research use only
Fostamatinib (R788) Syk inhibitor
Cat.No.S2625
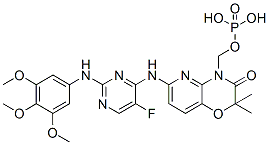
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 580.46
Quality Control
| Related Targets | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Other Syk Inhibitors | R406 R406 (free base) PRT062607 (P505-15) HCl Entospletinib (GS-9973) Piceatannol BAY 61-3606 dihydrochloride PRT-060318 2HCl TAK-659 Hydrochloride Lanraplenib (GS-SYK) RO9021 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human Ramos cells | Function assay | Inhibition of SYK in human Ramos cells, IC50=0.267 μM | ||||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 116 mg/mL
(199.84 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 580.46 | Formula | C23H26FN6O9P |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 901119-35-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)(O)O)C | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Converted into its active metabolite R406 in vivo.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Syk
41 nM
Adenosine A3 receptor
81 nM
Adenosine transporter
1.84 μM
Monoamine transporter
2.74 μM
|
| In vitro |
Fostamatinib (R788) is a prodrug of the spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor R406. It is a competitive inhibitor for ATP binding with a Ki of 30 nM. This compound dose-dependently inhibits anti-IgE-mediated CHMC degranulation with an EC50 of 56 nM. It also inhibits the anti-IgE-induced production and release of LTC4 and cytokines and chemokines, including TNFα, IL-8, and GM-CSF. Inhibition of Syk by R788 results in inhibition of all phosphorylation events downstream of Syk signaling. Next to FcϵRI signaling in CHMC, it most potently inhibits the signaling of IL-4 and IL-2 receptors. It specifically inhibits FcγR signaling in human mast cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. R788 can inhibit local inflammatory injury mediated by immune complexes. It induces apoptosis of the majority of examined DLBCL cell lines. In R788-sensitive DLBCL cell lines, this compound specifically inhibits both tonic- and ligand-induced BCR signaling (autophosphorylation of SYK525/526 and SYK-dependent phosphorylation of the B-cell linker protein [BLNK]).
|
| Kinase Assay |
Fluorescence polarization kinase assay and Ki determination
|
|
The fluorescence polarization reactions are performed. For Ki determination, duplicate 200-μL reactions are set up at eight different ATP concentrations from 200 μM (2-fold serial dilutions) in the presence of either DMSO or Fostamatinib (R788) at 125, 62.5, 31.25, 15.5, or 7.8 nM. At different time points, 20 μL of each reaction is removed and quenched to stop the reaction. For each concentration of this compound, the rate of reaction at each concentration of ATP is determined and plotted against the ATP concentration to determine the apparent Km and Vmax (maximal rate). Finally the apparent Km (or apparent Ki/Vmax) is plotted against the inhibitor concentration to determine the Ki.
|
|
| In vivo |
Oral administration of Fostamatinib (R788) to mice reduces immune complex-mediated inflammation in a reverse-passive Arthus reaction and two antibody-induced arthritis models. In another study, it effectively inhibits BCR signaling in vivo, resulting in reduced proliferation and survival of the malignant B cells and significantly prolongs survival of the treated animals. This compound also demonstrates a significant reduction in major inflammatory mediators such as TNFalpha, IL-1, IL-6 and IL-18, leading to reduced inflammation and bone degradation in models of rheumatoid arthritis.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Sickle Cell Disease|Hb-SS Disease|Hemoglobin S|Disease Sickle Cell Anemia|Sickle Cell Disorders|Hemoglobin Beta Thalassemia Disease |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Immune Mediated Anemia|Immune Mediated Thrombocytopenia|Chronic GVHD |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06071520 | Completed | Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Fundación Pública Andaluza para la gestión de la Investigación en Sevilla |
March 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05613296 | Not yet recruiting | ITP - Immune Thrombocytopenia|Chronic ITP|Refractory ITP |
Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell''Adulto |
February 2023 | -- |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Myelofibrosis|Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine|Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 3 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04904276 | Terminated | ITP|Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 18 2021 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
What’s the difference between S2625 and S2206?
Answer:
It is more stable than S2625. Its water solubility is better than S2625. However, its absorption is harder than S2625, so you need to test the suitable dosage if you use the product in animal assays. The potency of it and S2625 is similar.






































