research use only
D-Cycloserine Selection Antibiotics for Transfected Cell inhibitor
Cat.No.S1998
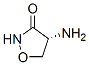
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 102.09
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Integrase Bacterial Antibiotics Anti-infection Fungal Antiviral COVID-19 Parasite Reverse Transcriptase HIV |
|---|---|
| Other Selection Antibiotics for Transfected Cell Inhibitors | Blasticidin S Hydrochloride Ribostamycin Sulfate |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 20 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 102.09 | Formula | C3H6N2O2 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 68-41-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | RO-1-9213 | Smiles | C1C(C(=O)NO1)N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| In vivo |
D-cycloserine (DCS) facilitates extinction of conditioned freezing to the light CS when no drug pre-exposure has occurred, but pre-exposure to DCS just prior to conditioning disrupted the facilitation of extinction effect in mice. D-cycloserine (DCS) which has a high affinity for the glycine modulatory site in the NMDA receptor complex modulated memory processing in a dose-dependent manner. DCS also facilitates retention in 'senescence-accelerated mice' in which impairment of learning andmemory increases with age. D-cycloserine (DCS) exhibits facilitated extinction of fear but are able to reacquire fear of that conditioned stimulus (CS) in a similar manner as saline-treated control rats. DCS-treated rats exhibits generalized extinction (i.e., they are less fearful of a non-extinguished CS) in comparison to controls. D-cycloserine (DCS), an antimycobacterial agent known to cross the blood-brain barrier, binds with high affinity to this glycine modulatory site, functions as a positive modulator, and facilitates performance of learningtasks in rats. DCS appears to be a potent cognitive enhancer at doses lower than those required for antibacterial activity. D-cycloserine injections (3.25, 15, or 30 mg/kg) before 30 non-reinforced light exposures dose-dependently enhances extinction but does not influence fear-potentiated startle in rats that does not receive extinction training.
|
References |
|
|---|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05731323 | Completed | Major Depressive Disorder |
University of Calgary |
October 12 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01399866 | Completed | Smoking Cessation |
Massachusetts General Hospital |
May 2011 | Phase 3 |
| NCT00964041 | Withdrawn | Schizophrenia |
Massachusetts General Hospital|National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) |
July 2009 | Phase 4 |
| NCT01062932 | Completed | Nicotine Addiction |
Baylor College of Medicine|National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) |
May 2009 | Phase 1 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































