research use only
Abacavir Reverse Transcriptase inhibitor
Cat.No.S5215
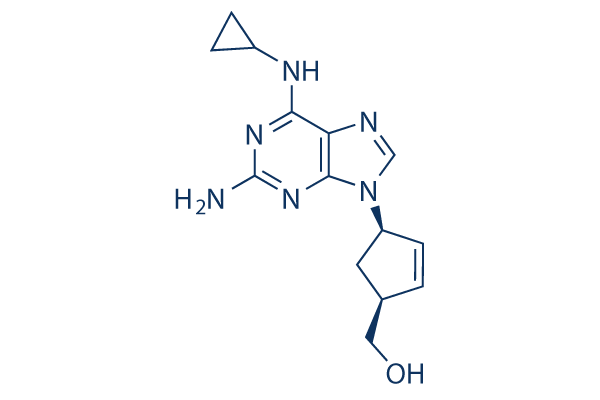
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 286.33
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Integrase Bacterial Antibiotics Anti-infection Fungal Antiviral COVID-19 Parasite HIV HCV Protease |
|---|---|
| Other Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors | Dapivirine (TMC120) Salicylanilide Fangchinoline Bifendate 3'-Fluoro-3'-deoxythymidine (Alovudine) Ulonivirine Lersivirine (UK-453061) 4-Chloro-2-(trifluoroacetyl)aniline hydrochloride |
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 57 mg/mL
(199.07 mM)
Ethanol : 57 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 286.33 | Formula | C14H18N6O |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 136470-78-5 | -- | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | 1592U89 | Smiles | C1CC1NC2=C3C(=NC(=N2)N)N(C=N3)C4CC(C=C4)CO | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Reverse transcriptase
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Abacavir (ABC) exhibits potent in vitro antiviral activity against wild-type HIV-1 (IC50 4.0 μM, MT-4 cells). This compound induces chromosomal DSBs and thereby kills ATL cells but not non-HTLV-1-infected cells. Once it is incorporated into the cells, it is phosphorylated in a unique stepwise anabolism to be converted to the triphosphated guanine analog carbovir (CBV) and then incorporated into host chromosomal DNA by replicative DNA polymerases, leading to premature termination of DNA replication, collapse of the replication fork, and DSB formation. This chemical induces S/G2-phase arrest and apoptosis in ED-40515(−) cells, but not in Jurkat cells.
|
| In vivo |
Abacavir efficiently inhibits the growth of ATL cell xenografts in NOD/SCID mice. In adults, this compound is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak concentrations occurring 0.63-1 hour after dosing. The absolute bioavailability of abacavir is approximately 83%. Its pharmacokinetics are linear and doseproportional over the range of 300-1200 mg/day. The apparent volume of distribution after intravenous administration is approximately 0.86 ± 0.15 L/kg, suggesting that it is distributed to extravascular spaces. Binding to plasma proteins is about 50% and is independent of the plasma abacavir concentration. This chemical is extensively metabolized by the liver; less than 2% is excreted as unchanged drug in the urine. It is primarily metabolized via two pathways, uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase and alcohol dehydrogenase, resulting in the inactive glucuronide metabolite and the inactive carboxylate metabolite. The terminal elimination half-life is approximately 1.5 hours. The antiviral effect is due to its intracellular anabolite, carbovirtriphosphate (CBV-TP). This compound is not significantly metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, nor does it inhibit these enzymes.
|
References |
|
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04133012 | Completed | HIV-1 Infection |
ANRS Emerging Infectious Diseases|ViiV Healthcare |
February 10 2020 | Not Applicable |
| NCT02708342 | Completed | HIV |
IRCCS San Raffaele|Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC |
April 2016 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































