- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Magnetic Separator
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
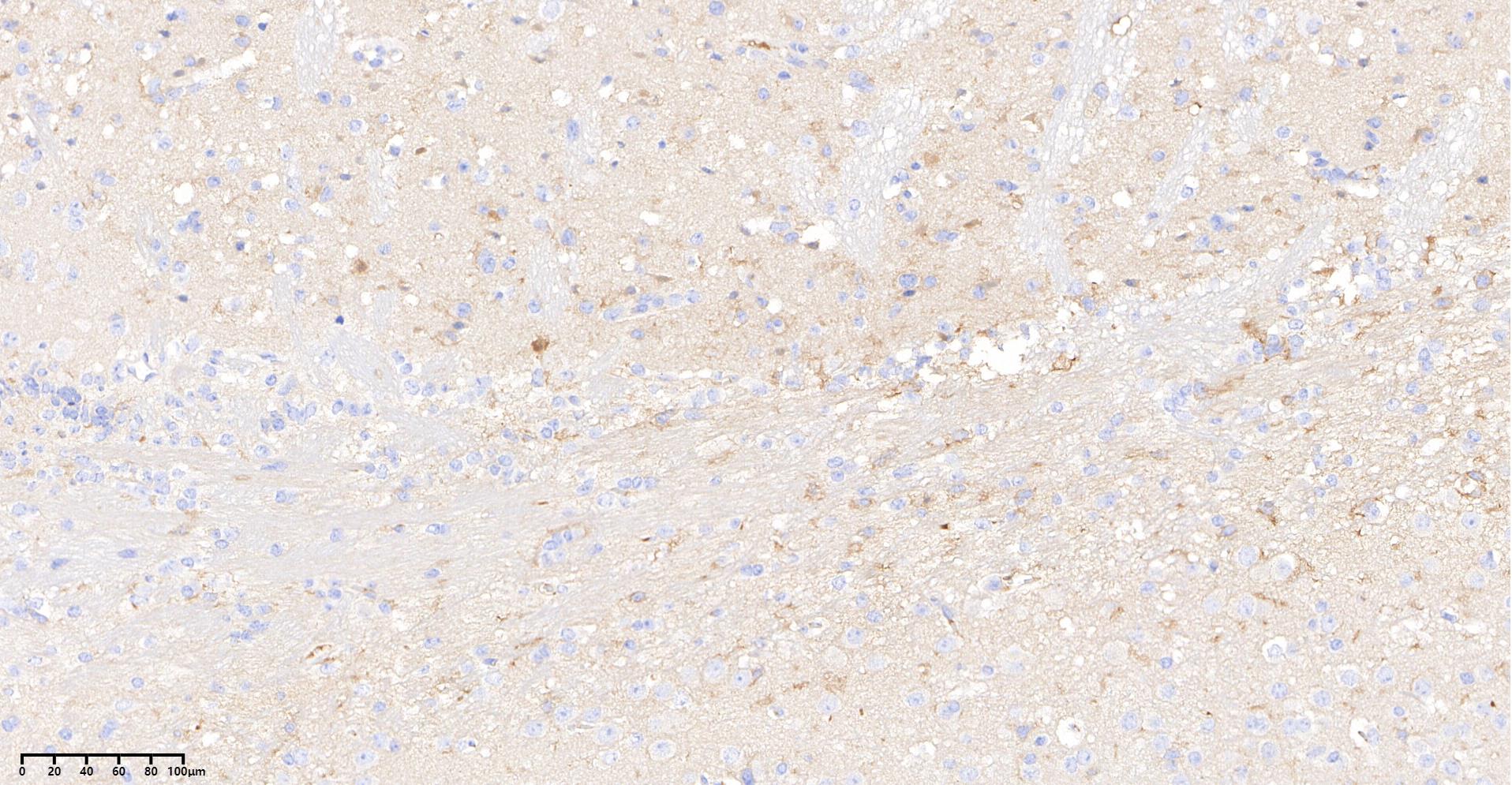
Anti-GLP-1 Mouse Antibody [B23D23]
Catalog No.: F1621
Application:
Reactivity:
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| IHC, sELISA |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Mouse, Human |
| Source |
|---|
| Mouse |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Positive Control | Human pancreas tissue; Diabetic mice pancreas tissue |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| IHC |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Deparaffinization/Rehydration
1. Deparaffinize/hydrate sections:
2. Incubate sections in three washes of xylene for 5 min each.
3. Incubate sections in two washes of 100% ethanol for 10 min each.
4. Incubate sections in two washes of 95% ethanol for 10 min each.
5. Wash sections two times in dH2O for 5 min each.
6.Antigen retrieval: For Citrate: Heat slides in a microwave submersed in 1X citrate unmasking solution until boiling is initiated; continue with 10 min at a sub-boiling temperature (95°-98°C). Cool slides on bench top for 30 min.
Staining
1. Wash sections in dH2O three times for 5 min each.
2. Incubate sections in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 min.
3. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
4. Wash sections in wash buffer for 5 min.
5. Block each section with 100–400 µl of blocking solution for 1 hr at room temperature.
6. Remove blocking solution and add 100–400 µl primary antibody diluent in to each section. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
7. Remove antibody solution and wash sections with wash buffer three times for 5 min each.
8. Cover section with 1–3 drops HRPas needed. Incubate in a humidified chamber for 30 min at room temperature.
9. Wash sections three times with wash buffer for 5 min each.
10. Add DAB Chromogen Concentrate to DAB Diluent and mix well before use.
11. Apply 100–400 µl DAB to each section and monitor closely. 1–10 min generally provides an acceptable staining intensity.
12. Immerse slides in dH2O.
13. If desired, counterstain sections with hematoxylin.
14. Wash sections in dH2O two times for 5 min each.
15. Dehydrate sections: Incubate sections in 95% ethanol two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in 100% ethanol, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each; Repeat in xylene, incubating sections two times for 10 sec each.
16. Mount sections with coverslips and mounting medium.
|
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
| GLP-1 Mouse mAb recognizes endogenous levels of total GLP-1 protein. |
| Subcellular Location |
|---|
| Secreted |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P01275 |
| Clone |
|---|
| B23D23 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Pro-glucagon, GCG |
| Background |
|---|
| Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30-amino-acid incretin hormone primarily secreted by intestinal L-cells in response to nutrient ingestion, produced through the enzymatic cleavage of the proglucagon precursor. GLP-1 contains a conserved N-terminal sequence critical for receptor activation, including key residues such as His7 that are essential for binding and signaling, and adopts α-helical conformations stabilizing its interaction with the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), a G-protein-coupled receptor expressed in pancreatic β-cells, brain, gastrointestinal tract, and other tissues. Upon binding GLP-1R, the receptor activates G-proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase, increasing intracellular cAMP, which triggers downstream effectors like protein kinase A (PKA) and Epac2, enhancing glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release mainly via somatostatin secretion from δ-cells, and slowing gastric emptying to control postprandial glucose levels. GLP-1 also reduces appetite and promotes satiety via central nervous system pathways. GLP-1R activation exerts neuroprotective effects by modulating inflammation and promoting neuronal survival through cAMP/PKA and ERK signaling pathways. Additionally, GLP-1 influences mitochondrial function and energy metabolism in muscle and neuronal cells and favors bone formation by modulating the osteoprotegerin (OPG)/RANKL ratio to support skeletal health. Endogenously, GLP-1 is rapidly degraded by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), limiting its half-life to about 1–2 minutes, prompting the development of GLP-1 receptor agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors as therapeutics for type 2 diabetes and obesity. |
| References |
|---|
|
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field