research use only
Mexiletine HCl Sodium Channel inhibitor
Cat.No.S4225
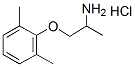
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 215.72
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor TRP Channel ATPase GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Sodium Channel Inhibitors | Camostat Mesilate Veratramine A-803467 cariporide Tolperisone HCl Bulleyaconi cine A Vinpocetine Tenapanor PF-06869206 Sparteine |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 43 mg/mL
(199.33 mM)
Water : 43 mg/mL Ethanol : 43 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 215.72 | Formula | C11H17NO.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 5370-01-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | KO1173,Mexitil | Smiles | CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)C)OCC(C)N.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Sodium channel
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Mexiletine is a local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic agent (Class Ib), structurally similar to lidocaine, but orally active. Mexiletine, inhibits the inward sodium current required for the initiation and conduction of impulses, thus reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. It achieves this reduced sodium current by inhibiting sodium channels. Mexiletine decreases the effective refractory period (ERP) in Purkinje fibers in the heart. The decrease in ERP is of lesser magnitude than the decrease in action potential duration (APD), which results in an increase in the ERP/APD ratio. It does not significantly affect resting membrane potential or sinus node automaticity, left ventricular function, systolic arterial blood pressure, atrioventricular (AV) conduction velocity, or QRS or QT intervals. |
| In vivo |
Mexiletine has fast onset and offset kinetics, meaning that they have little or no effect at slower heart rates, and more effects at faster heart rates. It shortens the action potential duration, reduces refractoriness, and decreases Vmax in partially depolarized cells with fast response action potentials. Mexiletine either does not change the action potential duration, or decreases the action potential duration. Mexiletine is well absorbed (bioavailability 90%) from the gastrointenstinal tract. |
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































