research use only
Hydrocortisone (Cortisol) Glucocorticoid Receptor agonist
Cat.No.S1696
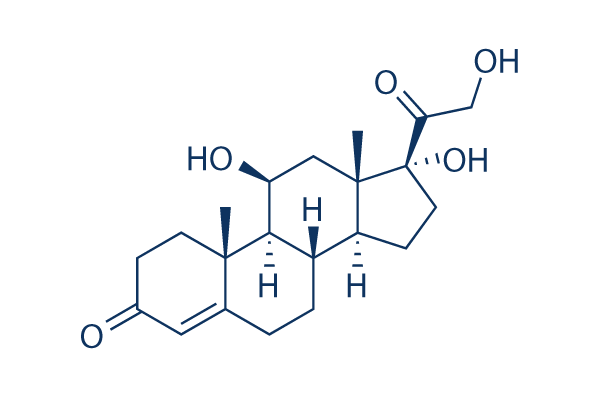
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 362.46
Quality Control
| Related Targets | Adrenergic Receptor Estrogen/progestogen Receptor GPR Androgen Receptor ACE RAAS Progesterone Receptor Opioid Receptor PGES THR |
|---|---|
| Other Glucocorticoid Receptor Inhibitors | Corticosterone AL082D06 (20S)-Protopanaxatriol Cortodoxone |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse RAW264.7 cells | Function assay | 24 h | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IFN-gamma induced NO production after 24 hrs by Griess reaction, IC50=0.061 μM | 21361338 | ||
| mouse L929 cells | Growth inhibition assay | 6 days | Growth inhibition of mouse L929 cells after 6 days | 926113 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced NO production by MTT assay, IC50 = 40.64 μM. | 20879743 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 24 hrs | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production in mouse RAW264.7 cells after 24 hrs by Griess reaction based spectrophotometry, IC50 = 40.64 μM. | 21807513 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 24 hrs | Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production in mouse RAW264.7 cells after 24 hrs by Griess reaction, IC50 = 40.64 μM. | 23067550 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production after 24 hrs by Griess assay, IC50 = 43.8 μM. | 23755850 | ||
| L929 | Function assay | 20 hrs | Displacement of 1 x 10'-8 M of [1,2,3-3H]-triamcinolone acetonide from glucocorticoid receptor in soluble fraction of mouse L929 cells after 20 hrs, Kd = 0.043 μM. | 926113 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Inhibition of MR-mediated transactivation of galactosidase reporter gene in HEK293 cells expressing 11betaHSD1 | 16759088 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 50 ug/ml | 4 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IL-10 production at 0.5 to 50 ug/ml pretreated for 4 hrs followed by challenge with 1 ug/mL LPS for 48 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 21384845 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 50 ug/ml | 4 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IL-6 production at 0.5 to 50 ug/ml pretreated for 4 hrs followed by challenge with 1 ug/mL LPS for 48 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 21384845 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 50 ug/ml | 4 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IL1-beta production at 0.5 to 50 ug/ml pretreated for 4 hrs followed by challenge with 1 ug/mL LPS for 48 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 21384845 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 50 ug/ml | 4 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of TNFalpha production at 0.5 to 50 ug/ml pretreated for 4 hrs followed by challenge with 1 ug/mL LPS for 48 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 21384845 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 50 ug/ml | 4 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of nitric oxide production at 0.5 to 50 ug/ml pretreated for 4 hrs followed by challenge with 1 ug/mL LPS for 48 hrs by Griess reaction method relative to control | 21384845 | |
| neural precursor cells | Function assay | Inhibition of neurosphere proliferation of mouse neural precursor cells by MTT assay | 17417631 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 10 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced increase in TNF-alpha level at 10 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 22 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 25515561 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 10 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced increase in IL-6 level at 10 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 22 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 25515561 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 10 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced increase in IL-1beta level at 10 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 22 hrs by ELISA relative to control | 25515561 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 10 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production at 10 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 22 hrs relative to vehicle-treated control | 25515561 | |
| B16F10 | Apoptosis assay | 20 uM | 36 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in mouse B16F10 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase 3 level at 20 uM after 36 hrs by western blot analysis | 26695732 | |
| B16F10 | Apoptosis assay | 20 uM | 36 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in mouse B16F10 cells assessed as increase in p53 expression at 20 uM after 36 hrs by propidium iodide staining based FACS analysis | 26695732 | |
| B16F10 | Apoptosis assay | 20 uM | 36 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in mouse B16F10 cells assessed as increased Bax expression at 20 uM after 36 hrs by western blot analysis | 26695732 | |
| B16F10 | Antitumor activity assay | 6.11 mg/kg | Antitumor activity against mouse B16F10 cells xenografted in C57BL/J mouse assessed as inhibition of tumor growth at 6.11 mg/kg, ip | 26695732 | ||
| B16F10 | Apoptosis assay | 20 uM | 36 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in mouse B16F10 cells assessed as increase in cytochrome C level at 20 uM after 36 hrs by western blot analysis | 26695732 | |
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 72 mg/mL
(198.64 mM)
Ethanol : 15 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 362.46 | Formula | C21H30O5 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 50-23-7 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | NSC 10483 | Smiles | CC12CCC(=O)C=C1CCC3C2C(CC4(C3CCC4(C(=O)CO)O)C)O | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Glucocorticoid receptor
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Hydrocortisone prevents endothelial barrier breakdown in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli (TNFalpha administration) in the human brain microvascular endothelial cell line hCMEC/D3, which could be demonstrated to be partly based on maintenance of occludin levels. This compound-treated dendritic cells (DCs) show a decreased expression of MHC II molecules, the costimulatory molecule CD86, and the DC-specific marker CD83, as well as a strongly reduced IL-12 secretion. It inhibits production of IFN-gamma but induces an increased release of IL-4 and no change in IL-5. This chemical reduces T-cell proliferation in dendritic cells. It prevents TNF-alpha induced severe degradation of the glycocalyx, increased coronary resistance, heightened vascular leak and permeability to hydroxyethyl starch and caused mast-cell degranulation in isolated guinea pig hearts. This compound reduces postischemic oxidative stress, perfusion pressure, and transudate formation in isolated guinea pig hearts. It inhibits postischemic shedding of syndecan-1, heparan sulfate, and hyaluronan, as well as release of histamine from resident mast cells. It increases the levels of IL-4-induced germ line C epsilon transcripts by twofold and delivers the signal required for transcription of mature C epsilon mRNA. This chemical induces S mu-S epsilon deletional switch recombination in IL-4-treated B cells, and support a model of sequential isotype switching from IgM to IgE via IgG4. |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
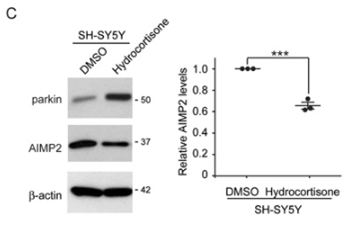
| Western blot | parkin / AIMP2 CREB |
|
28366931 |
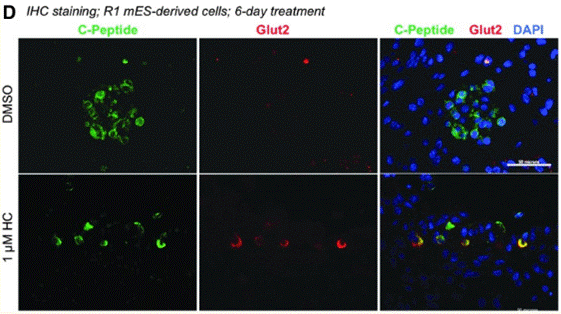
| Immunofluorescence | Glut2 |
|
29717618 |
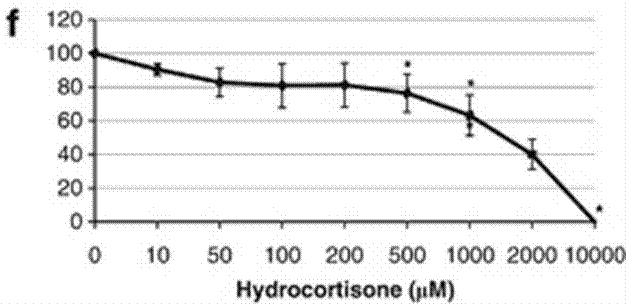
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
22829975 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05741762 | Active not recruiting | Critical Illness|Adrenal Insufficiency|Septic Shock |
Dr Adnan Agha|United Arab Emirates University |
January 31 2023 | -- |
| NCT05607901 | Recruiting | Dermatologic Disease |
Tanta University |
October 28 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05324618 | Completed | Atopic|Dermatitis |
Ain Shams University|National Hepatology & Tropical Medicine Research Institute |
May 15 2022 | Phase 4 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































