- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Diphenhydramine HCl Histamine Receptor antagonist
Cat.No.S1866
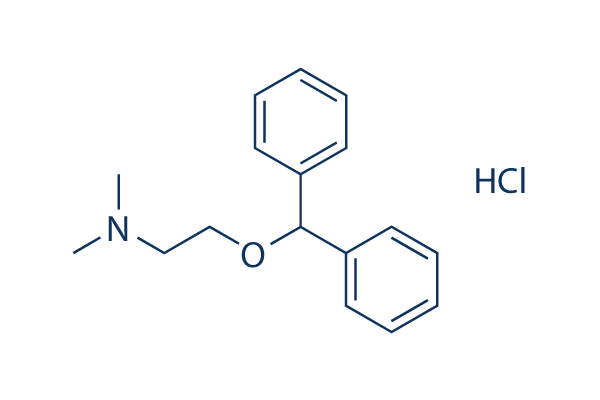
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 291.82
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.59%
99.59
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 58 mg/mL
(198.75 mM)
Water : 58 mg/mL Ethanol : 58 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 291.82 | Formula | C17H21NO.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 147-24-0 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | N/A | Smiles | CN(C)CCOC(C1=CC=CC=C1)C2=CC=CC=C2.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Histamine H1 receptor
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Diphenhydramine blocks tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX-S) and tetrodotoxin-resistant (TTX-R) sodium currents with K(d) values of 48 mM and 86 mM, respectively, at a holding potential of -80 mV. Diphenhydramine shifts the conductance-voltage curve for TTX-S sodium currents in the depolarizing direction but has little effect on that for TTX-R sodium currents. Diphenhydramine causes a shift of the steady-state inactivation curve for both types of sodium currents in the hyperpolarizing direction. Diphenhydramine produces a profound use-dependent block when the cells are repeatedly stimulated with high-frequency depolarizing pulses. Diphenhydramine induces apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner in both CCRF-CEM and Jurkat cell lines, whereas Cimetidine fails to induce significant effects at similar concentrations. Diphenhydramine-induced apoptosis is evaluated in terms of morphology, flow cytometry, and the release of cytochrome c to the cytosol. Diphenhydramine inhibits cell proliferation without inducing apoptosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Diphenhydramine (500 nM) significantly reduces the baseline firing of the periaqueductal gray neurons without a significant effect on the frequency of postsynaptic potentials. Diphenhydramine at high concentration inhibits periaqueductal gray neurons, but at low concentrations it has no effect on the baseline-firing rate and it blocks the response to neurotensin and tomedial preoptic nucleus stimulation.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05759481 | Recruiting | Post-operative Nausea and Vomiting |
Milton S. Hershey Medical Center |
February 1 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05674721 | Completed | Pain |
HALEON |
January 5 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05219604 | Terminated | Central Nervous System Effects of Diphenhydramine|Pharmacokinetics of Diphenhydramine |
Dent Neuroscience Research Center |
March 15 2022 | Phase 4 |
| NCT05244460 | Recruiting | Cannabis Hyperemesis Syndrome |
Mercy Health Ohio|Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine |
December 2 2021 | Phase 3 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































