research use only
Zonisamide Sodium Channel inhibitor
Cat.No.S1445
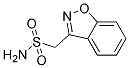
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 212.23
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor TRP Channel ATPase GluR |
|---|---|
| Other Sodium Channel Inhibitors | Camostat Mesilate A-803467 cariporide Veratramine Tolperisone HCl Bulleyaconi cine A Vinpocetine Tenapanor PF-06869206 Sparteine |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 42 mg/mL
(197.89 mM)
Ethanol : 11 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 212.23 | Formula | C8H8N2O3S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 68291-97-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Zonegran,CI-912,AD 810 | Smiles | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=NO2)CS(=O)(=O)N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Sodium channel
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
This compound inhibits monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) activity in vitro with an IC(50) of 25 μM. |
| In vivo |
Zonisamide modifies dopamine (DA) activity, provides protection in ischemia mice models and influences antioxidant systems. This compound attenuates the reduction in striatal contents of DA, its metabolite DOPAC and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). It (10 and 30 mg/kg) produces antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects in a dose-dependent manner, these effects are manifested by elevation of the withdrawal threshold in response to a thermal (plantar test) or mechanical (von Frey) stimulus, respectively.. This chemical produces antinociceptive effects against acute thermal and mechanical nociception in non-ligated mice. It reduces the cortical infarction volume to 6% from 68% in vehicle-treated controls and the striatal volume to 8% from 78% in rats. This compound also reduces neuronal necrosis in 5 hippocampal regions (the dentate gyrus, CA4, CA3, CA1, and the subiculum) in rats. It causes increase in the quantity of EAAC-1 protein in hippocampus and cortex and down regulation of the GABA transporter GAT-1 in rats with hippocampal seizures. This chemical inhibits both the 50 mM KCl-evoked hippocampal glutamate release (AUC for 60 min) from 9.2 mM to 5.8 mM in urethane-anaesthetized rats, as well as the stimulatory effects of Ca2+ on KCl-evoked hippocampal glutamate release. |
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04774250 | Terminated | Hearing Loss Noise-Induced |
Washington University School of Medicine|United States Department of Defense|University of Texas|Gateway Biotechnology Inc. |
November 10 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01830868 | Completed | Partial Onset Seizures |
Eisai Inc. |
March 2012 | -- |
| NCT01283256 | Completed | Partial Generalized and Combined Seizures |
Eisai Inc. |
January 2011 | -- |
| NCT01765608 | Completed | Sleep Apnea|Obstructive Sleep Apnea|Obesity |
Göteborg University|Eisai Inc. |
March 2010 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00203450 | Completed | Obesity |
Tuscaloosa Research & Education Advancement Corporation|Eisai Inc. |
May 2003 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































