- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Moexipril HCl RAAS inhibitor
Cat.No.S2079
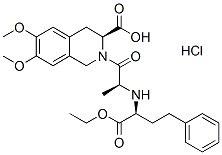
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 535.03
Jump to
Quality Control
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 20 mg/mL
(37.38 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 535.03 | Formula | C27H34N2O7.HCl |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 82586-52-5 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | RS-10085 | Smiles | CCOC(=O)C(CCC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(C)C(=O)N2CC3=CC(=C(C=C3CC2C(=O)O)OC)OC.Cl | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ACE
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Moexipril dose-dependently reduces the percentage of damaged neurons, as well as mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation induced by glutamate, staurosporine or Fe2+/3+. Moexipril and enalapril attenuates staurosporine-induced neuronal apoptosis as determined by nuclear staining with Hoechst 33258.
|
| In vivo |
Moexipril (0.3 mg/kg) significantly reduces brain damage after focal ischemia as compared to control mice. Moexipril (0.01 mg/kg) is able to reduce the infarct volume in the rat model after focal cerebral ischemia. Moexipril reduces blood pressure after the first week of treatment but it has no apparent effect on either the proximal tibial metaphysis or the tibial shaft in ovariectomized (OVX) spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Moexipril combined with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) exhibits a much more potent hypotensive effect and has the same effect on bone mass and dynamic end-points as HCTZ alone. Moexiprilat exhibits a higher inhibitory potency than enalaprilat against both plasma ACE and purified ACE from rabbit lung. Moexipril (0.1-30 mg/kg/day) lowers blood pressure and differentially inhibits ACE activity in plasma, lung, aorta, heart and kidney in a dose-dependent fashion. Moexipril (10 mg/kg/day) leads to comparable decreases in blood pressure, inhibition of plasma ACE and reduction of plasma angiotensinogen and to a similar attenuation of the pressor responses to angiotensin I and potentiation of the depressor responses to bradykinin.
|
References |
|
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































