research use only
Losartan Potassium (DuP 753) AT1 Receptor Antagonist
Cat.No.S1359
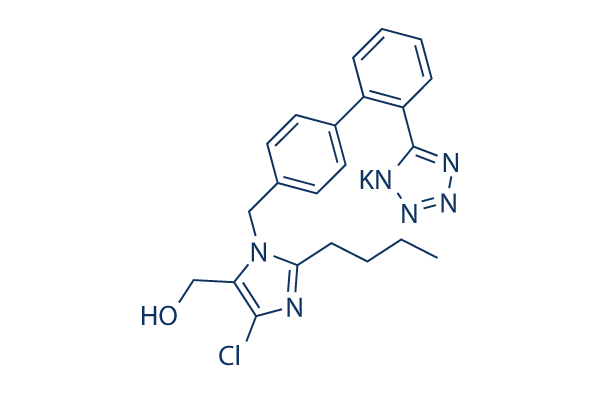
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 462.01
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CXCR Hedgehog/Smoothened PKA Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Other Angiotensin Receptor Inhibitors | PD123319 ML221 A-779 Fimasartan Olodanrigan (EMA401) Buloxibutid AVE 0991 |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 92 mg/mL
(199.12 mM)
Water : 92 mg/mL Ethanol : 92 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 462.01 | Formula | C22H23ClKN6O |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 124750-99-8 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | MK 954,DuP 753 | Smiles | CCCCC1=NC(=C(N1CC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3C4=NN=N[N-]4)CO)Cl.[K+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Losartan has a major active metabolite, EXP 3174.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
AT1 receptor
20 nM
|
| In vivo |
Losartan (180 mg/d) causes significant increases in plasma angiotensin II and angiotensin-(1-7) in monkeys with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Losartan (180 mg/d) reduces the extent of fatty streak in the aorta, the coronary arteries, and the carotid arteries by approximately 50% in monkeys with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Losartan reduces the susceptibility of LDL to in vitro oxidation, serum levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and circulating monocyte CD11b expression in monkeys with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Losartan (0.6 g/L in their drinking water) prevents elastic fiber fragmentation and blunted TGF-β signaling in the aortic media in pregnant Fbn1C1039G/+ mice, as evidenced by reduced nuclear accumulation of pSmad2. Losartan (0.6 g/L in their drinking water) shows a reduction in distal airspace caliber in pregnant Fbn1C1039G/+ mice. Losartan (0.6 g/L in their drinking water) improves disease manifestations in the lungs, an event that cannot plausibly relate to improved hemodynamics in pregnant Fbn1C1039G/+ mice. Losartan (5 mg/kg/d) leads to a significant decrease in the development of atherosclerotic lesions in the apo E deficient mice. Losartan (5 mg/kg/d) significantly reduces the susceptibility of the mice LDL to lipid oxidation following its incubation with CuSO4 in the apo E deficient mice. Losartan (10 mg/kg) administration increases blood angiotensin levels four fold to six fold, blood BK levels are unchanged in male Sprague Dawley rats. Losartan (10 mg/kg) increases plasma renin levels 100-fold, plasma angiotensinogen levels decreases to 24% of control and plasma aldosterone levels are unchanged in male Sprague Dawley rats.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00880386 | Withdrawn | Dyspnea|Lung Cancer|Pulmonary Complications|Radiation Fibrosis |
University of South Florida|National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
March 2009 | Not Applicable |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































