially inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat brain with ED50 of 7.6 μmol/kg and 78 μmol/kg, respectively. This compound also inhibits MAO-A and PEA in rat liver with ED50 of 8.4 μmol/kg and 6.6 μmol/kg, respectively, under the same conditions. In vitro, it (0.1 mM), which inhibits brain MAO-A activity by over 80%, does not affect benzylamine oxidase (rat heart) and diamine oxidase (rat small intestine) activity. When included in the culture medium during anoxia or with glutamate at concentrations of 10 mM-100 mM, it significantly increases in a concentration-dependent manner the amount of surviving neurons compared to controls in neuronal-astroglial cultures from rat cerebral cortex.
|
| In vivo |
Moclobemide (Ro 111163) (10 mg/kg p.o.) induces a significant decrease of all monoamine metabolites measured in rat brain. When given via the drinking water (4.5 mg/kg/day), this compound produces significant decreases in adrenal weight of rats after 5 (-23%) and 7 weeks (-16%) of treatment. It upregulates hippocampal mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) levels in rats by 65%, 76% and 19% at 2 weeks, 5 weeks and 7 weeks of treatment, and upregulates Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) levels in this limbic brain structure by 10% at 5 weeks. Treatment with this agent (5 weeks, 4.5 mg/kg/day) significantly attenuates stress (30 min novel environment)-induced plasma ACTH (-35%) and corticosterone (-29%) levels. At a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg/day, it decreases immobility and increases climbing behavior following treatment for 3 days, but increases in both swimming and climbing behaviors are measured following treatment for 14 days. When administered at 15 mg/kg/day, it decreased immobility and increased swimming for 3 days, whereas treatment for 14 days significantly increases both active behavior (swimming and climbing). At 100 mg/kg/day, this compound combined with triethyltin blocks the development of brain edema and the increase in the cerebral chloride content induced by triethyltin in rats. It also reduces the increase in the cerebral sodium content and attenuates the neurological deficit in rats.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































