- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Magnetic Separator
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
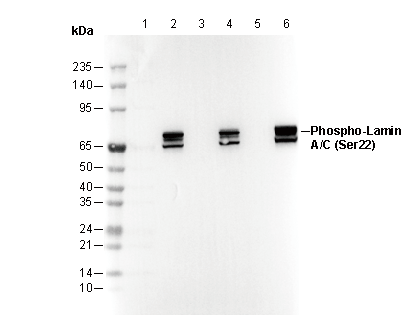
Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser22) Rabbit mAb
Catalog No.: F1962
Experiment Essentials
Subcellular Location: Intermediate filament, Nucleus.
WB
Recommending using RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer to prepare lysates.
WB
Recommending using RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer to prepare lysates.
Usage Information
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IP |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN₃ |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| –20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW |
|---|
| 69,78 kDa |
| Positive Control | Hela (Paclitaxel, 100 nM, 20 hr); NIH/3T3 (Paclitaxel, 100 nM, 20 hr); C6 (Paclitaxel, 100 nM, 20 hr) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control |
Exprimental Methods
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature or lyse it by sonication on ice, then incubate on ice for 30 minutes. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and transfer the cells into an EP tube. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Add an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail), sonicate to lyse the cells, and incubate on ice for 30 minutes. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice.Add an appropriate volume of RIPA/Nuclear Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail), sonicate to lyse the cells, and incubate on ice for 30 minutes. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution ( recommending 5% BSA solution)
for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
951. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Biological Description
| Specificity |
|---|
Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser22) Rabbit mAb recognizes endogenous levels of lamin A/C protein only when phosphorylated at Ser22. |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Phospho Lamin A (Ser 22), Phospho Lamin A (Ser 22) |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P02545 |
| Clone |
|---|
| D12F9 |
| Background |
|---|
Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser22) is a phosphorylated form of Lamin A/C, a type-V intermediate filament protein, encoded by the LMNA gene, which forms part of the nuclear lamina beneath the inner nuclear membrane. Lamin A/C, a tripartite is structured into a non-helical N-terminal head domain (containing Ser22), a central α-helical coiled-coil rod domain, and a C-terminal immunoglobulin-like fold. Phosphorylation at Ser22, mediated by kinases such as CDK1/cyclin B, PKC, and CK2, occurs during specific cell cycle stages and cellular contexts. This modification regulates nuclear stability, cell cycle progression, and signaling through the LINC complex. Phospho-Ser22 Lamin A/C is also involved in modulating ion channels like Nav1.5 and can act as a transcriptional activator by binding enhancer domains. Increased Ser22 phosphorylation enhances Lamin A mobility, potentially destabilizing the nuclear lamina, as observed in diseases like Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS). |
| References |
|---|
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field