research use only
Lixisenatide Glucagon Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S8517
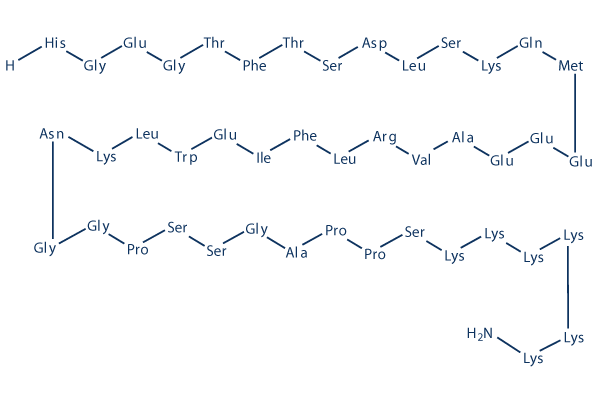
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 4858.49
Quality Control
| Related Targets | CXCR Hedgehog/Smoothened PKA Adrenergic Receptor AChR 5-HT Receptor Histamine Receptor Dopamine Receptor Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Other Glucagon Receptor Inhibitors | Orforglipron (LY3502970) Relacorilant (CORT125134) Avexitide Exendin-4 GLP-1 (7-37) V-0219 Adomeglivant DMB Shanzhiside methyl ester Retatrutide (LY3437943) |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
Water : 100 mg/mL |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 4858.49 | Formula | C215H347N61O65S |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 320367-13-3 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Lyxumia, Adlyxin, ZP10A peptide, AVE0010 | Smiles | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CC(=O)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NCC(=O)N3CCCC3C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(C)C(=O)N4CCCC4C(=O)N5CCCC5C(=O)NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC6=CC=CC=C6)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC7=CC=CC=C7)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC8=CNC=N8)N | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
GLP-1R
(Cell-free assay) 1.4 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Lixisenatide protects Ins-1 cells (a rat-derived β-cell line) from both lipid- and cytokine-induced apoptosis. More importantly, this compound also prevents lipotoxicity-induced insulin depletion in human islets and preserves insulin production, storage and pancreatic β-cell function in vitro. Binding studies in CHO-K1 cells overexpressing the human GLP-1 receptor show that it is a very potent and selective GLP-1 receptor agonist--the binding affinity of this chemical (Ki = 1.33 ± 0.22 nM) is ∼ 4-times greater than that of human GLP-1 (Ki = 5.09 ± 1.19 nM). In more than 80 different binding assays, it does not exhibit any relevant interaction with other potential drug targets, confirming its high selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor.
|
| In vivo |
The half-life of lixisenatide is 2-4 hours, and it is classed as a short-acting GLP-1-receptor agonist, compared with the long-acting GLP-1-based peptides, liraglutide and albiglutide. This compound can significantly improve glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In healthy normoglycemic dogs, single subcutaneous injections of this agent produces dose-dependent reductions in plasma glucose after an oral glucose challenge and significantly reduces postprandial glucose excursions by 67% compared with placebo without increasing insulin concentrations. The effect of this peptide on postprandial blood glucose excursions in dogs is, at least in part, related to inhibition of gastric emptying and delayed intestinal glucose absorption. Dose-dependent reductions in plasma glucose after an oral glucose challenge have also been demonstrated in both the db/db mouse and ZDF rat. Importantly, this activity is glucose-dependent with no effect at physiological glucose concentrations. In db/db mice, chronic administration of this compound preventes the progressive deterioration in glucose tolerance observed in control animals and is associated with significant dose-dependent reductions in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c). In ZDF rats, a continuous subcutaneous infusion of this agent 50 μg/kg/day for 12 weeks significantly decreases basal blood glucose and improves oral glucose tolerance compared with control animals. It has no hypoglycemic effect and does not change HbA1c in normoglycemic rats. This chemical can maintain beta cell mass and function through stimulation of islet cell proliferation and neogenesis, and inhibition of islet cell apoptosis. It preserves pancreatic responsiveness in diabetic animals.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02274740 | Terminated | Type II Diabetes Mellitus |
Sanofi |
April 2015 | Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































