research use only
Histamine Phosphate Histamine Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S4117
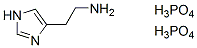
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 307.14
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor COX Calcium Channel Dopamine Receptor GABA Receptor TRP Channel Cholinesterase (ChE) GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Histamine Receptor Inhibitors | GSK2879552 Dihydrochloride JNJ-7777120 Ebastine Mianserin HCl Astemizole Ciproxifan Maleate Lafutidine Mizolastine Dimethindene maleate Rupatadine |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 61 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 307.14 | Formula | C5H9N.2H3O4P |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 51-74-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Histamine diphosphate | Smiles | C1=C(NC=N1)CCN.OP(=O)(O)O.OP(=O)(O)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Histamine phosphate is indicated as a diagnostic aid for evaluation of gastric acid secretory function.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Histamine H1 receptor
Histamine H2 receptor
|
| In vitro |
Histamine (10 μM) gives a larger inositol monophosphate accumulation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Histamine (10 μM) stimulates the level of radioactivity into the InsP3-containing fraction in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Histamine (100 μM) stimulates incorporation into the InsP3-containing eluate in a less extent than for angiotensin I1 and bradykinin. |
| In vivo |
Histamine phosphate (0.025 mg/kg) produces a mean increase in basilar blood flow of 145% of control in dogs. Histamine phosphate produces considerable increases in basilar blood flow as well as a decrease in femoral arterial blood pressure in dogs when injected intravenously and measured with an electromagnetic flow transducer. Histamine phosphate (4 μg/kg) causes lymph flow to increase from 6.0 to 27.0 (SEM) ml/h in unanesthetized sheep. Histamine phosphate (4 μg/kg) also causes increases in lung water, pulmonary vascular resistance, arterial PCO2, pH, and hematocrit, and decreases in cardiac output and arterial PO2 in unanesthetized sheep. Histamine phosphate (8.3 mg/kg/min) causes no significant change in pulmonary lymph flow (QL) or protein concentration (CL) in anesthetized open-chested dogs, however, both are increased after alloxan. Histamine phosphate (8.3 mg/kg/min) also causes no significant change in the pulmonary capillary membrane filtration coefficient (Kf) and the maximum capillary pressure (PCcritical) in anesthetized open-chested dogs. Histamine phosphate (50 mg/kg) produces a pronounced rise in acid secretion but the output of pepsin remained unchanged in the unanaesthetized intact rat. Histamine phosphate (50 mg/kg) produces maximal stimulation of gastric acid secretion and is free from toxic effects in the unanaesthetized intact rat. |
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06281366 | Recruiting | Pregnancy Complications |
Hospital Universitari Vall d''Hebron Research Institute|DR Healthcare |
February 16 2024 | -- |
| NCT05216133 | Enrolling by invitation | Airway Disease|Barrett Esophagus|Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
NYU Langone Health|National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH/CDC) |
March 22 2023 | -- |
| NCT05701826 | Completed | Skeletal Muscle Relaxation |
Fujian Shengdi Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. |
February 15 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05676346 | Completed | Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms|Histamine Intolerance |
Complexo Hospitalario Universitario de A Coruña |
October 11 2022 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































